Blank Army Risk PDF Template
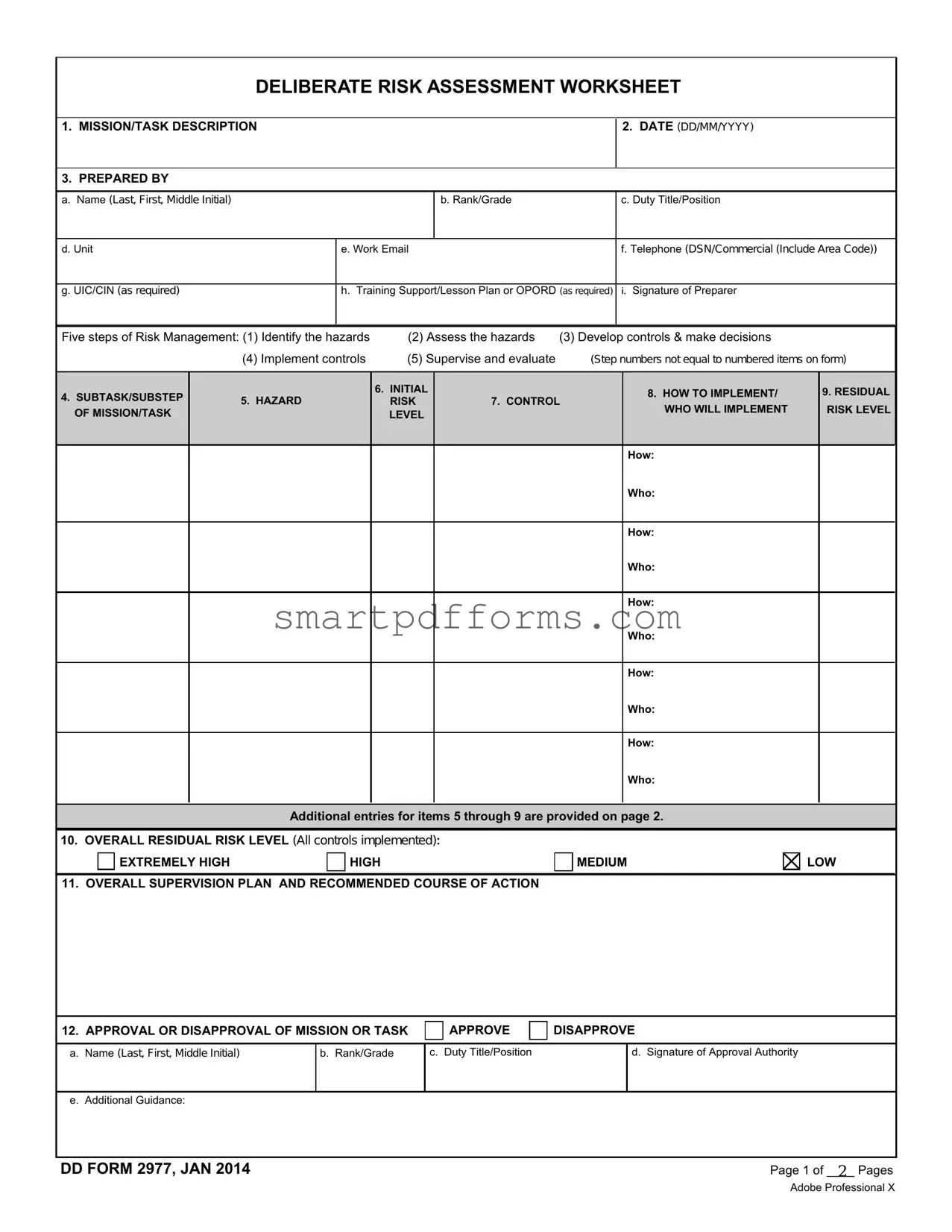
In the realm of military operations, the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, known formally as DD Form 2977, serves as a critical tool in the maneuvering and execution of tasks and missions with a keen eye on safety and risk mitigation. This document meticulously outlines the process by which military personnel identify, assess, and control risks associated with specific missions or tasks. Beginning with a comprehensive mission or task description, the form guides the user through a detailed process that includes the enumeration of subtasks/substeps, identification of hazards, and assessment of initial risk levels. Crucial to this process is the development and implementation of controls aimed at mitigating identified risks, followed by an assessment of residual risk levels post-control implementation. The worksheet further demands the articulation of an overall supervision plan and a recommendation for action, which culminates in an authoritative approval or disapproval of the mission or task based on the compiled risk assessment. A unique aspect of the form is its mandatory review process, designed to ensure ongoing relevance and effectiveness of risk assessment over time, along with a section dedicated to feedback and lessons learned to foster continuous improvement in risk management practices. Additionally, the form allows for detailed comments or remarks and acknowledges the necessity for supplemental pages, ensuring comprehensiveness in documentation. Through these elements, DD Form 2977 underscores the importance of deliberate risk assessment in preserving the safety and success of military operations.
Preview - Army Risk Form
DELIBERATE RISK ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET
1. MISSION/TASK DESCRIPTION
2.DATE (DD/MM/YYYY)
3. PREPARED BY
|
a. Name (Last, First, Middle Initial) |
|
|
|
|
b. Rank/Grade |
|
|
c. Duty Title/Position |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d. Unit |
|
e. Work Email |
|
|
|
f. Telephone (DSN/Commercial (Include Area Code)) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
g. UIC/CIN (as required) |
|
h. Training Support/Lesson Plan or OPORD (as required) |
i. Signature of Preparer |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Five steps of Risk Management: (1) Identify the hazards |
(2) Assess the hazards |
(3) Develop controls & make decisions |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(4) Implement controls |
(5) Supervise and evaluate |
|
(Step numbers not equal to numbered items on form) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. SUBTASK/SUBSTEP |
|
5. HAZARD |
6. INITIAL |
|
7. CONTROL |
|
|
8. HOW TO IMPLEMENT/ |
|
9. RESIDUAL |
||
|
|
RISK |
|
|
|
WHO WILL IMPLEMENT |
|
RISK LEVEL |
|||||
|
OF MISSION/TASK |
|
|
|
LEVEL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Additional entries for items 5 through 9 are provided on page 2. |
|
|
||||||||
|
10. OVERALL RESIDUAL RISK LEVEL (All controls implemented): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
EXTREMELY HIGH |
|
HIGH |
|
|
MEDIUM |
LOW |
||||||
|
11. OVERALL SUPERVISION PLAN AND RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12. APPROVAL OR DISAPPROVAL OF MISSION OR TASK
APPROVE
DISAPPROVE
a.Name (Last, First, Middle Initial)
b. Rank/Grade
c. Duty Title/Position
d. Signature of Approval Authority
e. Additional Guidance:
DD FORM 2977, JAN 2014 |
Page 1 of 2 Pages |
|
Adobe Professional X |
|
|
DELIBERATE RISK ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. SUBTASK/SUBSTEP |
|
5. HAZARD |
6. |
INITIAL |
7. CONTROL |
8. HOW TO IMPLEMENT/ |
9. RESIDUAL |
|
|
RISK |
|||||
OF MISSION/TASK |
|
|
|
|
WHO WILL IMPLEMENT |
RISK LEVEL |
|
|
|
|
LEVEL |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DD FORM 2977, JAN 2014 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Page ____ of ____ Pages |
|||
DELIBERATE RISK ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Probability (expected frequency) |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
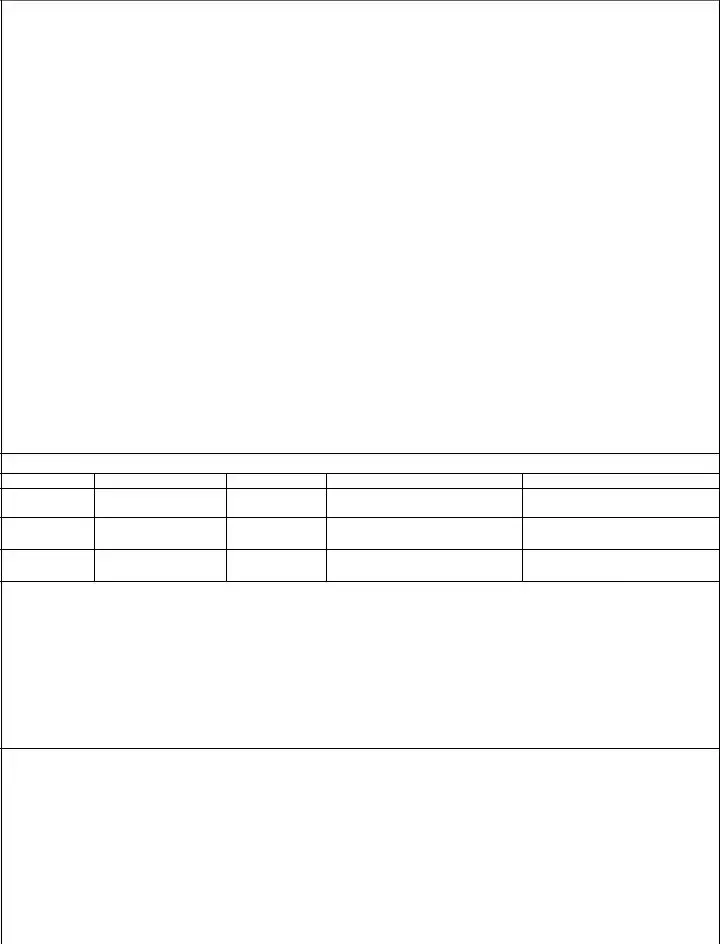
Risk Assessment Matrix |
|
|
Frequent: |
|
Likely: |
|
|
Occasional: |
|
Seldom: |
Unlikely: |
||||||
|
|
Continuous, |
|
Several or |
|
|
Sporadic or |
|
Infrequent |
Possible |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
regular, or |
|
numerous |
|
|
intermittent |
|
occurrences |
occurrences but |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
inevitable |
|
occurrences |
|
|
occurrences |
|
improbable |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
occurrences |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Severity (expected consequence) |
|
|
A |
|
B |
|
|
C |
|
D |
E |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Catastrophic: Death, unacceptable |
|
I |
|
EH |
|
|
EH |
|
|
H |
|
|
H |
M |
|
||
loss or damage, mission failure, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
or unit readiness eliminated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Critical: Severe injury, illness, loss, |
|
II |
|
EH |
|
|
H |
|
|
|
H |
|
M |
L |
|||
or damage; significantly degraded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
unit readiness or mission capability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Moderate: Minor injury, illness, loss, |
|
III |
|
H |
|
M |
|
|
M |
|
L |
L |
|||||
or damage; somewhat degraded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
unit readiness or mission capability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Negligible: Minimal injury, loss, |
|
IV |
|
M |
|
L |
|
|
L |
|
L |
L |
|||||
or damage; little or no impact |
to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
unit readiness or mission capability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EH – extremely high risk |
H – high risk |
|
M – medium risk |
L – low risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
13. RISK ASSESSMENT REVIEW 5HTXLUHGZKHQDVVHVVPHQWDSSOLHVWRRQJRLQJRSHUDWLRQVRUDFWLYLWLHV
a. Date
b. Last Name
c. Rank/Grade
d. Duty Title/Position
e. Signature of Reviewer
14. FEEDBACK AND LESSONS LEARNED
15. ADDITIONAL COMMENTS OR REMARKS
DD FORM 2977, JAN 2014 |
Page ____ of 2 Pages |
Instructions for Completing DD Form 2977, "Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet"
1.Mission/Task Description: Briefly describe the overall Mission or Task for which the deliberate risk assessment is being conducted.
2.Date ''00<<<<: Self Explanatory.
3.Prepared By: Information provided by the individual conducting the deliberate risk assessment for the operation or training .
Legend: UIC = Unit Identification Code; CIN = Course ID Number; OPORD = operation order; DSN = defense switched network; COMM = commercial
4.
5.Hazard: Specify hazards related to the subtask in block 4.
6.Initial Risk Level: Determine probability and severity. Using the risk assessment matrix (page 3), determine level of risk for each hazard specified. probability, severity and associated Risk Level; enter level into column.
7.Control: Enter risk mitigation resources/controls identified to abate or reduce risk relevant to the hazard identified in block 5.
8.How to Implement / Who Will Implement: Briefly describe the means of employment for each control (i.e., OPORD, briefing, rehearsal) and the name of the individual unit or office that has primary responsibility for control implementation.
9.Residual Risk Level: After controls are implemented, determine resulting probability, severity, and residual risk level.
10.Overall Risk After Controls are Implemented: Assign an overall residual risk level. This is the highest residual risk level (from block 9).
11.Supervision Plan and Recommended Course of Action: Completed by preparer. Identify specific tasks and levels of responsibility for supervisory personnel and provide the decision authority with a recommend course of action for approval or disapproval based upon the overall risk assessment.
12.Approval/Disapproval of Mission/Task: Risk approval authority approves or disapproves the mission or task based on the overall risk assessment, including controls, residual risk level, and supervision plan. Space provided for authority to provide additional guidance; use continuation page if needed.
13. Risk Assessment Review: Should be conducted on a regular basis. Reviewers should have sufficient oversight of the mission or activity and controls to provide valid input on changes or adjustments needed. If the residual risk rises above the level already approved, operations should cease until the appropriate approval authority is contacted and approves continued operations.
14.Feedback and Lessons Learned: Provide specific input on the effectiveness of risk controls and their contribution to mission success or failure. Include recommendations for new or revised controls, practicable solutions, or alternate actions. Submit and brief valid lessons learned as necessary to persons affected.
15.Additional Comments or Remarks: Preparer provides additional comments, remarks, or information to support the risk assessment. If block 15 is used as a continuation of block 14, strike through the block number and title.
Additional Guidance: Block
DD FORM 2977 INSTRUCTIONS, JAN 2014
Form Data
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Document Title | Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet |
| Form Number | DD Form 2977 |
| Revision Date | January 2014 |
| Contents Overview | Includes sections on mission/task description, preparation details, a five-step risk management process, and overall risk level assessment. |
| Risk Management Steps | Identify hazards, assess hazards, develop controls & make decisions, implement controls, supervise and evaluate |
| Assessment Tools Included | Risk Assessment Matrix detailing probability and severity |
| Approval Process | Includes sections for approval or disapproval of the mission or task based on risk assessment. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Sections for risk assessment review, feedback and lessons learned, and additional comments or remarks. |
Instructions on Utilizing Army Risk
Filling out the Army Risk Form, officially known as the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet (DD Form 2977), is an essential step in assessing and managing risks for military operations or training events. This process ensures that all possible hazards are identified, evaluated, and mitigated appropriately to minimize risks to personnel, equipment, and mission success. The instructions provided aim to guide individuals responsible for the assessment through each part of the form accurately and thoroughly.
Steps to Complete DD Form 2977
- Mission/Task Description: Clearly outline the main mission or task, including any relevant details that will provide context for the risk assessment.
- Date (DD/MM/YYYY): Enter the current date in the designated format.
- Prepared By: Include all required information about the individual completing the assessment:
- Name (Last, First, Middle Initial)
- Rank/Grade
- Duty Title/Position
- Unit
- Work Email
- Telephone (DSN/Commercial)
- UIC/CIN (as required)
- Training Support/Lesson Plan or OPORD (as required)
- Signature of Preparer
- Subtask/Substep of Mission/Task: Describe any subtasks or steps within the mission that require specific risk management.
- Hazard: For each subtask or step, identify any hazards that could potentially cause harm or impact mission success.
- Initial Risk Level: Utilize the provided Risk Assessment Matrix to evaluate the probability and severity of each identified hazard and determine the initial level of risk.
- Control: List the measures that can be implemented to mitigate each identified hazard, aiming to reduce the risk.
- How to Implement/Who Will Implement: Specify the method by which each control will be implemented and the individual or unit responsible for its execution.
- Residual Risk Level: After controls have been planned, reassess the probability, severity, and level of risk, noting the residual risk for each hazard.
- Overall Risk After Controls are Implemented: Determine the highest level of residual risk from all assessed hazards and assign this as the overall risk level for the mission or task.
- Supervision Plan and Recommended Course of Action: Outline the supervisory approach to managing the identified risks and propose a course of action for decision-makers to approve or disapprove the mission or task.
- Approval/Disapproval of Mission/Task: The risk approval authority will indicate their decision based on the comprehensive risk assessment provided, including any additional guidance if necessary.
- Risk Assessment Review: Regular reviews of the risk assessment should be conducted, especially if changes occur that may affect the level of risk.
- Feedback and Lessons Learned: Document the effectiveness of the risk controls implemented and offer any insights gained that could benefit future operations or missions.
- Additional Comments or Remarks: Use this section for any further details or information relevant to the risk assessment, employing continuation pages as needed.
Upon completing the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, the form should be reviewed, approved, and continuously monitored to manage risks effectively. This proactive approach ensures that efforts are focused on maintaining the wellbeing of personnel and the achievement of mission objectives with minimal disruptions.
Obtain Answers on Army Risk
-
What is the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet (DD Form 2977), and why is it important?
The Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, known as DD Form 2977, is a crucial document used by the military to evaluate and manage risks associated with specific missions or tasks. Its importance lies in its systematic approach to identifying hazards, assessing risks, developing and implementing controls, and supervising and evaluating the effectiveness of those controls. This process helps in minimizing risks to personnel and assets, ensuring mission success, and maintaining operational readiness.
-
How is the initial risk level determined on the DD Form 2977?
The initial risk level is determined by evaluating the probability and severity of potential hazards associated with a mission or task. This evaluation utilizes a risk assessment matrix that classifies risk levels based on the likelihood of an event occurring and the potential impact it would have. Once the probability and severity are pinpointed, they are cross-referenced to assign an initial risk level (Extremely High, High, Medium, Low) to each identified hazard.
-
What steps are involved in completing the DD Form 2977?
- Identify the mission or task and describe it briefly.
- Determine the date and provide details of the individual preparing the form.
- Enumerate all subtasks or substeps that need risk management.
- Specify potential hazards for each subtask or substep.
- Assess the initial risk levels using the risk assessment matrix.
- Develop and record control measures to mitigate identified risks.
- Detail the implementation of these controls and assign responsibility.
- Reassess the residual risk levels after controls are applied.
- Finalize the overall risk level and propose a supervision plan and course of action.
- Obtain approval or disapproval of the mission or task from the designated authority.
-
How should controls be implemented according to the worksheet?
Controls should be implemented by clearly describing how each control will be carried out and who is responsible for its implementation. This often involves operational orders, briefings, and rehearsals. It's imperative that the individual, unit, or office assigned responsibility has the necessary authority and capability to implement these controls effectively, ensuring that they mitigate the associated risks as intended.
-
What does "residual risk" mean, and how is it measured?
Residual risk refers to the level of risk that remains after controls have been implemented to mitigate the initial risks. It's measured by reassessing the probability and severity of each hazard with the controls in place, using the same risk assessment matrix. This reassessment helps in identifying the effectiveness of the controls and whether further measures are needed to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
-
Who needs to approve the DD Form 2977, and what happens once it's approved?
The DD Form 2977 requires approval from a designated authority, usually someone in a leadership position with the necessary oversight of the mission or task. Once approved, the mission or task can proceed, but with the stipulation that the approved controls are implemented, and the residual risk is managed as planned. The form also allows for disapproval, where the authority can halt the mission or task if the risks are deemed too great or if the controls are insufficient.
Common mistakes
Filling out an Army Risk Assessment form correctly is crucial for ensuring the safety and success of military operations. However, several common mistakes can hinder this process. Here’s a list of nine such errors:
Not providing a clear mission or task description. This foundational information sets the stage for the entire assessment, and being vague here can lead to inadequate hazard identification.
Incorrectly dating the form or using an incorrect format (DD/MM/YYYY). This may seem minor, but it's essential for record-keeping and ensuring the timely review and implementation of the risk assessment.
Omitting contact information like a work email or telephone number, which is critical for follow-up, clarification, and coordination.
Not adequately identifying hazards. A thorough evaluation of potential risks is vital. Skipping or glossing over this step can leave personnel unprepared for possible dangers.
Failing to assess the hazard’s initial risk level properly using the Risk Assessment Matrix. This step requires an understanding of both the likelihood of occurrence and the potential severity of outcomes.
Inadequate control measures. Controls are the actions taken to mitigate risks. Not being specific about these can lead to ineffective risk management.
Being unclear about how and who will implement controls. Without clear implementation plans and designated responsibilities, even well-thought-out controls may fail.
Miscalculating the residual risk level. After controls are implemented, it's critical to reassess the risk to understand what threats still persist.
Forgetting to determine the overall residual risk level or making a selection that does not accurately reflect the highest residual risk identified. This summary judgment is essential for approvers to understand the operation's final risk state.
Steering clear of these missteps can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, thereby safeguarding the mission and those involved.
Documents used along the form
When handling the complexities of planning and executing tasks within the military context, the Army Risk Form, officially known as the DD Form 2977, Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, serves as a crucial tool for managing potential risks associated with any operation or training exercise. However, this form does not stand alone. Several other forms and documents typically complement it to ensure a comprehensive approach to risk management and operational planning. Understanding these accompanying documents can enhance the effectiveness of the risk management process.
- Operation Order (OPORD): An OPORD outlines the plan for a military operation. It provides detailed instructions on the execution of the operation, including objectives, phases of the operation, and specific tasks. The OPORD is crucial for understanding the broader context within which risk assessments are conducted.
- After Action Review (AAR): The AAR is a structured review process conducted after an operation or training event. It allows participants to discuss what happened, why it happened, and how to improve future performance. Insights from AARs can feed into risk assessments by highlighting potential hazards and effective controls.
- Medical Plan: This document outlines the medical support plan for an operation or training exercise. It details the location of medical facilities, types of medical support available, and evacuation procedures for casualties. Integrating the medical plan with the risk assessment process helps in identifying and mitigating medical-related risks.
- Communication Plan: A communication plan specifies the communication protocols, frequencies, call signs, and other relevant information for an operation. Effective communication is pivotal for the implementation of controls and the management of risks, making this plan essential for risk assessment.
- Emergency Action Plan (EAP): The EAP outlines the procedures for dealing with sudden, unexpected events, such as natural disasters or security breaches. Incorporating the EAP into the risk management process ensures that contingency measures are in place for high-impact risks.
- Training Support/Lesson Plan: Related to the DD Form 2977's section on training support, the lesson plan provides a detailed outline of training objectives, methods, and materials. Aligning the lesson plan with the risk assessment helps in identifying risks specific to training activities and developing appropriate controls.
Collectively, these documents play a vital role in creating a well-rounded and effective risk management plan. By integrating the DD Form 2977 with these complementary documents, military planners and leaders can ensure that all aspects of risk are thoroughly evaluated and managed, ultimately enhancing the safety and success of military operations and training exercises.
Similar forms
The Job Safety Analysis (JSA) document is quite similar in that it also outlines potential hazards associated with specific job tasks, identifies the severity of those hazards, suggests controls to mitigate risks, and details the implementation of these controls, much like the Army Risk form does for military missions or tasks.
Health and Safety Risk Assessment forms used in various workplaces share the same core philosophy of identifying hazards, assessing the risks associated with those hazards, implementing controls to manage the risks, and monitoring the effectiveness of the controls, akin to the structured process of the Army Risk form.
The Operational Risk Management (ORM) worksheets, particularly used in aviation and other high-risk fields, also focus on identifying hazards, analyzing risks, making decisions to control those risks, implementing controls, and supervising the effectiveness, mirroring the Army Risk form’s approach to risk management.
Fire Risk Assessment forms evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of fire hazards within a property and suggest measures to minimize risks, paralleling the Army Risk form's methodology of risk assessment and control implementation.
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report, while broader in scope, shares similarities with the Army Risk form by identifying potential environmental hazards, assessing the impacts of these hazards, and outlining mitigation measures to address the identified risks.
Project Risk Management Plan documents closely resemble the Army Risk form as they involve the identification of project-specific risks, assessment of the probability and impact of those risks, and development of strategies to manage or mitigate the risks to project success.
The Chemical Hazard Risk Assessment forms, used in laboratories and industrial settings, entail the assessment of chemical hazards, determination of exposure risks, and implementation of control measures to reduce risks, reflecting the risk management steps detailed in the Army Risk form.
Construction Safety Plan documents, particularly those sections focused on hazard identification, risk assessment, and safety control measures, share a practical similarity with the Army Risk form in ensuring that risks are managed effectively on construction sites.
A Transportation Safety Risk Assessment outlines the hazards associated with transporting goods or personnel, assesses the risks presented by these hazards, and defines control measures to mitigate these risks, following a similar risk management process as the Army Risk form.
The Event Safety and Risk Management Plan, which is essential for planning large public or private events, involves identifying potential safety hazards, assessing the level of risk each hazard presents, and establishing control measures to manage these risks, mirroring the deliberate process of hazard identification and risk management found in the Army Risk form.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Army Risk Form, also known as the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, it's important to both follow best practices and avoid common pitfalls. Below are essential do's and don'ts to keep in mind:
- Do provide a clear and concise description of the mission or task in the section of Mission/Task Description. It's crucial for setting the context of the risk assessment.
- Do ensure all dates are formatted correctly (DD/MM/YYYY) to avoid any confusion or misinterpretation of the assessment timeline.
- Do carefully identify hazards for each subtask or substep accurately in the Hazard identification section to ensure all risks are assessed.
- Do use the Risk Assessment Matrix properly to determine Initial and Residual Risk Levels, providing a standardized evaluation of risks.
- Do describe the controls and their implementation clearly in the Control and How to Implement/Who Will Implement sections.
- Do not leave sections blank; if a section does not apply, note it as N/A (Not Applicable) to indicate a thorough review was conducted.
- Do not forget to sign the form as both the preparer and the approval authority, where applicable, as unsigned forms may lack validity or may not be processed.
By adhering to these guidelines, the risk assessment process is streamlined and ensures that the form is both accurate and complete. This attention to detail supports the overall mission planning and safety processes.
Misconceptions
Understanding the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, commonly referred to as the Army Risk Form, is crucial for ensuring safety and preparedness in military operations. However, several misconceptions exist around its use and purpose. By dispelling these myths, we can appreciate the form's importance in mission planning and execution.
It's only for combat operations: Many believe the Army Risk Form is solely for combat-related activities. However, it's used for a wide range of operations, from training exercises to daily routine tasks within the military environment. Its purpose is to identify and mitigate risks across the board, not just in combat scenarios.
Completing the form guarantees safety: While the form is a comprehensive tool for risk assessment, it doesn't guarantee absolute safety. The unpredictability of both human behavior and environmental conditions means there's always some level of risk. The form helps in managing these risks to acceptable levels, rather than eliminating them entirely.
It's time-consuming and unnecessary: Some might view the form as bureaucratic and a waste of time, especially if they've never encountered issues without it. However, this proactive approach to identifying and controlling hazards can save time, resources, and lives in the long run, making it an essential part of mission planning.
Only high-ranking officers need to understand it: While it might seem like a task for senior personnel, understanding the Risk Assessment Worksheet is crucial for everyone involved in the mission. Everyone has a role in identifying hazards and implementing controls, so broad familiarity with the process enhances teamwork and safety.
The process is completed once the form is filled out: Filling out the form is just the beginning. Implementing the identified controls and continuously monitoring and adjusting them as conditions change is vital for the process to be effective. The form is a living document that requires ongoing attention and updates as the mission unfolds.
Understanding and properly utilizing the Army Risk Form is a collective responsibility that significantly contributes to operational success and safety. By addressing these misconceptions, military personnel can approach risk assessment with the seriousness and diligence it demands.
Key takeaways
When filling out the Army Risk Assessment form, also known as the DD Form 2977, "Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet," it's vital to understand its purpose and how to accurately complete it. This form is designed to systematically evaluate potential risks associated with Army missions or tasks, with a focus on identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards. Below are key takeaways for properly utilizing this form:
- It's crucial to provide a concise description of the mission or task at hand in the designated section to set the context for the risk assessment.
- The date of the assessment helps in tracking the evaluation process over time, making it essential to fill this out accurately.
- Details of the preparer are necessary for accountability and follow-up questions. This section requires comprehensive information about the individual conducting the risk assessment.
- For each subtask or step of the mission, hazards must be clearly identified. This systematic approach helps in breaking down the mission into manageable segments for thorough analysis.
- Use the risk assessment matrix provided to determine the initial risk level of each hazard. This step involves assessing both the probability and severity of potential incidents.
- Developing controls to mitigate identified risks is a collaborative effort. The form requires specifying both the control measures and the responsible parties for implementation.
- After control measures are planned, assess the residual risk level. This step evaluates the effectiveness of the controls in reducing the risk.
- Assigning an overall residual risk level provides a summary indicator of the mission or task's safety status post-control implementation.
- The supervision plan section is critical for outlining how the risks will be monitored and by whom, ensuring that the controls are effectively implemented and adjusted as needed.
- The approval or disapproval of the mission or task hinges on the comprehensive assessment of risks, controls, and residual risks, underscoring the importance of thorough and accurate completion of the form.
- Regular risk assessment reviews are mandated to account for any changes or updates in the mission or task environment.
- Feedback and lessons learned contribute to organizational learning, offering insights into risk management effectiveness and opportunities for improvement.
Proper completion and use of the DD Form 2977 are fundamental in promoting safety and reducing the likelihood of adverse events in Army operations. By meticulously following the guidelines and instructions, those responsible can make informed decisions that safeguard personnel and resources effectively.
Popular PDF Forms
Tax Donation Receipt Template - Presents an easy-to-navigate form for making in-memory or in-honour donations, fostering a means of tribute that benefits charitable work.
Ohio Repossession Laws - The form acts as a direct communication tool between the legal owner and the facility holding the vehicle, expediting the repossession process.