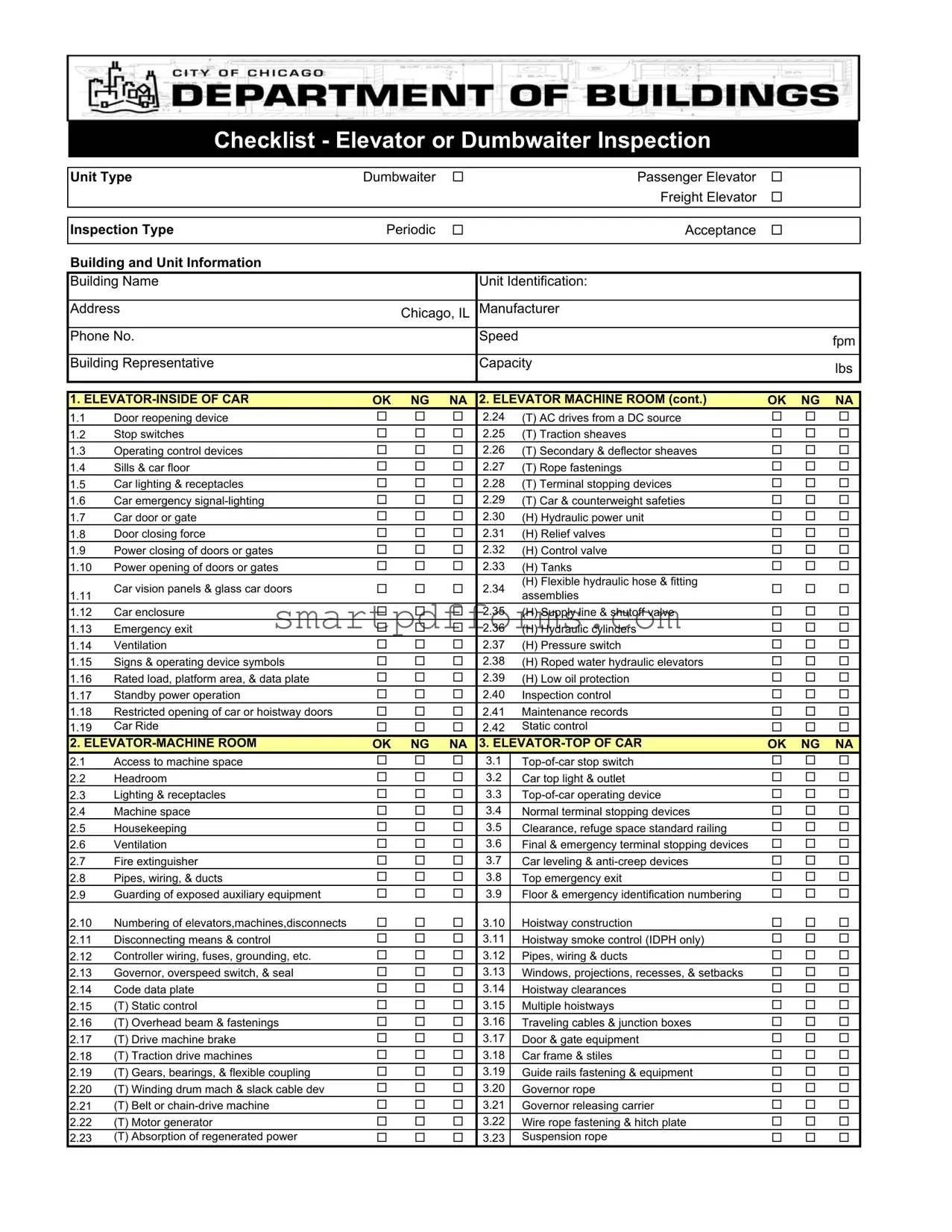
Blank Elevator Inspection Checklist PDF Template
Ensuring the safety and operational efficiency of elevators and dumbwaiters is paramount, necessitating a comprehensive inspection process guided by a meticulously structured Elevator Inspection Checklist. This essential document addresses a wide array of elements, including distinct unit types such as passenger elevators, freight elevators, and dumbwaiters, alongside specifying whether the inspection is periodic or for acceptance purposes. Key information about the building and unit, such as the building name, unit identification, and manufacturer details, are integral parts of the form, ensuring a tailored inspection approach to each unique setup. The checklist delves into various inspection aspects covering the inside of the car, machine room, top of the car, outside the hoistway, and the elevator pit, categorically listing critical elements such as door reopening devices, car lighting, emergency exits, ventilation, and many more. Each item is subject to an evaluation marked as OK, NG (No Good), or NA (Not Applicable), indicating the condition and compliance of each component with established standards. Special notations for traction and hydraulic elevator specific items are included, highlighting the nuanced differences in inspection criteria based on elevator type. Traction elevators, for instance, are scrutinized for components like traction sheaves and rope fastenings, while hydraulic elevators are checked for elements like hydraulic power units and relief valves. Moreover, the form allows inspectors to note the inspection status, the inspection company's details, and any pertinent comments regarding the items checked, making it an indispensable tool for ensuring elevator safety and regulatory compliance.
Preview - Elevator Inspection Checklist Form

Checklist - Elevator or Dumbwaiter Inspection
Unit Type |
Dumbwaiter |
Passenger Elevator |
|
|
Freight Elevator |
|
|
|
Inspection Type |
Periodic |
Acceptance |
|
|
|
Building and Unit Information
Building Name |
|
|
|
Unit Identification: |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Address |
|
Chicago, IL |
Manufacturer |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Phone No. |
|
|
|
Speed |
|
|
|
fpm |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Building Representative |
|
|
|
Capacity |
|
|
lbs |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
2. ELEVATOR MACHINE ROOM (cont.) |
OK |
NG |
NA |
|||
1.1 |
Door reopening device |
|
|
|
2.24 |
|
(T) AC drives from a DC source |
|
|
|
1.2 |
Stop switches |
|
|
|
2.25 |
|
(T) Traction sheaves |
|
|
|
1.3 |
Operating control devices |
|
|
|
2.26 |
|
(T) Secondary & deflector sheaves |
|
|
|
1.4 |
Sills & car floor |
|
|
|
2.27 |
|
(T) Rope fastenings |
|
|
|
1.5 |
Car lighting & receptacles |
|
|
|
2.28 |
|
(T) Terminal stopping devices |
|
|
|
1.6 |
Car emergency |
|
|
|
2.29 |
|
(T) Car & counterweight safeties |
|
|
|
1.7 |
Car door or gate |
|
|
|
2.30 |
|
(H) Hydraulic power unit |
|
|
|
1.8 |
Door closing force |
|
|
|
2.31 |
|
(H) Relief valves |
|
|
|
1.9 |
Power closing of doors or gates |
|
|
|
2.32 |
|
(H) Control valve |
|
|
|
1.10 |
Power opening of doors or gates |
|
|
|
2.33 |
|
(H) Tanks |
|
|
|
|
Car vision panels & glass car doors |
|
|
|
2.34 |
|
(H) Flexible hydraulic hose & fitting |
|
|
|
1.11 |
|
|
|
|
assemblies |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1.12 |
Car enclosure |
|
|
|
2.35 |
|
(H) Supply line & shutoff valve |
|
|
|
1.13 |
Emergency exit |
|
|
|
2.36 |
|
(H) Hydraulic cylinders |
|
|
|
1.14 |
Ventilation |
|
|
|
2.37 |
|
(H) Pressure switch |
|
|
|
1.15 |
Signs & operating device symbols |
|
|
|
2.38 |
|
(H) Roped water hydraulic elevators |
|
|
|
1.16 |
Rated load, platform area, & data plate |
|
|
|
2.39 |
|
(H) Low oil protection |
|
|
|
1.17 |
Standby power operation |
|
|
|
2.40 |
|
Inspection control |
|
|
|
1.18 |
Restricted opening of car or hoistway doors |
|
|
|
2.41 |
|
Maintenance records |
|
|
|
1.19 |
Car Ride |
|
|
|
2.42 |
|
Static control |
|
|
|
2. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
3. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
|||
2.1 |
Access to machine space |
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
Headroom |
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
Car top light & outlet |
|
|
|
2.3 |
Lighting & receptacles |
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.4 |
Machine space |
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
Normal terminal stopping devices |
|
|
|
2.5 |
Housekeeping |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
Clearance, refuge space standard railing |
|
|
|
2.6 |
Ventilation |
|
|
|
3.6 |
|
Final & emergency terminal stopping devices |
|
|
|
2.7 |
Fire extinguisher |
|
|
|
3.7 |
|
Car leveling & |
|
|
|
2.8 |
Pipes, wiring, & ducts |
|
|
|
3.8 |
|
Top emergency exit |
|
|
|
2.9 |
Guarding of exposed auxiliary equipment |
|
|
|
3.9 |
|
Floor & emergency identification numbering |
|
|
|
2.10 |
Numbering of elevators,machines,disconnects |
|
|
|
3.10 |
|
Hoistway construction |
|
|
|
2.11 |
Disconnecting means & control |
|
|
|
3.11 |
|
Hoistway smoke control (IDPH only) |
|
|
|
2.12 |
Controller wiring, fuses, grounding, etc. |
|
|
|
3.12 |
|
Pipes, wiring & ducts |
|
|
|
2.13 |
Governor, overspeed switch, & seal |
|
|
|
3.13 |
|
Windows, projections, recesses, & setbacks |
|
|
|
2.14 |
Code data plate |
|
|
|
3.14 |
|
Hoistway clearances |
|
|
|
2.15 |
(T) Static control |
|
|
|
3.15 |
|
Multiple hoistways |
|
|
|
2.16 |
(T) Overhead beam & fastenings |
|
|
|
3.16 |
|
Traveling cables & junction boxes |
|
|
|
2.17 |
(T) Drive machine brake |
|
|
|
3.17 |
|
Door & gate equipment |
|
|
|
2.18 |
(T) Traction drive machines |
|
|
|
3.18 |
|
Car frame & stiles |
|
|
|
2.19 |
(T) Gears, bearings, & flexible coupling |
|
|
|
3.19 |
|
Guide rails fastening & equipment |
|
|
|
2.20 |
(T) Winding drum mach & slack cable dev |
|
|
|
3.20 |
|
Governor rope |
|
|
|
2.21 |
(T) Belt or |
|
|
|
3.21 |
|
Governor releasing carrier |
|
|
|
2.22 |
(T) Motor generator |
|
|
|
3.22 |
|
Wire rope fastening & hitch plate |
|
|
|
2.23 |
(T) Absorption of regenerated power |
|
|
|
3.23 |
|
Suspension rope |
|
|
|
Checklist - Elevator or Dumbwaiter Inspection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Continuation) |
||||
Unit ID: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
|
|
5. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
|||
3.24 |
(T) Top counterweight clearance |
|
|
|
5.1 |
|
Pit access, lighting, stop switch, & condition |
|
|
|
||
3.25 |
(T) Car, overhead, & deflector sheaves |
|
|
|
5.2 |
|
Bottom clearance, runby & min. refuge space |
|
|
|
||
|
(T) Broken rope, chain, or tape switch |
|
|
|
5.3 |
|
(T) Final & emergency terminal stopping |
|
|
|
||
3.26 |
|
|
|
|
devices |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3.27 |
Crosshead data plate & rope data tags |
|
|
|
5.4 |
|
Normal terminal stopping devices |
|
|
|
||
3.28 |
Counterweight & counterweight buffer |
|
|
|
5.5 |
|
Traveling cables |
|
|
|
||
3.29 |
Counterweight safeties |
|
|
|
5.6 |
|
|
|
|
|||
3.30 |
(H) Speed test |
|
|
|
5.7 |
|
Car Frame & platform |
|
|
|
||
|
(H) Slack rope device – |
|
|
|
5.8 |
|
Car safeties & guiding members - including |
|
|
|
||
3.31 |
elevators (*) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
(H) Traveling sheave – |
|
|
|
5.9 |
|
(T) Buffers & emergency terminal speed |
|
|
|
||
3.32 |
(*) |
|
|
|
|
|
limiting devices |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
3.33 |
(T) Compensating ropes & chains |
|
|
|
5.10 |
|
(T) Compensating chains, ropes & sheaves |
|
|
|
||
4. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
5.11 |
|
(H) Plunger & cylinder |
|
|
|
|||
4.1 |
Car platform guard |
|
|
|
5.12 |
|
(H) Car buffer |
|
|
|
||
4.2 |
Hoistway doors |
|
|
|
5.13 |
|
(H) Guiding members |
|
|
|
||
4.3 |
Vision panels |
|
|
|
5.14 |
|
(H) Supply piping |
|
|
|
||
4.4 |
Hoistway door locking devices |
|
|
|
6. |
OK |
NG |
NA |
||||
4.5 |
Access to hoistway |
|
|
|
6.1 |
|
Phase I Operation |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
Power closing of hoistway doors |
|
|
|
6.2 |
|
Phase II Operation |
|
|
|
||
4.7 |
Sequence operation |
|
|
|
6.3 |
|
FAID (Fire Alarm Initiating Device) Operation |
|
|
|
||
4.8 |
Hoistway enclosure |
|
|
|
OK – meets requirement |
|
|
|
||||
4.9 |
Elevator Parking devices |
|
|
|
NG – No Good (Insert number to identify comment on form) |
|
||||||
4.10 |
Emergency doors in blind hoistways |
|
|
|
NA – not applicable |
|
|
|
||||
4.11 |
(T) Separate counterweight hoistway |
|
|
|
(T) – Traction Elevators only |
|
|
|
||||
4.12 |
Standby power selection switch |
|
|
|
(H) – Hydraulic elevators only |
|
|
|
||||
4.13 |
Inspection control |
|
|
|
(*) - |
installed under |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
|
Comment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Code |
|
|
No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reference |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inspection Status: |
|
|
Inspection Company & Inspector’s Information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Company Name |
Date of Inspection: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Street Address |
Code Edition: |
|
|
|
|
FAIL |
|
City, State, Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inspector QEI # |
|
|
Permit Req'd |
|
|
PASS |
|
Inspector’s State License # |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inspector’s Signature: |
|
|
|
|
Revised |
Page 2 of 2 |
|
Form Data
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Form Type | Elevator or Dumbwaiter Inspection Checklist |
| Application Types | Dumbwaiter, Passenger Elevator, Freight Elevator |
| Inspection Types | Periodic, Acceptance |
| Key Sections | Elevator Inside of Car, Elevator Machine Room, Elevator Top of Car, Elevator Pit, Elevator Outside Hoistway, Elevator Fire Service |
| Inspection Status Options | OK, NG (No Good), NA (Not Applicable) |
| Location | Chicago, IL |
| Governing Law(s) | Code Edition referenced in the form; ASME A17.1 Safety Code for Elevators and Escalators |
| Inspection Company Information | Includes Company Name, Address, Inspector's QEI Number, License Number, Signature, and Inspection Date |
| Special Notation Codes | (T) for Traction Elevators only, (H) for Hydraulic Elevators only, (*) for items installed under A17.1b-1989 and later editions |
| Form Revision Date | Revised 2-10-2011 |
| Permit Requirement | Indication if a permit is required for the inspection |
Instructions on Utilizing Elevator Inspection Checklist
Completing the Elevator Inspection Checklist form is a critical step in ensuring the safety and compliance of elevator units within a building. This form is designed to document the condition of various components of the elevator system, from the inside of the car to the pit, and ensure they meet the required standards. It encompasses checking the functionality and safety mechanisms of both passenger and freight elevators, as well as dumbwaiters. Individuals responsible for this task should approach it with thoroughness, ensuring that every item on the checklist is inspected accurately and any issues are recorded for further action.
- Begin with the "Checklist - Elevator or Dumbwaiter Inspection" section by selecting the unit type: Dumbwaiter, Passenger Elevator, or Freight Elevator.
- Indicate the type of inspection being carried out: Periodic or Acceptance.
- Fill in the "Building and Unit Information" section, including the Building Name, Unit Identification, Address, Manufacturer, Phone No., Speed (fpm), Building Representative, and Capacity (lbs).
- Proceed to the "ELEVATOR-INSIDE OF CAR" section. For each item listed (1.1 to 1.19), mark the appropriate box with OK, NG, or NA, depending on the condition observed during the inspection.
- In the "ELEVATOR MACHINE ROOM (cont.)" section, fill out the conditions of items 2.1 to 2.42 using the same OK, NG, or NA indicators.
- Continue this process through the "ELEVATOR-TOP OF CAR," "ELEVATOR-PIT," and "ELEVATOR-OUTSIDE HOISTWAY" sections, carefully reviewing and indicating the condition of each listed item.
- For the "ELEVATOR-FIRE SERVICE" segment, assess the Phase I Operation, Phase II Operation, and FAID (Fire Alarm Initiating Device) Operation, marking their status accordingly.
- For any section where NG (No Good) is marked, insert a number to identify a comment on the form, explaining the issue found. This will be used in the "Item Comment" section later.
- Fill in the "Inspection Status:" section by indicating whether the inspection resulted in a FAIL or PASS outcome.
- Complete the "Inspection Company & Inspector’s Information" area with the Company Name, Date of Inspection, Street Address, City, State, Zip, Code Edition, Inspector's QEI #, Permit Required, Inspector’s State License #, and Inspector’s Signature. Ensure all information is accurate and legible.
After filling out the Elevator Inspection Checklist meticulously, the document must be reviewed to ensure all parts are completed and any areas requiring attention are addressed. This comprehensive review process aids in maintaining the safety standards of elevator units and ensures that any necessary repairs or adjustments are identified and implemented promptly. It is essential for the longevity and reliability of the elevator systems within the building.
Obtain Answers on Elevator Inspection Checklist
What is the purpose of the Elevator Inspection Checklist form?
The Elevator Inspection Checklist form is designed to ensure the safety and reliability of elevator or dumbwaiter systems within buildings. It serves as a comprehensive tool for inspectors to verify that all components of these systems meet the required safety standards and are in good working condition. The checklist covers various aspects of the elevator system including the inside of the car, machine room, top of car, pit, outside hoistway, and fire service. Through periodic and acceptance inspections, it aims to identify any deficiencies that could potentially compromise the safety of users or disrupt the operation of the elevator or dumbwaiter.
Who is responsible for conducting inspections using this checklist?
Inspections using the Elevator Inspection Checklist form are typically conducted by licensed inspectors or professionals who have received specialized training in elevator and dumbwaiter system evaluation. These inspectors could be either third-party entities or part of local government agencies responsible for building safety. The inspector's qualifications are often denoted by a Qualified Elevator Inspector (QEI) certification or a similar credential. They are required to have a comprehensive understanding of the relevant safety standards and mechanical components of elevator systems as set forth in building codes and regulations.
How often should elevator inspections be performed?
The frequency of elevator inspections can vary based on local regulations, the type of elevator or dumbwaiter system, and its usage level. Generally, most jurisdictions require a periodic inspection at least once a year. Some situations may require more frequent inspections, such as when a new elevator system is installed (acceptance inspection) or when modifications have been made to an existing system. It’s important for building owners or managers to consult with local building departments or elevator maintenance providers to adhere to the specific inspection schedule mandated in their area.
What do the terms OK, NG, and NA stand for on the checklist?
On the Elevator Inspection Checklist form, the terms "OK," "NG," and "NA" are used to indicate the inspection status of each item. "OK" means that the item meets the required standards and is in good working condition. "NG" stands for "No Good" and indicates that the item does not meet the required standards or is in need of repair or adjustment. "NA" means "Not Applicable" and is used for items that do not apply to the specific elevator or dumbwaiter system being inspected. These designations help streamline the inspection process and clearly identify areas needing attention.
What happens if an item fails the inspection?
If an item on the checklist is marked as "NG," indicating it has failed the inspection, corrective actions must be taken to address the deficiency. The specific steps to rectify the failure may involve repairs, replacements, or adjustments to the elevator or dumbwaiter system components. The building owner or manager typically must hire a qualified elevator maintenance company to perform the necessary work. After the corrective measures are completed, a follow-up inspection may be required to ensure that the issue has been adequately resolved and the system now complies with safety standards.
Are maintenance records important for the inspection process?
Yes, maintenance records play a crucial role in the inspection process. They provide a detailed history of the elevator or dumbwaiter system’s upkeep, modifications, and any repairs that have been conducted. This information can help the inspector understand the condition of the system, identify patterns of recurring issues, and verify that regular maintenance has been carried out in accordance with safety regulations. Proper documentation of maintenance activities can also expedite the inspection process and support compliance with local codes.
Can an elevator pass the inspection if some items are marked as NA?
Yes, an elevator or dumbwaiter can pass the inspection if certain items are marked as "NA," provided that all applicable items are in compliance with the required standards. The "NA" marker is used for components that are not present in the specific system being inspected, indicating they are not relevant to the safety and functionality evaluation of that system. The overall inspection outcome is determined based on the condition and compliance of relevant components.
Common mistakes
Filling out an Elevator Inspection Checklist is crucial for the safety and compliance of building operations. However, people often make mistakes during this process. Understanding these common errors can help avoid complications and ensure a thorough evaluation. Here are six mistakes frequently encountered:
- Overlooking the type of unit: Not specifying whether the unit is a dumbwaiter, passenger elevator, or freight elevator can lead to an incomplete assessment of the unit's specific requirements.
- Skipping sections not immediately applicable: Marking sections as “Not Applicable” without proper consideration. Every part of the checklist is designed to ensure comprehensive safety and operational standards.
- Incorrect identification of the unit: Failing to accurately identify the unit or providing vague identification details compromises the inspection’s integrity and can cause confusion in maintenance records.
- Inconsistent information: Providing inconsistent information regarding the building and unit details, such as differing addresses or misstated capacity and speed, can lead to an ineffective inspection.
- Ignoring the inspection type: Not clearly indicating whether the inspection is periodic or for acceptance. This mistake can greatly affect the inspection's scope and the detail level required.
- Incomplete documentation of issues: Not fully documenting issues found or skipping the “comments” section can result in unresolved safety hazards. Every observation, whether compliant (OK) or non-compliant (NG), should be accurately recorded to ensure proper follow-up.
In summary, when completing an Elevator Inspection Checklist, it’s vital to give full attention to every section and provide accurate, thorough information. This will ensure the safety and compliance of elevator operations, identifying any potential issues before they become major problems.
Documents used along the form
When carrying out an inspection of an elevator or dumbwaiter system, a comprehensive assessment is facilitated by the utilization of a variety of forms and documents, in addition to the Elevator Inspection Checklist. These documents ensure that all safety, regulatory, and maintenance aspects of the elevator system are thoroughly reviewed and properly documented. Below is a list of other forms and documents that are often used alongside the Elevator Inspection Checklist to provide a complete and detailed evaluation of elevator systems.
- Incident Report Forms: These forms are used to document any accidents, malfunctions, or incidents that occurred with respect to the elevator system. Detailed records of such events are crucial for ensuring accountability and for improving future safety measures.
- Repair and Maintenance Logs: Maintenance logbooks are essential for tracking the history of repairs, maintenance schedules, and the persons or entities responsible for such tasks. They help in identifying patterns that may necessitate preventive measures or upgrades.
- Compliance Certificates: Elevators must operate in accordance with certain standards and regulations. Compliance certificates demonstrate that the elevator systems meet the required safety and operational benchmarks set by relevant authorities.
- Permit Documentation: These documents include any permits required by local or state jurisdictions for the operation, repair, or alteration of elevator systems. They ensure that all work on the elevator system adheres to legal and regulatory standards.
- Inspection Notices: Notices that are issued either before or after inspections. They might inform building owners or managers about upcoming inspections or summarize findings and required actions following an inspection.
- Fire Safety Inspection Reports: Specifically focusing on the aspects related to the elevator’s integration with fire safety systems within a building, these reports assess compliance with fire codes, including the operation of fire service features of the elevator.
- Accessibility Compliance Documents: These documents ensure that the elevator system complies with regulations regarding accessibility for individuals with disabilities, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States.
Together, these documents play a critical role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and compliance of elevator systems. Building owners and maintenance personnel rely on them, not just for routine inspections and maintenance, but also for providing a historical record of the system's performance and interventions. They serve to protect both the physical integrity of the elevator systems and the safety of their users.
Similar forms
Fire Safety Inspection Checklist: Similar to the Elevator Inspection Checklist, this document ensures compliance with safety regulations within a building. It focuses on fire safety measures like the presence of extinguishers, smoke alarms, and clear evacuation routes. Both checklists aim to identify risks and ensure the safety and well-being of occupants by adhering to strict safety standards.
Building Safety Inspection Checklist: This document covers a wide range of safety considerations in a building, much like the Elevator Inspection Checklist surveys various aspects of elevator safety. It examines structural integrity, emergency exits, electrical systems, and more, ensuring all parts of a building are up to code, similar to how the elevator checklist ensures all components of the elevator system are functioning safely.
Construction Site Safety Inspection Checklist: This checklist is used to identify hazards and enforce safety regulations on construction sites. It shares similarities with the Elevator Inspection Checklist in its detailed approach to safety, focusing on specific items and conditions that must be met to ensure a safe environment, whether it's on a construction site or within elevator systems.
Electrical Inspection Checklist: Dedicated to ensuring all electrical systems and components meet safety standards, this checklist parallels the Elevator Inspection Checklist by focusing on a specific aspect of building operations. Both highlight the importance of maintaining systems to prevent accidents, focusing on electrical integrity in one and elevator safety in the other.
Facility Maintenance Checklist: This document aids in the regular upkeep and inspection of a facility's infrastructure, similar to how the Elevator Inspection Checklist is used for elevator maintenance. Both checklists ensure operational efficiency, safety, and longevity of building systems by regular monitoring and corrective actions.
HVAC System Inspection Checklist: Examining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, this checklist ensures these systems are operating correctly and efficiently, similar to how the Elevator Inspection Checklist focuses on elevator systems. Both are vital for the comfort, safety, and health of building occupants, emphasizing the importance of regular inspections.
Plumbing Inspection Checklist: This checklist examines plumbing systems to prevent leaks, blockages, and other issues. Like the Elevator Inspection Checklist, it ensures a critical component of a building's infrastructure is functioning correctly, avoiding potential hazards and ensuring compliance with health and safety standards.
Vehicle Inspection Checklist: Though focused on vehicles, this checklist shares the same principle with the Elevator Inspection Checklist by ensuring all parts are in safe, working order. It serves to prevent accidents due to mechanical failures, much like the elevator checklist's aim to ensure the safe operation of elevator systems.
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Audit Checklist: This comprehensive document is designed to ensure workplaces meet health and safety regulations, similar to the Elevator Inspection Checklist's role in ensuring elevator safety. Both aim to identify and mitigate risks, creating a safer environment for all individuals on the premises.
Dos and Don'ts
When it comes to ensuring the safety and compliance of elevators or dumbwaiters, filling out the Elevator Inspection Checklist form thoroughly and correctly is crucial. Below are four key dos and don'ts to keep in mind during this process:
Do:
- Review every item carefully. Each section, whether it's concerning the inside of the car, the machine room, or the pit, serves a purpose in maintaining the elevator's operation and safety. Overlooking an item can lead to potential hazards.
- Check for accuracy. When entering information about the building, unit identification, manufacturer, and inspection type, ensure all details are correct and up-to-date. Mistakes here could affect the validity of the inspection.
- Understand the codes. The checklist references various codes such as (T) for traction elevators or (H) for hydraulic elevators. Knowing what each code means is essential for conducting the right checks and understanding the equipment you are inspecting.
- Sign and date the form. The inspector's signature, state license number, and the date of inspection are required to authenticate the inspection process. A lack of signature or incorrect details can render the form invalid.
Don't:
- Skimp on detail. When noting the condition of equipment (OK, NG, NA), provide specific comments or observations that led to your assessment. Vague descriptions or omissions may result in inadequate follow-up or maintenance.
- Gloss over new updates or changes to the checklist. If there have been recent updates to safety standards or checklist items, ensure you're familiar with these changes and apply them during your inspection.
- Forget to check for the latest code edition reference. The form requires the inspector to note the code edition used during the inspection. Using an outdated version can lead to non-compliance with current safety standards.
- Rush through the inspection. Given the detailed nature of the form and the critical importance of each item for safety and compliance, take your time to conduct a thorough and comprehensive inspection.
Misconceptions
Many people have misconceptions about the Elevator Inspection Checklist form. Here are four common misunderstandings along with explanations to clarify them:
- Misconception 1: The checklist only covers basic safety features.
- Misconception 2: The inspection checklist is the same for all types of elevators.
- Misconception 3: Any issues found are immediately fixed during the inspection.
- Misconception 4: The checklist is irrelevant if the elevator seems to be working fine.
This is incorrect. While safety features are a major focus, the checklist is comprehensive and covers various aspects of elevator operation, including but not limited to door reopening devices, machine room equipment, lighting, the operation of control devices, and even the conditions of car top and pit. These areas ensure the elevator operates smoothly and safely under all conditions.
The document differentiates between different types of units – dumbwaiters, passenger elevators, and freight elevators. Each type has unique requirements and specifications for inspection. For instance, items specifically marked with (T) for traction elevators or (H) for hydraulic elevators acknowledge the different mechanisms these types of elevators operate on and thus have tailored inspection points.
The role of the inspection is to identify whether each item meets requirements (OK), does not meet requirements (NG), or is not applicable (NA). While identifying issues is a key part of the process, immediate fixes are not the responsibility of the inspector. Instead, the inspection results are reported to the building manager or elevator maintenance company to address.
Even if an elevator appears to be operating correctly, the checklist covers areas that may not be immediately obvious but are crucial for long-term safety and functionality. Regular inspections using the checklist can identify potential problems before they lead to malfunction or safety hazards, ensuring the elevator's reliability and compliance with safety regulations.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the Elevator Inspection Checklist form is crucial for ensuring the safety and compliance of elevator units within buildings. Understanding the key components of this list can help you navigate through the process efficiently. Here are eight key takeaways:
- Identify the unit type: Make sure to correctly specify if the inspection is for a dumbwaiter, passenger elevator, or freight elevator, as different standards and checks might apply.
- Understand the inspection type: Know whether you're conducting a periodic or acceptance inspection. Periodic inspections are routine checks, while acceptance inspections are for newly installed elevators or after major repairs.
- Provide detailed building and unit information: Accurately fill out the building name, unit identification, address, and other necessary details to ensure clear identification and records.
- Check each item carefully: Each item listed under sections like the elevator machine room, top of car, and pit require diligent inspection for OK (satisfactory), NG (not good), or NA (not applicable) statuses.
- Pay close attention to safety features: Special attention should be given to emergency and safety features, including door reopening devices, emergency signals, and car safeties, to ensure they are fully operational.
- Inspect mechanical components thoroughly: Mechanical parts such as gears, bearings, ropes, and sheaves are critical for safe operation and must be inspected meticulously for wear and proper function.
- Maintenance records are key: The availability and status of maintenance records (item 2.41) can provide insights into the unit's upkeep and potential issues that may not be immediately visible.
- Finalize the inspection correctly: Ensure the inspection status is clearly marked as PASS or FAIL, and complete the inspector's information section accurately, including the date of inspection, company name, and inspector's signature.
This checklist is foundational in maintaining elevator safety and compliance, providing a structured approach to evaluating a unit's condition and functionality. By adhering to these key takeaways, you can help ensure the safety of users and the longevity of the elevator units.
Popular PDF Forms
How Do X Rays Work - Used by patients undergoing a change in insurance providers, requiring the transfer of their medical imaging records.
Secondary Leaving Certificate - Essential for Jackson Henry Agarwal’s archival records, signifying a pivotal completion point in his education.
Isf Shipping - By including details like the ocean container number and voyage number, the ISF form allows for precise tracking of shipments across the globe.