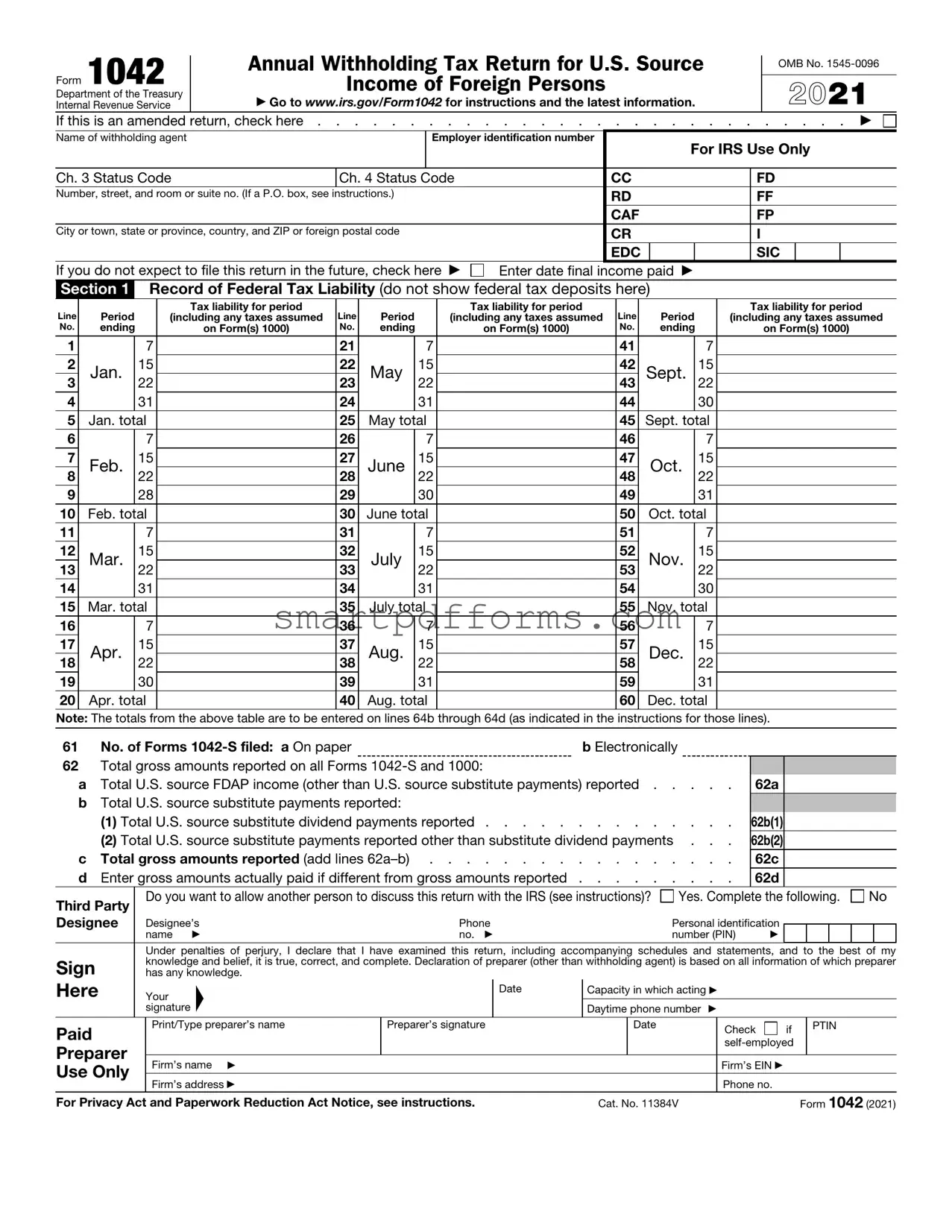
Blank 1042 PDF Template
The Form 1042, formally known as the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons, serves as a critical document managed by the Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service, delineating the tax obligations for income sourced within the United States and paid to foreign individuals or entities. This comprehensive form, identified under OMB No. 1545-0096 for the year 2021, encapsulates various sections including the initial identification of the withholding agent, detailed records of the federal tax liability over specific periods, calculations for tax due or overpayment, and reconciliation of payments pertaining to U.S. source Fixed, Determinable, Annual, or Periodical (FDAP) income. Its extensive coverage extends to adjustments in withholding, the application of credits and overpayments, as well as specific provisions under chapters 3 and 4, touching on aspects like excise taxes on specified federal procurement payments and compliance with regulations concerning dividend equivalent payments and potential Section 871(m) transactions. Moreover, it emphasizes the reporting nuances for payments made under certain conditions, such as those for substituted dividends and payments not subject to withholding due to the nature of the payment or the recipient's status. The flexibility to amend a return for correcting previously submitted information, alongside the provision to designate a third party for IRS correspondence, underscores the form's adaptability and the importance of accuracy in reporting U.S. source income payments to foreign parties.
Preview - 1042 Form
Form 1042 |
Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source |
|
|
|
OMB No. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Income of Foreign Persons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021 |
||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service |
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1042 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
If this is an amended |
return, check here |
. . . |
. |
. |
. . . . . . ▶ |
||||||||||||||||||
Name of withholding agent |
|
|
|
|
Employer identification number |
|
|
|
|
For IRS Use Only |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ch. 3 Status Code |
|
Ch. 4 Status Code |
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
FD |
|||||||||||||
Number, street, and room or suite no. (If a P.O. box, see instructions.) |
|
|
|
|
RD |
|
|
|
|
|
FF |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CAF |
|
|
|
|
|
FP |
|||||
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
|
|
|
|
CR |
|
|
|
|
|
I |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EDC |
|
|
|
|
|
SIC |
|
|
|||
If you do not expect to file this return in the future, check here ▶ |
Enter date final |
income |
paid ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Section 1 |
Record of Federal Tax Liability (do not show federal tax deposits here) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Line |
|
Period |
|
|
Tax liability for period |
Line |
Period |
|
|
|
Tax liability for period |
|
Line |
|
|
Period |
|
|
|
Tax liability for period |
|||
|
|
(including any taxes assumed |
|
|
(including any taxes assumed |
|
|
|
|
(including any taxes assumed |
|||||||||||||
No. |
|
ending |
|
|
on Form(s) 1000) |
No. |
ending |
|
|
|
on Form(s) 1000) |
|
No. |
|
|
ending |
|
|
|
|
on Form(s) 1000) |
||
1 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
21 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
41 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
Jan. |
15 |
|
|
22 |
May |
15 |
|
|
|
42 |
|
Sept. |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
3 |
|
22 |
|
|
23 |
22 |
|
|
|
43 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
4 |
|
|
31 |
|
|
24 |
|
31 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
Jan. total |
|
|
25 |
May total |
|
|
|
45 |
|
Sept. total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
6 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
26 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
46 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
Feb. |
15 |
|
|
27 |
June |
15 |
|
|
|
47 |
|
|
Oct. |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
22 |
|
|
28 |
22 |
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
9 |
|
|
28 |
|
|
29 |
|
30 |
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
Feb. total |
|
|
30 |
June total |
|
|
|
50 |
|
Oct. total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
11 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
31 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
51 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
Mar. |
15 |
|
|
32 |
July |
15 |
|
|
|
52 |
|
Nov. |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
13 |
|
22 |
|
|
33 |
22 |
|
|
|
53 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
14 |
|
|
31 |
|
|
34 |
|
31 |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
Mar. total |
|
|
35 |
July total |
|
|
|
55 |
|
Nov. total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
16 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
36 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
56 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
Apr. |
15 |
|
|
37 |
Aug. |
15 |
|
|
|
57 |
|
Dec. |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18 |
|
22 |
|
|
38 |
22 |
|
|
|
58 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
19 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
39 |
|
31 |
|
|
|
59 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
Apr. total |
|
|
40 |
Aug. total |
|
|
|
60 |
|
Dec. total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note: The totals from the above table are to be entered on lines 64b through 64d (as indicated in the instructions for those lines). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
61 |
|
No. of Forms |
|
|
|
|
b Electronically |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
62 Total gross amounts reported on all Forms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
a Total U.S. source FDAP income (other than U.S. source substitute payments) reported |
. . . |
. |
. |
|
62a |
|||||||||||||||||
|
b Total U.S. source substitute payments reported: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
(1) Total U.S. source substitute dividend payments reported |
. . . |
. |
. |
|
62b(1) |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
(2) Total U.S. source substitute payments reported other than substitute dividend payments . |
. |
. |
|
62b(2) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
c |
Total gross amounts reported (add lines |
. . . |
. |
. |
|
62c |
||||||||||||||||
dEnter gross amounts actually paid if different from gross amounts reported . . . . . . . . . 62d
Third Party |
Do you want to allow another person to discuss this return with the IRS (see instructions)? |
Yes. Complete the following. |
No |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Designee |
Designee’s |
Phone |
Personal identification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
name ▶ |
no. ▶ |
number (PIN) |
▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this return, including accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct, and complete. Declaration of preparer (other than withholding agent) is based on all information of which preparer has any knowledge.
Your |
▲ |
Date |
|
||
signature |
|
|
|
|
|
Paid |
Print/Type preparer’s name |
Preparer’s signature |
|
|
|
Preparer |
Firm’s name ▶ |
|
Use Only |
|
|
Firm’s address ▶ |
|
|
|
|
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see instructions.
Capacity in which acting ▶
Daytime phone number |
▶ |
|
|
|
||
|
Date |
|
Check |
if |
|
PTIN |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Firm’s EIN ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone no. |
|
|
|
Cat. No. 11384V |
|
|
|
Form 1042 (2021) |
||
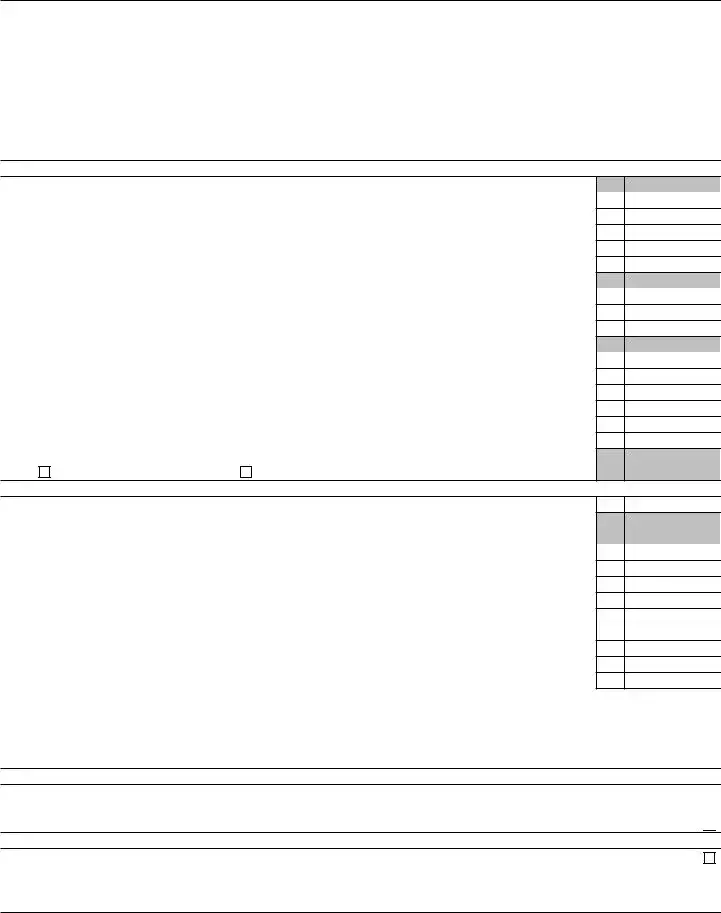
Form 1042 (2021) |
Page 2 |
63Total tax reported as withheld or paid by withholding agent on all Forms
a Tax withheld by withholding agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
bTax withheld by other withholding agents:
(1) |
For payments other than substitute dividends |
(2) |
For substitute dividends |
cAdjustments to withholding:
(1) |
Adjustments to overwithholding |
(2) |
Adjustments to underwithholding |
d Tax paid by withholding agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
eTotal tax reported as withheld or paid (add lines
Computation of Tax Due or Overpayment
|
|
|
63a |
|
|
|
|
|
63b(1) |
|
|
63b(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
63c(1) |
( |
) |
63c(2) |
|
|
63d |
|
|
63e |
|
|
|
|
|
64Total net tax liability
a |
Adjustments to total net tax liability |
b |
Total net tax liability under chapter 3 |
c |
Total net tax liability under chapter 4 |
d |
Excise tax on specified federal procurement payments (total payments made x 2% (0.02)) . . . . |
e |
Total net tax liability (add lines |
65Total paid by electronic funds transfer (or with a request for extension of time to file):
a |
Total paid during calendar year |
b |
Total paid during subsequent year |
66 |
Enter overpayment applied as credit from 2020 Form 1042 |
67Credit for amounts withheld by other withholding agents:
a |
For payments other than substitute dividend payments |
b |
For substitute dividend payments |
68 |
Total payments. Add lines 65 through 67 |
69If line 64e is larger than line 68, enter balance due here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
70a |
Enter overpayment attributable to overwithholding on U.S. source income of foreign persons . . . |
b |
Enter overpayment attributable to excise tax on specified federal procurement payments . . . . |
71Apply overpayment (sum of lines 70a and 70b) to (check one):
Credit on 2022 Form 1042 or |
Refund |
Section 2 Reconciliation of Payments of U.S. Source FDAP Income
64a
64b
64c
64d
64e
65a
65b
66
67a
67b
68
69
70a
70b
1 Total U.S. source FDAP income required to be withheld upon under chapter 4 . . . . . . . .
2Total U.S. source FDAP income required to be reported under chapter 4 but not required to be withheld upon under chapter 4 because:
aAmount of income paid to recipients whose chapter 4 status established no withholding is required .
b |
Amount of excluded nonfinancial payments |
c |
Amount of income paid with respect to grandfathered obligations |
dAmount of income effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the U.S. . . .
eTotal U.S. source FDAP income required to be reported under chapter 4 but not required to be
|
withheld upon under chapter 4 (add lines |
3 |
Total U.S. source FDAP income reportable under chapter 4 (add lines 1 and 2e) |
4 |
Total U.S. source FDAP income reported on all Forms |
5 |
Total variance, subtract line 3 from line 4; if amount other than zero, provide explanation on line 6 . . |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
2a
2b
2c
2d
2e
3
4
5
Section 3 Potential Section 871(m) Transactions
Check here if any payments (including gross proceeds) were made by the withholding agent under a potential section 871(m) transaction, including a notional principal contract or other derivatives contract that references (in whole or in part) a U.S. stock or other underlying security. See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 

Section 4 Dividend Equivalent Payments by a Qualified Derivatives Dealer (QDD)
Check here if any payments were made by a QDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
If box is checked, you must:
(1)Attach Schedule Q (Form 1042). See instructions.
(2)Enter the EIN (not the
Form 1042 (2021)
Form Data
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Form 1042 | Used for annual withholding tax return on U.S. source income of foreign persons. |
| Governing Body | Administered by the Department of the Treasury, Internal Revenue Service. |
| OMB Number | 1545-0096 |
| Amendment Option | Provides an option to check if the submission is an amended return. |
| Record of Federal Tax Liability Section | Includes detailed record of tax liability by period, but without showing federal tax deposits. |
Instructions on Utilizing 1042
Filing the Form 1042 is a vital step for withholding agents to comply with U.S. tax obligations concerning payments made to foreign persons. This document serves as an annual withholding tax return, specifically targeting U.S. source income paid to non-U.S. entities or individuals. Ensuring accuracy and completeness while filling out this form is crucial for avoiding potential penalties and ensuring compliance with tax laws. The following instructions provide a step-by-step approach to help withholding agents accurately complete the Form 1042.
- Start by visiting the official IRS website to access the latest version of Form 1042 and its instructions.
- Enter the tax year at the top of the form to specify the reporting period.
- If you are amending a previously filed Form 1042, check the box indicated for an amended return.
- Provide the name of the withholding agent as shown on tax documents.
- Fill in the Employer Identification Number (EIN) of the withholding agent.
- Enter the complete address of the withholding agent, including number, street, room or suite number. If a P.O. box is used, refer to the specific instructions provided.
- Detail the city, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code, as applicable.
- Check the boxes corresponding to the Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Status Codes, utilizing the proper codes from the provided guidance in the instructions.
- If you do not expect to file Form 1042 in future years, check the appropriate box.
- Enter the date the final income payment was made in the tax year being reported.
- Complete Section 1 regarding the Record of Federal Tax Liability meticulously for each period as per the instructions.
- List the number of Forms 1042-S filed, separating those submitted on paper from those submitted electronically.
- Report the total gross amounts on all Forms 1042-S and total gross amounts actually paid, if they differ.
- If allowing a Third Party Designee to discuss this return with the IRS, complete the relevant section. If not, check "No."
- Review the declaration carefully, then sign and date the return. If a preparer other than the withholding agent completed the form, ensure they complete the Preparer section.
- Remember to attach any required schedules or documents, such as Schedule Q for QDDs, if applicable.
- Review the entire form to ensure accuracy and completeness before submission.
- Submit the form to the IRS by the prescribed deadline, using the method indicated in the instructions (paper filing or electronic submission).
Following these steps meticulously will help ensure the accurate and timely filing of Form 1042, thereby fulfilling your obligations as a withholding agent. Keep a copy of the submitted form and all related documentation for your records.
Obtain Answers on 1042
What is a Form 1042?
Who is required to file Form 1042?
What types of income are reported on Form 1042?
What is the difference between Form 1042 and Form 1042-S?
When is Form 1042 due?
Can Form 1042 be filed electronically?
What happens if the withholding agent overpays or underpays the tax?
What should a withholding agent do if they need to amend a Form 1042?
Form 1042, known as the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons, is used by the IRS to report taxes withheld from non-U.S. residents' income derived from U.S. sources. This includes earnings, royalties, and other types of income.
Any withholding agent, which can be an individual, business, or institution, that has paid income to foreign persons must file this form. The responsibility falls on the agent to report the total taxes withheld and ensure they're submitted to the IRS.
The income reported includes, but is not limited to, salaries, dividends, rents, royalties, and scholarship or fellowship grants. Essentially, any U.S. source income paid to a foreign person is subject to reporting on this form.
Form 1042 is a summary of the annual withholding tax on US source income paid to foreign persons, while Form 1042-S is an individual statement reporting the income paid to each foreign person and the tax withheld. The totals from 1042-S forms contribute to the amounts reported on Form 1042.
The form must be submitted by March 15 of the year following the payments made. If the due date falls on a weekend or holiday, the next business day becomes the deadline.
Yes, withholding agents have the option to file Form 1042 electronically through the IRS FIRE (Filing Information Returns Electronically) system. Electronic filing is recommended for efficiency and accuracy.
If there's an overpayment, the withholding agent can apply for a credit on the next year's Form 1042 or request a refund. For underpayments, additional tax owing must be settled promptly to avoid penalties and interest.
If errors are discovered after submission, the withholding agent should file an amended return. It's important to check the appropriate box to indicate that the submission is an amendment, correct the errors, and resubmit the form to the IRS.
Common mistakes
Not checking the box to indicate that the form is an amended return. This mistake can lead to confusion and delays in processing by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), especially when updates or corrections to previously submitted information are necessary.
Incorrect or incomplete reporting of the withholding agent's information, including the name and Employer Identification Number (EIN). Accurate identification is crucial for the IRS to properly attribute the tax responsibilities and payments.
Failing to properly address the use of a P.O. Box. Specific instructions provided by the IRS for cases where a P.O. Box is used instead of a physical address must be carefully followed to ensure the form is accepted and processed without issue.
Omitting to check the box if the withholding agent does not expect to file Form 1042 in the future. This information is necessary for the IRS to update its records regarding the filer's anticipated future filing requirements.
Not accurately entering the date final income was paid. This date is critical for the IRS to determine the tax period and ensure that withholding is accounted for correctly.
Errors in the Record of Federal Tax Liability section, including miscalculation of tax liability for specific periods or failing to assume taxes as indicated on Form(s) 1000. Precision in recording tax liabilities ensures accurate reconciliation of withheld taxes.
Incorrect number of Forms 1042-S filed or incorrect reporting of total gross amounts, which can significantly impact tax calculations and result in underpayment or overpayment of taxes.
Forgetting to designate a third party to discuss the return with the IRS, if desired, and not providing complete information for the designated individual. This oversight can complicate or delay communication between the IRS and designated representatives.
Under the penalties of perjury section, signatories sometimes neglect to ensure that all accompanying schedules and statements are true, correct, and complete to the best of their knowledge. Moreover, paid preparers must properly identify themselves, including their firm’s information and Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN), to fulfill legal requirements and facilitate follow-up by the IRS if questions arise regarding the return.
Mistakes in completing Form 1042 can lead to delayed processing, errors in recorded tax liabilities, potential penalties, or incorrect tax assessments by the IRS. Individuals responsible for filing should meticulously review the form and accompanying instructions provided by the IRS to ensure compliance and accuracy in reporting U.S. source income of foreign persons.
Documents used along the form
Filing the Form 1042, the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons, is a critical step for entities acting as withholding agents. This form helps ensure compliance with U.S. tax obligations regarding payments made to foreign persons. However, it is not the only document involved in the process. Understanding related forms and documents can provide a clearer picture of the reporting and withholding requirements and facilitate smoother interactions with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Form 1042-S: This form, titled the "Foreign Person's U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding," accompanies Form 1042. It is used to report amounts paid to foreign persons, including freelancers, contractors, and vendors, that are subject to income tax withholding. Each recipient of the U.S. source income must receive a separate Form 1042-S to detail the income and withholding amount.
- Form W-8BEN: The "Certificate of Foreign Status of Beneficial Owner for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting (Individuals)," or Form W-8BEN, is completed by foreign individuals to assert their foreign status and, if applicable, claim any tax treaty benefits. This form helps withholding agents determine the correct withholding rate.
- Form W-8BEN-E: Similar to Form W-8BEN, the Form W-8BEN-E is completed by entities, not individuals, to claim foreign status or benefits under a tax treaty. This form is crucial for businesses and organizations operating in the U.S. that make payments to foreign entities.
- Form 8804: This form, titled "Annual Return for Partnership Withholding Tax (Section 1446)," is used by partnerships to report and pay the withholding tax on the income effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States that is allocable to its foreign partners. While not directly related to the 1042 and 1042-S forms, it's part of the broader tax withholding and reporting regime for payments made to foreign persons.
In addition to ensuring compliance through accurate and timely filing, understanding the interplay between these forms can enhance an organization's ability to manage its tax liabilities effectively. Withholdings and reporting are complex processes, made more so when they involve international participants. Entities are encouraged to consult with tax professionals to ensure they meet all their obligations properly and maintain good standing with the IRS.
Similar forms
The Form 1042-S shares similarities with Form 1042 in that it is also focused on the reporting of U.S. source income paid to foreign persons. The distinction lies in their specific roles: while Form 1042 serves as the annual withholding tax return summarizing the total tax withheld from all foreign persons, Form 1042-S provides detailed information about each recipient of U.S. source income, including the type of income and the amount of withholding tax deducted.
Form W-8 series (such as W-8BEN and W-8ECI), unlike Form 1042, are used by foreign persons to certify their status and claim benefits under the income tax treaty or to attest that their income is connected with a U.S. trade or business. These forms help withholding agents determine the correct withholding rate for payments made to foreign individuals or entities, which is crucial information needed to accurately complete Form 1042.
The Form 8804, similar to Form 1042, pertains to the taxation of income with an international aspect. Form 8804 is used to report the annual withholding tax on effectively connected income allocable to foreign partners of a partnership conducting trade or business in the United States. While addressing different types of income and entities, both forms ensure compliance with U.S. tax obligations on foreign entities and individuals.
Form 1099 series, including forms like 1099-INT and 1099-DIV, are analogous to Form 1042 in their function of reporting certain types of income. Though Form 1099 is primarily for domestic payees, both this series and Form 1042 necessitate the reporting of income payments and applicable withholding to the IRS, ensuring appropriate tax compliance. The key difference is the recipient's tax status - resident (Form 1099) versus nonresident alien (Form 1042).
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Form 1042, Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons, it's crucial to pay attention to both what you should do and what you should avoid to ensure accurate and compliant submission. Below are essential dos and don'ts to assist you in this process.
Do:
- Thoroughly review the instructions available on the IRS website to ensure you understand the form's requirements.
- Ensure that all information, including the name of the withholding agent and their employer identification number, is complete and accurate.
- Record the Federal Tax Liability accurately in Section 1, including any taxes assumed on Form(s) 1000.
- Indicate if this return is amended by checking the appropriate box.
- Complete the Third Party Designee section if you want another person to discuss this return with the IRS, providing all the requested information.
- Use the totals from the Record of Federal Tax Liability table to correctly fill in lines 64b through 64d, as instructed.
- Sign and date the form, providing the preparer’s information if prepared by someone other than the withholding agent.
Don't:
- Forget to check whether you expect to file this form in the future and indicate your decision appropriately.
- Omit the date final income was paid, as this information is crucial for the IRS.
- Ignore the necessity to attach Schedule Q (Form 1042) if any payments were made by a Qualified Derivatives Dealer (QDD).
- Leave the total amount of tax reported, withheld, or paid sections incomplete in Section 2 and Section 3.
- Fail to apply overpayments correctly, either as a credit to the next year’s Form 1042 or as a refund, as indicated in Section 2.
- Misreport the total U.S. source FDAP income required to be withheld upon and the total amounts paid, which could result in discrepancies and potential IRS queries.
- Disregard the need for accuracy and completeness in filling out the form, as errors or omissions can lead to delays or penalties.
Misconceptions
Understanding the Form 1042, "Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons," involves navigating complex tax regulations. Misconceptions about this form can lead to errors in compliance and reporting. Here are five common misunderstandings:
Form 1042 is only for large corporations: This misconception assumes that only large multinational corporations need to file Form 1042. However, any U.S. entity, including individuals, partnerships, corporations, trusts, or estates, that pays certain types of U.S. source income to foreign persons must use this form to report and, in many cases, withhold taxes.
All U.S. income paid to foreign persons is subject to withholding: While it's true that many types of U.S. source income paid to foreign persons require withholding, there are exceptions and varying rates depending on the type of income and the tax treaties between the U.S. and the payee's country of residence. It's crucial to understand these nuances to apply the correct withholding rates.
If no tax was withheld, Form 1042 isn't necessary: This statement is false. Even if no tax was withheld because of exemptions, treaty benefits, or other reasons, the payer still needs to file Form 1042 to report the payments. Failure to do so can result in penalties.
Filing Form 1042-S is sufficient for reporting purposes: While Form 1042-S, "Foreign Person's U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding," is closely related to Form 1042 and is used to report income paid to and taxes withheld from foreign persons on an individual basis, filing Forms 1042-S alone does not fulfill the obligation to file Form 1042. Both forms serve different purposes and are necessary for complete reporting.
Electronic filing is optional for everyone: The IRS mandates electronic filing of Form 1042 for entities submitting 250 or more forms, including Form 1042-S. This requirement emphasizes the IRS's movement towards modernized and efficient electronic processing systems, aiming to streamline the filing process and expedite the handling of taxpayer information.
Correcting these misconceptions is vital for ensuring compliance with U.S. tax laws and avoiding potential penalties. It's important for entities making payments of U.S. source income to foreign persons to fully understand their obligations under the Internal Revenue Code and to accurately complete and file Form 1042 and associated documentation.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the Form 1042, the Annual Withholding Tax Return for U.S. Source Income of Foreign Persons, is an important task for any withholding agent responsible for reporting U.S. source income paid to foreign individuals. Understanding the key aspects of this form can significantly streamline the compliance process. Here are seven key takeaways to consider:
- Identify the role of the withholding agent: The person or entity that has the responsibility of withholding taxes from U.S. source income paid to foreign persons must complete Form 1042.
- Understand what income is reportable: The form is used to report amounts paid that include, but are not limited to, interest, dividends, rents, royalties, and compensation for services. Identifying and correctly reporting each type of income is crucial.
- Amended returns: If errors are found after the original submission, the agent needs to check the box indicating that the form is an amended return and correct the information accordingly.
- Record of federal tax liability: Withholding agents must meticulously record the tax liability for each period within the tax year, ensuring that all information matches any forms 1000 that might have been issued.
- Third-party designees: The form allows the withholding agent to designate another person to discuss the return with the IRS, which can be helpful if the agent needs someone else, like a tax professional, to handle queries on their behalf.
- Declaration and Preparer's information: Completing this section accurately is tantamount to declaring under penalties of perjury that the information provided is correct. If someone other than the withholding agent prepares the form, their information must also be included.
- Computation and reconciliation of payments: It is critical to accurately compute the tax due or overpayment and reconcile the payments of U.S. source fixed, determinable, annual, or periodical (FDAP) income. This includes any adjustments for overwithholding or underwithholding, and understanding the total net tax liability.
Adherence to these key points when dealing with Form 1042 can help in managing the complexities of tax compliance for payments made to foreign persons. Proper attention to detail and an understanding of the requirements will also mitigate potential errors and discrepancies in reported information.
Popular PDF Forms
Transfer Cna License to South Carolina - Instructs on the importance of including all suffixes and hyphens in legal names to avoid discrepancies in the application process.
Guardianship Vs Power of Attorney - Equipped with instructions on serving notice to family members and any interested parties, promoting transparency.