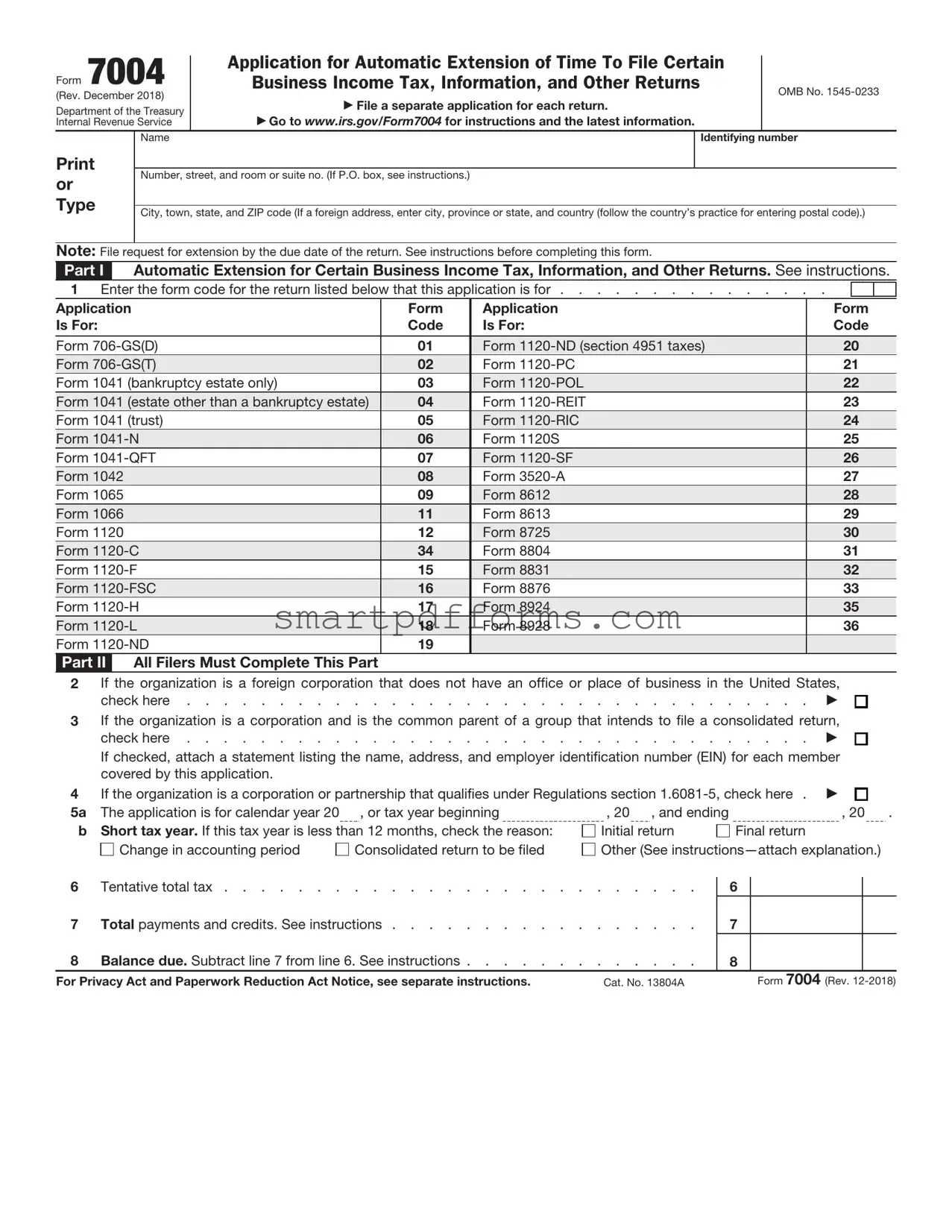
Blank IRS 7004 PDF Template
Every year, businesses and various entities find themselves navigating the complex landscape of tax submission deadlines. In this context, the IRS Form 7004 serves as a crucial tool, providing a means for an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. This form is particularly important for entities that are not ready to file their final tax returns by the original due date, whether due to the need for more time to gather information, unforeseen circumstances, or the complexity of their tax situations. By submitting Form 7004, organizations can avoid penalties for late submissions, thereby allowing them to maintain compliance with federal tax obligations without rushing the process. The form caters to a broad spectrum of entities including corporations, partnerships, and trusts, each with its own set of deadlines and requirements. Understanding the nuances of Form 7004, from its applicability to the specific instructions for completion and submission, is pivotal for any entity looking to ensure they meet their federal tax obligations accurately and on time.
Preview - IRS 7004 Form
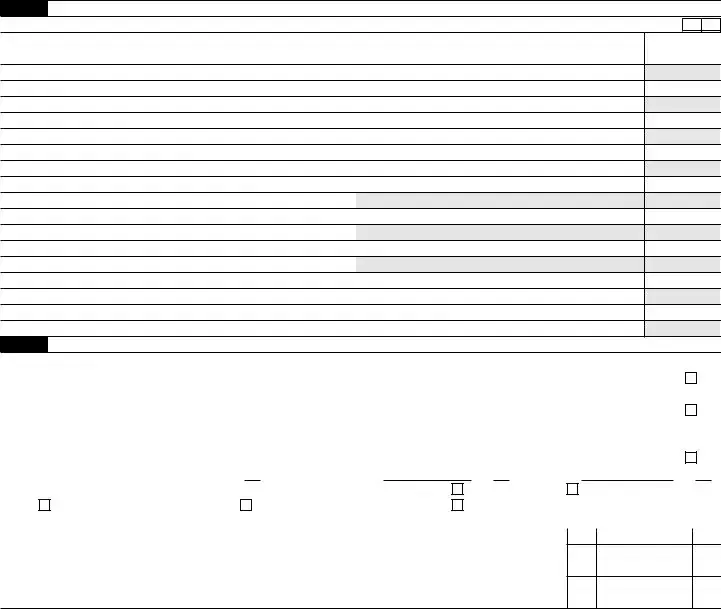
Form 7004 |
Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain |
|
||||
Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns |
|
OMB No. |
||||
(Rev. December 2018) |
|
|
|
|||
File a separate application for each return. |
|
|
||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
||||
Go to www.irs.gov/Form7004 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
||||
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
||||
|
Name |
|
|
Identifying number |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Number, street, and room or suite no. (If P.O. box, see instructions.) |
|
|
||||
or |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
City, town, state, and ZIP code (If a foreign address, enter city, province or state, and country (follow the country’s practice for entering postal code).) |
||||||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: File request for extension by the due date of the return. See instructions before completing this form.
Part I Automatic Extension for Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns. See instructions.
1 Enter the form code for the return listed below that this application is for . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Application |
Form |
Application |
Is For: |
Code |
Is For: |
|
01 |
|
Form |
Form |
|
Form |
02 |
Form |
Form 1041 (bankruptcy estate only) |
03 |
Form |
Form 1041 (estate other than a bankruptcy estate) |
04 |
Form |
Form 1041 (trust) |
05 |
Form |
Form |
06 |
Form 1120S |
Form |
07 |
Form |
Form 1042 |
08 |
Form |
Form 1065 |
09 |
Form 8612 |
Form 1066 |
11 |
Form 8613 |
Form 1120 |
12 |
Form 8725 |
Form |
34 |
Form 8804 |
Form |
15 |
Form 8831 |
Form |
16 |
Form 8876 |
Form |
17 |
Form 8924 |
Form |
18 |
Form 8928 |
Form |
19 |
|
Form Code
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
35
36
Part II All Filers Must Complete This Part
2If the organization is a foreign corporation that does not have an office or place of business in the United States,
check here . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3If the organization is a corporation and is the common parent of a group that intends to file a consolidated return,
|
check here |
|
|||
|
If checked, attach a statement listing the name, address, and employer identification number (EIN) for each member |
|
|||
|
covered by this application. |
|
|
|
|
4 |
If the organization is a corporation or partnership that qualifies under Regulations section |
|
|||
5a |
The application is for calendar year 20 |
, or tax year beginning |
, 20 , and ending |
, 20 |
. |
b |
Short tax year. If this tax year is less than 12 months, check the reason: |
Initial return |
Final return |
|
|
|
Change in accounting period |
Consolidated return to be filed |
Other (See |
|
|
6 Tentative total tax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
7 Total payments and credits. See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
8 Balance due. Subtract line 7 from line 6. See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 13804A |
Form 7004 (Rev. |
Form Data
| Fact Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The IRS Form 7004 is used to request an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. |
| 2 | Form 7004 does not extend the time for payment of taxes due. Taxes owed are still due by the original filing deadline. |
| 3 | Depending on the type of business and the form they are required to file, the extension period granted by Form 7004 can vary, generally it is 6 months. |
| 4 | The form is applicable for several types of entities including partnerships, certain corporations, and trusts. |
| 5 | For C Corporations using calendar year reporting, the due date for filing Form 7004 is April 15. |
| 6 | Partnerships and S Corporations, also following a calendar year, need to file Form 7004 by March 15. |
| 7 | The form can be filed electronically, which is encouraged for faster processing, or by mail. |
| 8 | If filing by mail, the specific address to which Form 7004 should be sent can vary based on the entity's location and the tax form they are requesting an extension for. |
| 9 | Form 7004 includes separate parts for different types of filers, ensuring entities only provide information relevant to their specific extension request. |
| 10 | Each state has its own rules regarding extensions for filing state income taxes. Some states accept Form 7004, while others require a separate state-specific form. |
Instructions on Utilizing IRS 7004
Filing taxes is a critical annual task for businesses, and sometimes, an extension is necessary to gather all the required information accurately. The IRS Form 7004 serves as a lifeline for businesses that need extra time. It's important to approach this form meticulously to ensure that your request for an extension is approved without delay. The process can be straightforward, but it does require your attention to detail and an understanding of your business status and the specific tax form you are requesting an extension for. Follow these step-by-step instructions to fill out the form effectively:
- Identify the type of business entity you are filing for. This is critical as it determines the form number you'll need to enter in Part I, line 1.
- Enter your business's name and address in Part I, lines 2-4. Ensure the information is accurate and matches your other tax documents.
- Provide your business's Employer Identification Number (EIN) in Part I, line 5.
- Determine the tax form number for which you are requesting an extension (e.g., Form 1120, 1120-S, 1065, etc.) and enter this in Part I, line 6.
- For foreign corporations that do not have an office or place of business in the United States, check the box on line 7.
- If your business is a foreign trust, you'll check the box on line 8.
- Enter the tax year end date in MM/DD/YYYY format in Part II, line 9.
- In Part III, estimate the total tax liability for the year, if applicable, and enter this amount in line 10.
- Record the total payments and refundable credits you expect to report on your tax return in line 11.
- If applicable, complete line 12, the balance due. Remember, filing an extension does not extend the time to pay taxes owed.
- Sign and date the form. If you're filing on behalf of a corporation or partnership, ensure that an authorized individual completes this section.
After completing the form, review it thoroughly to ensure all the entered information is correct and matches your records. Submitting a form with errors or incomplete information can lead to processing delays or denial of your extension request. Once satisfied, follow the instructions for submission, which typically include mailing it to the IRS or filing electronically. Acting promptly and ensuring accuracy are your keys to securing the extra time you need to file your business taxes properly.
Obtain Answers on IRS 7004
What is the IRS 7004 form?
The IRS 7004 form is an application for an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. It is used by various entities, including corporations, partnerships, and trusts, to request additional time to complete their tax returns. However, it's important to note that this extension applies to the filing of the tax return, not to any tax payment due. Any owed taxes are still due by the original due date of the return.
Who needs to file Form 7004?
Entities that may need to file Form 7004 include corporations (both C corporations and S corporations), partnerships, real estate investment trusts (REITs), certain trusts, and estates that cannot complete their tax returns by the original due date. This form is particularly relevant for businesses and organizations that need more time to gather information, complete extensive tax documents, or consult with tax professionals.
How does one determine the extension period?
The extension period granted after filing Form 7004 depends on the type of entity filing the form. For most corporations, the extension is typically for 6 months. For partnerships and certain trusts, the extension is also usually 6 months. However, it's crucial to check the specific instructions for Form 7004, as the extension period can vary depending on the tax year and type of filer.
Is there a deadline for filing Form 7004?
Yes, there is a specific deadline for filing Form 7004. It must be filed by the original due date of the return for which an extension is requested. For many entities, this means the form must be submitted by March 15 or April 15, depending on the entity's tax year. Filing the form after the due date generally means the request for extension will not be granted.
How can Form 7004 be filed?
Form 7004 can be filed electronically through the IRS e-file system or sent by mail. Filing electronically is faster, more secure, and provides immediate confirmation that the IRS has received the form. If filing by mail, it's important to send the form to the correct IRS address, which varies depending on the location of the entity and whether a payment is included with the form.
What happens if taxes are owed but not paid by the original due date?
If taxes are owed but not fully paid by the original due date, the IRS will assess interest and penalties on the unpaid amount, starting from the original due date until the tax is paid in full. Filing Form 7004 does not extend the time for paying taxes. Entities should estimate and pay any owed taxes by the original due date to avoid or minimize penalties and interest.
Can the extension be denied?
While it is rare, the IRS can deny the request for an extension if Form 7004 is not properly completed or filed by the due date. It's crucial to ensure that all required information is accurately provided on the form and that it is submitted on time. Receiving confirmation of the filed extension, especially when filing electronically, can help provide assurance that the extension has been granted.
What should be done after receiving the extension?
After receiving the extension, entities should use the additional time to accurately complete their tax returns. It's important to gather all necessary documentation, consult with tax professionals if needed, and review the tax return thoroughly before submission. The extended filing deadline should be noted, and the tax return must be filed by that date to avoid late filing penalties.
Common mistakes
-
Incorrect Entity Classification: Many filers get tripped up right from the start by misclassifying their business entity. Whether it's an LLC, S Corporation, or Partnership, selecting the wrong entity type can lead to processing delays or even the rejection of your extension request.
-
Misunderstanding Due Dates: It’s easy to assume that all tax extension requests have the same deadline. However, the due date can vary depending on your entity type. This misunderstanding often leads to late submissions, thereby invalidating the request for an extension.
-
Failing to Provide All Required Information: The IRS 7004 form requests specific details about your entity. Omitting information such as the tax identification number (TIN) or the entity’s full legal name can lead to an incomplete submission, causing unnecessary delays.
-
Incorrect or Missing Signatures: Even if all information on the form is accurate, forgetting to sign the document or providing the wrong signature (e.g., a manager signing in a place where an owner’s signature is required) jeopardizes the validity of your form.
-
Failure to Estimate Tax Liability Correctly: Part of the extension process involves estimating the amount of tax owed. Underestimating this amount can lead to penalties and interest later on. It’s crucial to make this estimate as accurate as possible.
-
Not Checking for Updates or Changes to the Form: Tax forms and regulations can change from year to year. Failing to use the most current version of the IRS 7004 form can mean that you're not complying with the latest tax laws and instructions, leading to potential complications with your extension.
Steering clear of these mistakes involves paying close attention to detail and staying informed about current tax regulations. If you're ever in doubt, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance. Remember, the goal is not just to get an extension but to ensure that the process contributes to smoother, penalty-free tax management.
Documents used along the form
Businesses often need to extend the deadline for filing their tax returns. The IRS Form 7004 serves this precise function, offering companies the ability to push their filing dates for up to six months. However, preparing for tax season is not just about getting an extension. Various other forms and documents play a pivotal role in ensuring businesses meet their tax obligations comprehensively. Below is a list of forms and documents commonly used alongside the IRS 7004 form, each vital in its own right to the filing process.
- IRS Form 1120: Primarily used by corporations, this form reports the company's income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits to the Internal Revenue Service. It is the starting point for corporations to determine their income tax liability.
- IRS Form 1065: Designed for partnership businesses, this form is used to report the partnership's income, deductions, gains, losses, etc. It is essential because it helps determine the tax responsibilities of each partner based on the partnership’s financial operations.
- IRS Form 1041: For estates and trusts, Form 1041 is necessary to report income, allocations, and distributions for the entity. It determines how the estate or trust’s income tax obligations are handled.
- IRS Form 1120-S: This form is specific to S corporations, entities electing to pass corporate income, losses, deductions, and credits through to their shareholders for federal tax purposes. It embodies the S corporation’s annual income and tax liability.
- IRS Form 990: Non-profit organizations use Form 990 to provide the IRS with annual financial information. It includes details on the organization's mission, programs, and overall financial health.
- IRS Form 940: This form pertains to unemployment taxes. Businesses use Form 940 to report their annual Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) tax. This tax is part of funding state workforce agencies.
- IRS Form 941: Employers use Form 941 to report income taxes, social security tax, or Medicare tax withheld from employees' paychecks. It also reports the employer's portion of social security or Medicare tax.
In the journey of tax preparation and filing, the IRS 7004 form is merely the starting point for many businesses seeking extensions. The subsequent completion of relevant forms ensures that all aspects of a business’s financial responsibilities are transparent and accounted for, aligning with federal tax obligations. Understanding and using these forms correctly is crucial for maintaining compliance and achieving a favorable tax position. Engaging with these documents thoughtfully can help businesses navigate tax season with confidence and precision.
Similar forms
The IRS 4868 form is quite similar to the IRS 7004 in its function. It's used by individuals to request an extension of time to file their personal income tax return. The key similarity lies in their primary purpose: both forms are designed to give taxpayers more time to file their taxes, though the 4868 is specifically for personal taxes.
IRS 8868 is another form that shares a common goal with the 7004, targeting tax-exempt organizations, charitable trusts, and section 527 political organizations that need extra time filing their returns. Like the 7004, this form is about requesting an extension, demonstrating how different types of taxpayers can seek additional time to meet their filing obligations.
The Form 8809, used for requesting an extension to file information returns (Forms W-2, 1099, and others), parallels the IRS 7004 by facilitating more time for compliance. Although the specifics of the forms they extend differ, both serve the essential function of delaying the filing deadline, allowing filers to ensure their submissions are accurate and complete.
Form 1138 extends the parallel further, aimed at corporations expecting net operating loss carrybacks. It allows corporations to extend the time for paying taxes due, which is a variance on the theme of seeking additional time. While 7004 provides a broad application for extending the filing deadline, 1138 targets a very specific financial situation, showing the flexibilities in tax management and planning.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS Form 7004, which is the Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns, it's important to follow specific guidelines to ensure your request is accepted. Below are lists of dos and don'ts that will guide you through the process.
Dos:- Verify the tax year for which you are applying for an extension to ensure accuracy.
- Double-check the tax form number you need an extension for, as Form 7004 covers several types of returns.
- Provide all required information, including the name of the business, Employer Identification Number (EIN), and the address.
- Calculate the total tax estimate accurately and report any payments you have already made.
- Sign and date the form. If you're filing on behalf of an entity, ensure you have the authority to do so.
- File before the due date of the return for which you're requesting an extension.
- Use the correct IRS address or electronic filing method specific to the type of return and the business location.
- Keep a copy of the filed extension and any confirmation from the IRS for your records.
- Be aware of the duration of the extension (usually 6 months) and prepare to file by the extended due date.
- Don't leave any fields blank. If a section doesn't apply, enter “N/A” or “0” as appropriate.
- Don't underestimate your tax liability if you're required to make an estimate; doing so can result in penalties.
- Don't miss the filing deadline. Filing late can invalidate your extension request.
- Don't forget to check the specific requirements for your type of business or tax form; not all entities use Form 7004 in the same way.
- Don't ignore IRS notices. If you receive any communication from the IRS, respond promptly to avoid additional issues.
- Don't assume the extension applies to tax payments — the extension is only for filing the return, and any due payments are still expected by the original due date.
- Don't send incomplete forms. Inaccuracies or missing information can delay processing or lead to rejection of your extension request.
- Don't forget to file your actual return by the extended due date. The extension does not exempt you from filing.
- Don't hesitate to seek professional assistance if you're unsure about the process or have complex tax situations.
Misconceptions
The IRS Form 7004 is an essential document for businesses, granting an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. However, numerous misconceptions surround its usage, requirements, and implications. Here's a clearer understanding to dispel these myths.
- Misconception 1: Filing Form 7004 grants an extension for tax payment.
It's a common misunderstanding that Form 7004 also extends the time to pay taxes due. In reality, it only provides additional time to file the necessary paperwork. Taxes owed are still due by the original deadline, and failing to pay on time can result in penalties and interest.
- Misconception 2: Form 7004 applies to all tax returns.
Another misconception is that this form is a universal solution for all tax extension needs. However, Form 7004 is specifically for certain business returns, including partnerships, corporations, and trusts. Individual taxpayers must use Form 4868 for a personal extension.
- Misconception 3: The extension is for a full year.
Some believe that once Form 7004 is filed, the extension period is for a full year. The reality is the extension period varies, generally providing an additional six months to file. Yet, specific returns might have different extension durations, so it's crucial to verify the details applicable to your situation.
- Misconception 4: The form is complicated to file.
There's a notion that Form 7004 is complex and challenging to file. While tax forms can be daunting, Form 7004 is relatively straightforward. It requires basic information about the filer and the type of return. Filing can also be done electronically, simplifying the process.
- Misconception 5: Automatic acceptance.
Submitting Form 7004 doesn't guarantee acceptance. While rejections are rare, they can occur, often due to basic errors in the form, such as incorrect taxpayer identification numbers or mismatched names. Ensuring accuracy before submission is essential.
- Misconception 6: Only businesses in good standing can file Form 7004.
It's a misconception that only businesses without any compliance issues or outstanding taxes can file for an extension. Any business can file Form 7004, regardless of its standing. However, resolving compliance issues and paying owed taxes promptly is always advisable.
- Misconception 7: Extensions affect audits.
Some believe that filing an extension through Form 7004 increases the likelihood of an IRS audit. There is no evidence to support this claim. Audit decisions are based on various factors, including random selection, and not whether an extension was filed.
- Misconception 8: The process is the same for all entities.
While Form 7004 is used by multiple types of entities, the specific tax forms covered can vary. Additionally, the extension length and the particular lines to be completed can differ depending on the entity type and tax form being extended. Always refer to the instructions specific to your return type.
- Misconception 9: Once filed, the extension can be canceled.
Once Form 7004 is filed and accepted, the extension cannot be revoked or canceled. If the filer completes their taxes before the extended deadline, they can file their return early, but the extension itself remains in effect until it naturally expires.
- Misconception 10: Extensions can be filed after the due date.
Some believe that it's possible to file Form 7004 after the original deadline has passed. However, for the extension to be valid, Form 7004 must be filed by the original due date of the return. Filing late may result in penalties and interest on any taxes owed.
Key takeaways
The IRS Form 7004 is an application used by businesses to request an automatic extension of time to file certain business income tax, information, and other returns. Understanding how to correctly fill out and use this form ensures businesses can effectively manage their tax filing obligations. Here are six key takeaways:
- Filing Deadline: The due date for filing Form 7004 varies by the type of tax return you are requesting an extension for. It is generally due on the regular filing date of the return for which you are requesting an extension.
- Automatic Extension: Submitting Form 7004 grants an automatic extension to file the designated return, but it does not extend the time to pay any taxes due. Taxes owed should still be paid by the original due date to avoid penalties and interest.
- Form Completion: Accurately complete all required sections of Form 7004, including the type of form for which an extension is being requested, the tax year, and the business’s name and address. Any error in these fields can lead to processing delays or denial of the extension request.
- Mailing and Electronic Filing Options: Form 7004 can be submitted electronically or by mail. Electronic submission is quicker and offers immediate confirmation of receipt. If mailing, ensure it's addressed to the correct IRS office, which varies by state and the type of return.
- Multiple Extensions: You cannot request more than one extension per tax period. Form 7004 only provides a one-time extension, usually for 5 or 6 months, depending on the specific form you need more time to file.
- Special Instructions for Certain Filers: Some entities, such as trusts, estates, and certain types of corporations, may have special instructions or additional requirements when filing Form 7004. Review the form instructions carefully to understand these specifics.
Proper use of Form 7004 can help businesses avoid penalties associated with late filing. However, remember that this form is for obtaining an extension to file the return, not an extension to pay any taxes owed. Estimate and pay any taxes by the original due date to minimize interest and penalties.
Popular PDF Forms
Mc-040 - Suitable for use in any California Superior Court, accommodating changes for plaintiffs, defendants, petitioners, and respondents alike.
Jurat Form California 2023 - In the process of notarization, the notary public must verify the identity of the signer, ensuring that the individual signing the document is who they claim to be.
Wt7 Wisconsin - A section for declaring no change in employee numbers despite active account status ensures accurate state records.