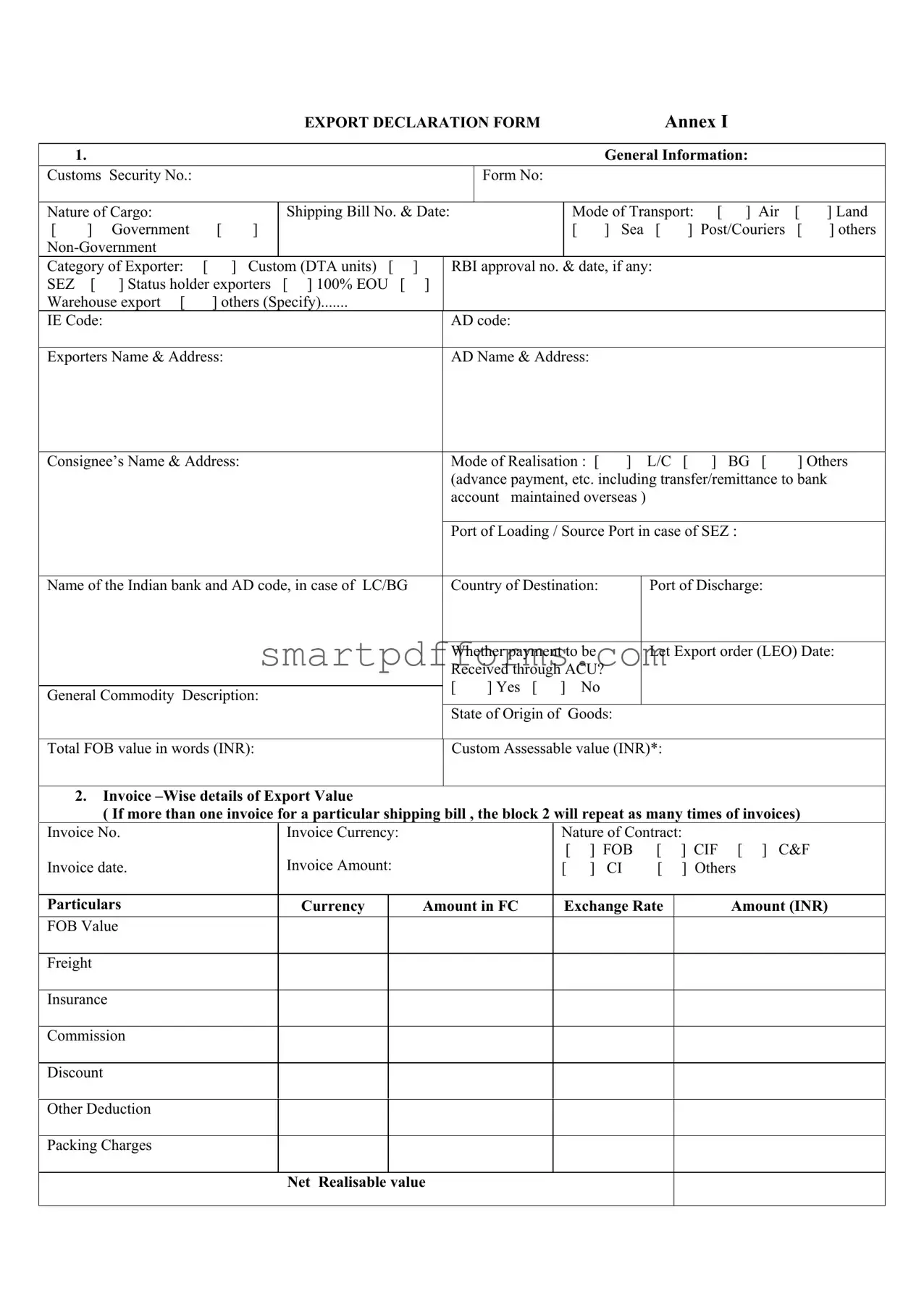
Blank Export Decleration PDF Template
The Export Declaration Form serves as a crucial document for businesses engaged in international trade, encapsulating a wide range of information essential for the export process. This comprehensive form covers general information such as the nature of cargo, shipping bill details, mode of transport, and exporter category, which are necessary for customs and regulatory purposes. It demands specifics, including customs security and form numbers, the mode of transport (air, land, sea, or others), and details about the exporter and consignee, including names, addresses, and relevant codes. Furthermore, it outlines the financial aspects related to the transaction, like the method of payment realization, total value in both foreign currency and INR, and the detailed breakdown of costs including freight, insurance, and discounts. The form also requires invoice-wise details of export value, ensuring accurate and detailed financial records are maintained for each shipment. Additionally, for exports under the Foreign Post Office or couriers, specific sections are to be filled, emphasizing the form’s versatility and comprehensive nature in accommodating various types of exports. Another significant aspect is the declaration by exporters, where they affirm the accuracy of the information provided and their commitment to repatriating the proceeds within the stipulated time frame, further reinforcing the form’s role in compliance and financial integrity. Custom authorities or Special Economic Zone (SEZ) units utilize the document to certify that the goods and declared values match the invoice details provided by the exporter, ensuring a level of scrutiny and verification in the export process. This declaration not only facilitates smooth customs clearance but also serves as a testament to the commitment of businesses to adhere to regulatory requirements and international trade norms.
Preview - Export Decleration Form
|
|
|
|
|
EXPORT DECLARATION FORM |
|
|
|
|
|
Annex I |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General Information: |
|
|
|
|||||
Customs Security No.: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form No: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Nature of Cargo: |
|
|
Shipping Bill No. & Date: |
|
|
|
Mode of Transport: |
[ |
] |
Air |
[ |
] Land |
|||||||||||
[ |
] |
Government |
[ |
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[ |
|
] Sea |
[ |
] |
Post/Couriers |
[ |
] others |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Category of Exporter: |
[ ] |
Custom (DTA units) [ |
] |
|
RBI approval no. & date, if any: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
SEZ |
[ |
] Status holder exporters [ ] 100% EOU |
[ |
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Warehouse export [ |
] others (Specify) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
IE Code: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD code: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Exporters Name & Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
AD Name & Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Consignee’s Name & Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
Mode of Realisation : [ |
] |
|
L/C |
[ |
] |
BG |
[ |
] Others |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(advance payment, etc. including transfer/remittance to bank |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
account maintained overseas ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port of Loading / Source Port in case of SEZ : |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Name of the Indian bank and AD code, in case of LC/BG |
|
Country of Destination: |
|
|
Port of Discharge: |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Whether payment to be |
|
|
Let Export order (LEO) Date: |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Received through ACU? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[ |
] Yes [ |
] |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
General Commodity Description: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State of Origin of |
|
Goods: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Total FOB value in words (INR): |
|
|
Custom Assessable value (INR)*: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
2. Invoice |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
( If more than one invoice for a particular shipping bill , the block 2 will repeat as many times of invoices) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Invoice No. |
|
|
Invoice Currency: |
|
|
|
|
|
Nature of Contract: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[ |
] FOB |
[ |
] CIF |
[ |
] C&F |
|
|||||
Invoice date. |
|
|
Invoice Amount: |
|
|
|
|
|
[ |
] |
CI |
[ |
] |
Others |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Particulars |
|
|
Currency |
|
|
Amount in FC |
|
|
Exchange Rate |
|
|
Amount (INR) |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
FOB Value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Freight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insurance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Commission |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other Deduction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Packing Charges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Net Realisable value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

EXPORT DECLARATION FORM- Cont.
3.Applicable for Export under FPO/Couriers Name of the post Office:
Number & date of Parcel receipts :
Stamp & Signature of Authorised Dealer
4.Declaration by the Exporters (All types of exports)
I /We hereby declare that I/we @am/are the seller/consignor of the goods in respect of which this declaration is made and that the particulars given above are true and that the value to be received from the buyer represents the export value contracted and declared above. I/We undertake that I/we will deliver to the authorised dealer bank named above the foreign exchange representing the full
value of the goods exported as above on or before |
(i.e. within the period of realisation stipulated by RBI from time to |
|
time ) in the manner specified in the Regulations made under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999. |
||
I/We |
@ am/are not in the Caution List of the Reserve Bank of India. |
|
Date: |
|
(Signature of Exporter) |
5.Space for use of the competent authority (i.e. Custom/SEZ) on behalf of Ministry concerned:
Certified, on the basis of above declaration by the Custom/SEZ unit, that the Goods described above and the export value declared by the exporter in this form is as per the corresponding invoice/gist of invoices submitted and declared by the Unit.
Date:
(Signature of Designated/Authorised officials of Custom /SEZ )
@ Strike out whichever is not applicable.
*Unit declared Value in case of exports affected from SEZs
Form Data
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| General Information | Includes Customs Security No., Form No., Nature of Cargo, Shipping Bill No. & Date, Mode of Transport, Category of Exporter, RBI approval no. & date (if any), IE Code, AD code, Exporters Name & Address, AD Name & Address, Consignee’s Name & Address, Mode of Realisation, Port of Loading / Source Port in case of SEZ, Name of the Indian bank and AD code (in case of LC/BG), Country of Destination, Port of Discharge, Whether payment to be Received through ACU, Let Export order (LEO) Date, General Commodity Description, State of Origin of Goods, Total FOB value in words (INR), Custom Assessable value (INR). |
| Invoice-Wise Details | For multiple invoices under a single shipping bill, details such as Invoice No., Invoice Currency, Nature of Contract, Invoice date, Invoice Amount, Particulars Currency Amount in FC, Exchange Rate, Amount (INR), and breakdown of costs including FOB Value, Freight, Insurance, Commission, Discount, Other Deduction, Packing Charges, Net Realisable value are provided. |
| Export under FPO/Couriers | Specifies details applicable for exports under FPO/Couriers, like the Name of the post office, Number & date of Parcel receipts. |
| Declaration by the Exporters | Exporters declare that they are the seller/consignor of the goods, the particulars given are true, the value received from the buyer represents the export value contracted and declared. They undertake to deliver the full value of goods exported to the authorized dealer bank within the RBI stipulated period, adhering to the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and confirm not being on the Reserve Bank of India's Caution List. |
Instructions on Utilizing Export Decleration
Completing the Export Declaration Form is a critical step toward ensuring a smooth process for shipping goods internationally. This document is mandatory for exporters and serves as a declaration to customs authorities, providing details about the goods being shipped, their destination, and the value of these goods. The form must be filled out accurately to avoid any delays or legal complications. Below are the steps to fill out the Export Declaration Form efficiently.
- General Information:
- Enter the Customs Security Number, Form Number, and the Nature of Cargo.
- Fill in the Shipping Bill Number and Date.
- Choose the Mode of Transport by checking the appropriate box (Air, Land, Sea, Government, Post/Couriers, or others).
- Select the Category of Exporter and specify if it falls under other categories not listed.
- Provide the RBI approval number and date, if relevant.
- Input the IE Code and AD code.
- Enter the Exporters Name & Address, AD Name & Address, and the Consignee’s Name & Address.
- Select the Mode of Realisation and specify if it's other than L/C or BG.
- List the Port of Loading or Source Port in case of SEZ exports.
- State the Name of the Indian bank and AD code, in case of LC/BG.
- Enter the Country of Destination, Port of Discharge, and whether payment to be received through ACU (Yes or No).
- Provide a General Commodity Description and the State of Origin of Goods.
- Write down the Total FOB value in words (INR) and Custom Assessable value in INR.
- Invoice – Wise details of Export Value:
- For each invoice, repeat this block and provide Invoice No., Currency, and Nature of Contract.
- Fill in the Invoice Date, Amount, and select if the nature is CI or others.
- Detail the Particulars Currency Amount in Foreign Currency, Exchange Rate, and Amount in INR including FOB Value, Freight, Insurance, Commission, Discount, Other Deduction, and Packing Charges to calculate the Net Realisable value.
- Applicable for Export under FPO/Couriers:
- Enter the Name of the Post Office and Number & date of Parcel receipts.
- Declaration by the Exporters:
- Read the declaration carefully.
- Fill in the date and provide the Signature of Exporter, making sure to strike out the non-applicable sections.
- Space for use of the competent authority:
- This section is for the Custom/SEZ official's certification based on the declaration and documents provided by the exporter. It is not to be filled out by the exporter.
After completing the form with accurate information, the next step involves submission to the competent authority, typically the customs or the designated Special Economic Zone (SEZ) unit, along with the required documents. This submission initiates the process of evaluation and verification by the authorities to ensure compliance with export regulations. Prompt and accurate completion of the Export Declaration Form facilitates a smoother customs clearance process, thereby expediting the shipment of goods.
Obtain Answers on Export Decleration
What is an Export Declaration Form?
An Export Declaration Form is a crucial document used in international trade. It provides comprehensive details about the goods being exported from one country to another. This includes general information such as the nature of cargo, mode of transport, and details of the exporter and consignee. The form also covers financial aspects like the method of payment realization, invoice details, and the total value of goods being shipped. It's a key form that facilitates customs clearance and ensures compliance with export regulations.
Who needs to complete the Export Declaration Form?
Any exporter sending goods out of the country must complete the Export Declaration Form. This includes individual sellers, companies, or any legal entity partaking in the export operation. The form must be accurately filled out and submitted to the relevant customs or export authority, such as the Customs or Special Economic Zone (SEZ) unit, before the goods are dispatched.
What information must be provided in the Export Declaration Form?
Exporters must supply detailed information across several sections:
- General information: Including the customs security number, form number, shipping bill details, and the nature of cargo.
- Exporter and consignee details: Names and addresses, along with banking and payment realization methods.
- Invoice details: Covering currency, amount, and nature of contract among others.
- Declaration by exporters: A confirmation of the accuracy of provided information and compliance with reserve bank guidelines.
How is the Export Declaration Form submitted?
The specific procedure for submitting the Export Declaration Form could vary based on the country's regulations and the nature of goods being exported. Generally, it can be submitted electronically through a designated customs or trade authority's platform, or manually at the approval offices like Custom or SEZ units. The exporter or their authorized dealer bank usually carries out the submission before the goods are exported.
Why is the Export Declaration Form important?
This form serves multiple important functions. It ensures that the export complies with the country’s trade policies and foreign exchange regulations. Furthermore, it facilitates the smooth clearance of goods through customs, helps in the accurate calculation of export duties (if applicable), and supports the compilation of trade statistics. By declaring the value of goods accurately, it also assists in preventing any potential disputes over valuation. Completing and submitting this form correctly is vital for successful and compliant international trade operations.
Common mistakes
When filling out the Export Declaration form, attention to detail is crucial. Avoiding common mistakes can save time and prevent delays in your shipment. Here are six frequent errors to watch out for:
- Incorrect or Incomplete General Information: Every section under General Information must be filled out correctly. Leaving out essential details such as the Customs Security No., Form No., Nature of Cargo, or incorrect Mode of Transport selections can cause unnecessary setbacks.
- Failing to Specify the Category of Exporter Correctly: Exporters often overlook the need to accurately specify their category — be it Custom (DTA units), SEZ, 100% EOU, or status holder exporters. Incorrect classification can lead to processing errors and possible legal complications.
- Misrepresentation of Export Value: Under the Invoice-Wise details section, accurately reporting the Invoice Amount, FOB Value, Freight, Insurance, and other deductions is crucial. Misrepresentation, whether intentional or accidental, can lead to severe penalties.
- Omission of Consignee’s Name & Address: Completeness of the consignee’s details is not optional. Every export requires the full name and address of the consignee to be clearly stated. Failing to do so can cause significant delays.
- Error in Banking Details: The name of the Indian bank, along with the AD code, must be accurately mentioned if the payment mode involves L/C (Letter of Credit) or BG (Bank Guarantee). Incorrect banking details can hinder the transaction process.
- Declaration By Exporters Section Left Unsigned or Undated: The declaration at the end of the form is a legal affirmation of the accuracy and truthfulness of the provided information. Leaving this section unsigned or undated nullifies the document.
Mistakes in these areas can not only delay the export process but also lead to legal issues. Diligence and thoroughness in completing the Export Declaration form ensure smooth customs clearance and compliance with international trade regulations.
Documents used along the form
When it comes to exporting goods abroad, the Export Declaration Form is just the tip of the iceberg. This document is vital as it provides the necessary information about the goods being exported, which is required by customs. However, to ensure a smooth and compliant export process, several other forms and documents are often needed alongside the Export Declaration Form. Understanding these additional documents can help exporters navigate the complexities of international trade more efficiently.
- Commercial Invoice: This is a critical document for every export shipment. It provides information about the product, including price, quantity, and the terms of sale. It’s used by customs worldwide to assess the value of the goods and determine duties and taxes.
- Bill of Lading: For sea shipments, this document is issued by the carrier to the shipper. It serves as a receipt for the goods, a document of title that allows its holder to claim the goods at the destination, and a contract of carriage.
- Air Waybill: Similar to a Bill of Lading but for air transport. It's a receipt for goods and a contract for delivery between the shipper and the carrier. However, it is not a document of title.
- Packing List: This complements the commercial invoice and provides detailed information about the cargo, including the types, quantities, and dimensions of the packages. It helps in the identification and handling of goods during transit.
- Certificate of Origin: A document that certifies the country in which the goods were manufactured. The Certificate of Origin may be required by the destination country for purposes of applying tariffs and import quotas.
- Insurance Certificate: It provides evidence that the goods have been insured against loss or damage during transit. Depending on the Incoterms used, insurance might be the responsibility of the exporter or the importer.
- Export License: Depending on the type of goods being shipped and their destination, an export license may be required. This document is issued by the relevant government department and authorizes the export of goods in compliance with export control regulations.
Together, these documents play a crucial role in ensuring that the export process runs smoothly and in compliance with international trade laws and regulations. Each document serves a specific purpose, from proving the value and origin of the goods to ensuring their safe and legal transportation. By familiarizing themselves with these documents, exporters can avoid potential delays or complications and help ensure a successful transaction.
Similar forms
The Commercial Invoice serves a similar function to the Export Declaration Form in that it provides detailed information on the goods being shipped, including the description, value, and the parties involved in the transaction. Both documents are crucial for customs clearance and validate the transaction between exporter and importer.
The Bill of Lading shares similarities with the Export Declaration Form as it acts as a receipt of freight services, a contract between a freight carrier and shipper, and a document of title. Both documents include details about the cargo, the mode of transport, and destination.
Shippers Export Declaration (SED) closely aligns with the Export Declaration Form because it is used to control exports and compile trade statistics. Both forms record the nature of goods being shipped, their value, and destination. The SED is particularly necessary for shipments exceeding a certain value and destined outside the country.
The Certificate of Origin also shares aspects with the Export Declaration Form as it certifies the country in which the goods were produced. Information pertaining to the commodity’s origin in the Export Declaration Form is vital for adherence to trade agreements and customs clearance.
The Packing List parallels the Export Declaration Form in detailing the specifics of the cargo included in the shipment. While the packing list focuses more on the physical aspects of the cargo, such as weight and packaging details, both documents are essential for logistics and customs verification purposes.
Pro Forma Invoice is akin to the Export Declaration Form in that it describes the goods being sent, including their value and other crucial trade details. Though typically used for customs purposes, the pro forma invoice also serves as a preliminary bill of sale.
Letter of Credit (L/C) documentation bears resemblance to aspects of the Export Declaration Form as it guarantees payment to the exporter under specified conditions, including details about the transaction and proof of shipment. Both documents facilitate international trade by providing assurances to the parties involved.
The Electronic Export Information (EEI) is similar to the Export Declaration Form since it is the electronic version of what used to be the SED. Required by the U.S. Census Bureau for compiling export statistics, it includes detailed information about the export transaction, much like the Export Declaration Form.
Import General Manifest (IGM) shares certain characteristics with the Export Declaration Form. While the IGM details the cargo arriving at an import location, including the shipper and consignee details, the Export Declaration outlines information for goods leaving the country. Both are critical for customs processing.
The Customs Bond similarly encompasses the security of compliance with all laws and regulations pertaining to the importation and exportation of goods. While its primary function differs from the Export Declaration Form, both documents are integral to the movement of goods through customs.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing the Export Declaration Form, careful attention to accuracy and detail is essential. Here are key dos and don'ts to guide you through the process:
Do:
Ensure all the information provided is accurate and up-to-date, including exporter's details, consignee information, and invoice details.
Choose the correct mode of transport and category of exporter as specified in the form to avoid processing delays.
Clearly specify the nature of the cargo, along with the correct Invoice-Wise details of export value for each item if there are multiple invoices.
Provide the total FOB value in both words and figures to prevent any misunderstandings or errors in valuation.
Sign and date the declaration at the end of the form, affirming that all provided information is true and committing to abide by the relevant foreign exchange regulations.
Don't:
Omit the IE Code, AD code, or any other mandatory field that could lead to rejection of the export declaration.
Misrepresent the value of goods or the nature of the transaction, as this can result in legal penalties.
Forget to provide detailed information about the mode of realisation, including whether payment will be received through ACU, to ensure compliance with financial regulations.
Overlook the need to strike out inapplicable options in sections like the declaration by exporters, which could cause confusion about the accuracy of the form.
Leave the section for the competent authority blank, as this part is crucial for the official validation and certification of the export details provided.
Misconceptions
When dealing with the Export Declaration form, it's crucial to understand it thoroughly to ensure compliance and to facilitate smooth international transactions. However, several misconceptions can lead to confusion and errors. Here are eight common misunderstandings:
- It's only necessary for large shipments: Some people believe that the Export Declaration form is only required for large-scale exports. However, this document is necessary for a wide range of exports, regardless of size, to comply with customs and export control regulations.
- The form is complicated and hard to fill out: While it may appear daunting at first, the Export Declaration form is designed to collect essential information about the shipment. With the right guidance and understanding, filling it out becomes straightforward.
- Only physical goods need to be declared: There's a misconception that only tangible goods require declaration. In fact, the form covers a wide range of exports, including services and intellectual property, depending on the country’s export control regulations.
- All fields are mandatory for every exporter: Although the form is comprehensive, not all fields are applicable to every exporter. It's important to understand which sections are relevant to your specific export situation.
- The exporter can decide the value of goods arbitrarily: The value of the goods declared must reflect their true market value and adhere to the terms of the sale (e.g., FOB, CIF). Misdeclaring this value can lead to legal issues and penalties.
- No need to specify the mode of transport in detail: It's essential to accurately indicate the mode of transport as it can affect the export process, including the paperwork required and the customs procedures at the destination country.
- Once submitted, the form cannot be amended: Mistakes happen, and if you realize there’s an error after submission, it's critical to contact the relevant customs or export authority immediately. In many instances, amendments can be made to correct errors.
- The form is only for customs’ use: While primarily used by customs to control and record exports, this document also serves multiple purposes, including export compliance, international trade analysis, and as support for insurance claims.
Understanding these misconceptions and the truth behind the Export Declaration form can greatly simplify the export process, ensuring legal compliance and facilitating smoother operations in international trade.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using the Export Declaration form is a critical process for businesses involved in the export of goods. This form serves as a key document for customs clearance and compliance with export regulations. Here are six key takeaways to ensure its proper use and completion:
- The General Information section must be thoroughly completed, providing specific details like the Customs Security Number, Form Number, Nature of Cargo, and Shipping Bill Number and Date. This foundational information is crucial for tracking and processing the export.
- Exporter needs to clearly specify the Mode of Transport (Air, Land, Sea, Post/Couriers, etc.), as this will affect the handling and shipping requirements of the cargo.
- It is important to properly categorize the type of exporter (Custom DTA units, SEZ, 100% EOU, etc.) and provide the relevant IE Code and AD Code. This helps in identifying the nature of the business and applying appropriate regulations and benefits.
- Details regarding the Payment Realisation Mode (L/C, BG, others) must be provided, including information on the Indian bank and its AD code if applicable. This ensures that financial transactions related to the export are properly documented and traceable.
- The form requires a detailed commodity description, including the Invoice-Wise details of Export Value. This section is critical for determining the value of the goods exported and ensuring that the declared value matches the commercial invoice value to comply with customs and export controls.
- A Declaration by the Exporters section is included for the exporter to assert that the information provided is accurate and to commit to delivering the foreign exchange earnings as per regulatory requirements. This legal commitment is crucial for compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999.
Additionally, the form must be stamped and signed by an Authorised Dealer, and a designated space is provided for the use of the competent authority (Custom/SEZ) to certify the correctness of the declared information. Proper completion and certification of the Export Declaration Form facilitate smooth export transactions and compliance with international trade regulations.
Popular PDF Forms
Hvcc Appraisal - An endorsement by the lending party that all procedures leading to the completion of the appraisal were in strict accordance with the Home Valuation Code of Conduct, ensuring reliability.
Louisiana Pilot Car Certification - Contains fields for detailed vehicle information, including make, model, year, and serial number, to accurately identify the escort vehicle.
How to Claim Rent on Taxes Ontario - It begins with basic property details such as address, purchase date, and price, adjusting for the less value of land to calculate depreciated amounts.