Blank IRS 8233 PDF Template
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations in the United States can be a daunting task, especially for individuals who are not citizens or resident aliens but are earning income within the country. In the midst of this complicated landscape, the IRS 8233 form emerges as a critical document. It serves a vital role in ensuring that those eligible can claim exemption from withholding on compensation for independent personal services and certain other types of income. This exemption is particularly relevant for individuals from countries that have tax treaties with the United States, allowing them to benefit from reduced rates or exemptions as dictated by these agreements. Completing and submitting the 8233 form requires a detailed understanding of one's tax status, the specifics of the applicable tax treaty, and the nature of the income received. The form not only demands precise information but also necessitates a declaration of the taxpayer's eligibility for the benefits claimed. This process, while intricate, is imperative for those looking to navigate their tax responsibilities efficiently and legally minimize their tax burden in accordance with international agreements.
Preview - IRS 8233 Form
Form 8233
(Rev. September 2018)
Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service
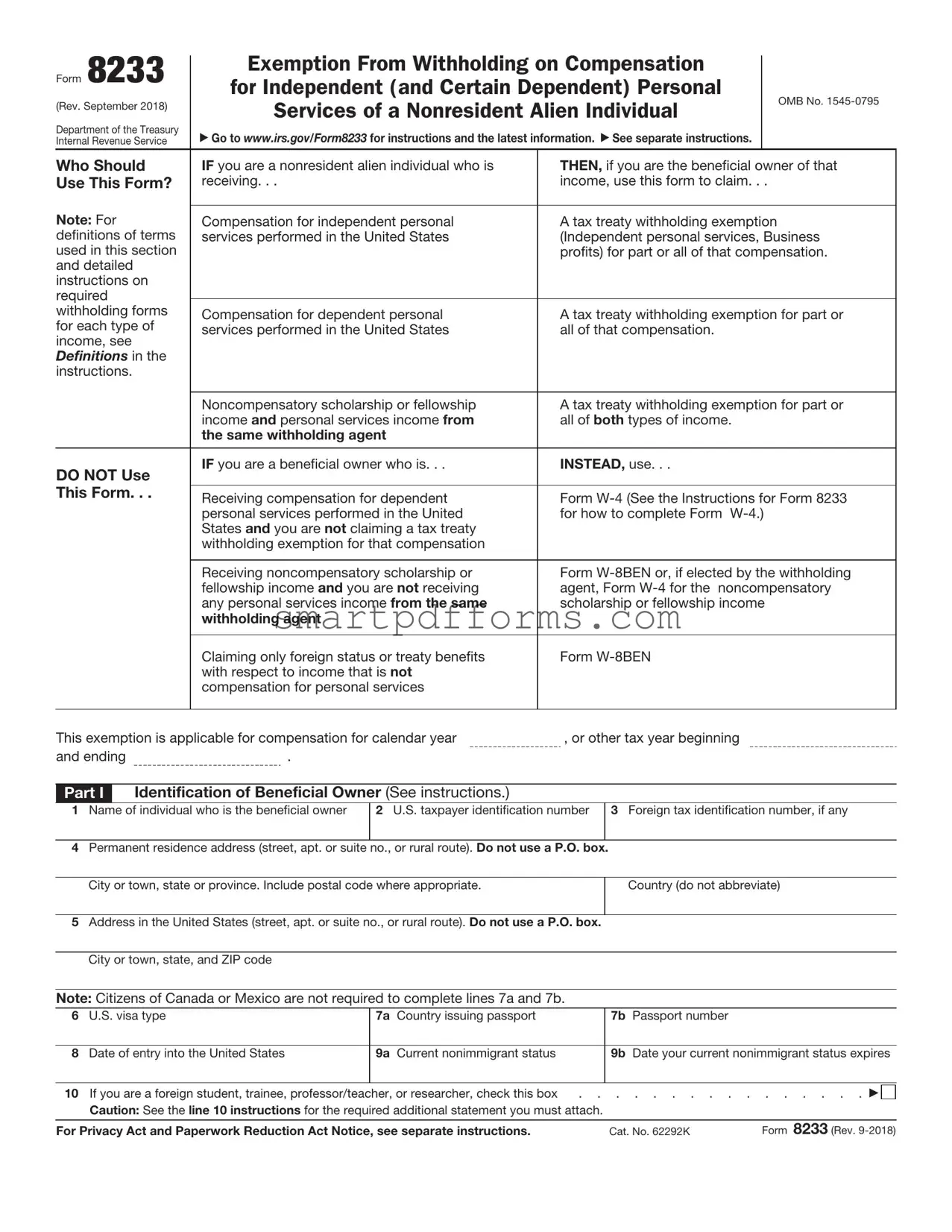
Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual
Go to www.irs.gov/Form8233 for instructions and the latest information. See separate instructions.
OMB No.
Who Should |
IF you are a nonresident alien individual who is |
THEN, if you are the beneficial owner of that |
Use This Form? |
receiving. . . |
income, use this form to claim. . . |
Note: For |
|
|
Compensation for independent personal |
A tax treaty withholding exemption |
|
definitions of terms |
services performed in the United States |
(Independent personal services, Business |
used in this section |
|
profits) for part or all of that compensation. |
and detailed |
|
|
instructions on |
|
|
required |
|
|
|
|
|
withholding forms |
Compensation for dependent personal |
A tax treaty withholding exemption for part or |
for each type of |
services performed in the United States |
all of that compensation. |
income, see |
|
|
Definitions in the |
|
|
instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noncompensatory scholarship or fellowship |
A tax treaty withholding exemption for part or |
|
income and personal services income from |
all of both types of income. |
|
the same withholding agent |
|
|
|
|
DO NOT Use |
IF you are a beneficial owner who is. . . |
INSTEAD, use. . . |
|
|
|
This Form. . . |
Receiving compensation for dependent |
Form |
|
||
|
personal services performed in the United |
for how to complete Form |
|
States and you are not claiming a tax treaty |
|
|
withholding exemption for that compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
Receiving noncompensatory scholarship or |
Form |
|
fellowship income and you are not receiving |
agent, Form |
|
any personal services income from the same |
scholarship or fellowship income |
|
withholding agent |
|
|
|
|
|
Claiming only foreign status or treaty benefits |
Form |
|
with respect to income that is not |
|
|
compensation for personal services |
|
|
|
|
This exemption is applicable for compensation for calendar year |
, or other tax year beginning |
|
and ending |
. |
|
Part I Identification of Beneficial Owner (See instructions.)
1Name of individual who is the beneficial owner
2U.S. taxpayer identification number
3Foreign tax identification number, if any
4Permanent residence address (street, apt. or suite no., or rural route). Do not use a P.O. box.
City or town, state or province. Include postal code where appropriate.
Country (do not abbreviate)
5Address in the United States (street, apt. or suite no., or rural route). Do not use a P.O. box.
City or town, state, and ZIP code
Note: Citizens of Canada or Mexico are not required to complete lines 7a and 7b.
6U.S. visa type
7a Country issuing passport
7b Passport number
8Date of entry into the United States
9a Current nonimmigrant status
9b Date your current nonimmigrant status expires
10 If you are a foreign student, trainee, professor/teacher, or researcher, check this box |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
Caution: See the line 10 instructions for the required additional statement you must attach. |
|
|
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 62292K |
Form 8233 (Rev. |

Form 8233 (Rev. |
Page 2 |
|
Part II |
Claim for Tax Treaty Withholding Exemption |
|
11Compensation for independent (and certain dependent) personal services: a Description of personal services you are providing
b Total compensation you expect to be paid for these services in this calendar or tax year $
12If compensation is exempt from withholding based on a tax treaty benefit, provide: a Tax treaty on which you are basing exemption from withholding
b Treaty article on which you are basing exemption from withholding
c Total compensation listed on line 11b above that is exempt from tax under this treaty $ d Country of residence
Note: Do not complete lines 13a through 13d unless you also received compensation for personal services from the same withholding agent.
13Noncompensatory scholarship or fellowship income:
aAmount $
bTax treaty on which you are basing exemption from withholding
cTreaty article on which you are basing exemption from withholding
dTotal income listed on line 13a above that is exempt from tax under this treaty $
14Sufficient facts to justify the exemption from withholding claimed on line 12 and/or line 13 (see instructions)
Part III Certification
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined the information on this form and to the best of my knowledge and belief it is true, correct, and complete. I further certify under penalties of perjury that:
•I am the beneficial owner (or am authorized to sign for the beneficial owner) of all the income to which this form relates.
•The beneficial owner is not a U.S. person.
•The beneficial owner is a resident of the treaty country listed on line 12a and/or 13b above within the meaning of the income tax treaty
between the United States and that country, or was a resident of the treaty country listed on line 12a and/or 13b above at the time of, or immediately prior to, entry into the United States, as required by the treaty.
Furthermore, I authorize this form to be provided to any withholding agent that has control, receipt, or custody of the income of which I am the beneficial owner or any withholding agent that can disburse or make payments of the income of which I am the beneficial owner.
Sign Here |
▶ Signature of beneficial owner (or individual authorized to sign for beneficial owner) |
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
Part IV |
|
Withholding Agent Acceptance and Certification |
|
Name
Employer identification number
Address (number and street) (Include apt. or suite no. or P.O. box, if applicable.)
City, state, and ZIP code
Telephone number
Under penalties of perjury, I certify that I have examined this form and any accompanying statements, that I am satisfied that an exemption from withholding is warranted, and that I do not know or have reason to know that the nonresident alien individual is not entitled to the exemption or that the nonresident alien’s eligibility for the exemption cannot be readily determined.
Signature of withholding agent |
Date |
Form 8233 (Rev.
Form Data
| Fact Number | Fact Detail |
|---|---|
| 1 | The IRS Form 8233 is used by non-resident aliens to claim a tax treaty exemption from U.S. income taxes. |
| 2 | This form allows individuals to claim exemptions for certain types of income, such as compensation for personal services performed in the United States. |
| 3 | Form 8233 requires detailed information about the individual claiming the exemption, including their visa type, nationality, and the specific article of the tax treaty under which they are claiming exemption. |
| 4 | Individuals must also provide a U.S. taxpayer identification number (SSN or ITIN) when submitting Form 8233. |
| 5 | The form must be filed with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and a copy must also be provided to the withholding agent or the payer of the income. |
| 6 | Failure to submit a valid Form 8233 may result in the withholding of taxes at the maximum rate from the individual’s income. |
| 7 | Form 8233 must be filed each tax year for which the individual claims the exemption. |
| 8 | There are no state-specific versions of Form 8233; it is a federal form governed by the Internal Revenue Code of the United States. |
| 9 | The IRS may request additional documentation or information to verify eligibility for the tax treaty exemption claimed on Form 8233. |
Instructions on Utilizing IRS 8233
Filling out the IRS 8233 form is crucial for individuals who are claiming exemption from withholding on income from the United States due to a tax treaty. By completing this form accurately, you ensure that the correct amount of tax is withheld from your income, potentially making you eligible for a refund or a reduced tax obligation under the provisions of a tax treaty between the United States and your country of residence. The process involves providing personal and tax-related information to clearly establish your eligibility for the exemption. The following steps have been designed to guide you through this process seamlessly.
- Start by entering your full name as it appears on your passport. Ensure that it matches exactly to avoid any discrepancies.
- Next, fill in your U.S. taxpayer identification number (TIN) if you have one. If not, include your foreign tax identifying number in the space provided.
- Provide your permanent residence address in your country of citizenship. This address must reflect where you claim to be a resident for tax purposes.
- List your U.S. address, if applicable. This is the location where you currently reside while in the United States.
- Specify your country of citizenship in the field provided to establish which tax treaty you are claiming exemption under.
- For visa type, visa number, and current U.S. immigration status, fill in the details accurately as they appear on your visa and immigration documents.
- Enter the name of the academic institution or company in the United States that you are receiving income from along with its address.
- Detail the type of income for which you are claiming the treaty exemption. This could range from wages, scholarships, stipends, to fellowships, among others.
- Select the article of the tax treaty that you are relying on for the exemption, and explain how you meet the terms of that article. This might require you to briefly interpret the tax treaty provisions and how they apply to your situation.
- Indicate whether you have previously claimed a tax treaty exemption. If so, provide the last year of such claim.
- Sign and date the form in the designated area to certify the accuracy of the information provided. If you are using a preparer, ensure they also sign and date the form.
Once completed, the form should be submitted to your payer, not directly to the IRS. The payer serves as the withholding agent and will be responsible for applying the treaty benefits to your income and submitting the form to the IRS. It's important to retain a copy of the form for your records. Final processing by the payer and the subsequent steps, including potential adjustments to your withholding, will be completed based on the payer's internal procedures and the guidelines set by the IRS. This step is critical in ensuring that your tax obligations are accurately met according to the treaty benefits you are entitled to.
Obtain Answers on IRS 8233
-
What is the IRS Form 8233?
IRS Form 8233, "Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual," is a document used by nonresident aliens in the United States to claim exemption from withholding of federal income tax on compensation related to independent personal services and, in some cases, dependent personal services. The form is used to certify that an individual is entitled to treaty benefits that exempt them from U.S. income tax on specific income.
-
Who needs to file Form 8233?
Nonresident alien individuals who receive compensation for independent personal services, or in certain circumstances, dependent personal services, and who believe that their income is exempt from U.S. federal income tax under a tax treaty between the United States and their country of residence, need to file Form 8233. This includes researchers, visiting professors, and other similar professionals temporarily working in the U.S. under a nonimmigrant visa.
-
How does one determine if they are eligible for exemption under a tax treaty?
Eligibility for exemption under a tax treaty varies by the individual's country of residence and the specific provisions of the tax treaty between that country and the United States. Individuals should carefully review the text of the relevant tax treaty to understand the criteria for exemption, which commonly includes limits on residency duration and the amount of compensation. The IRS Publication 901, "U.S. Tax Treaties," can be a helpful resource for determining if an exemption might apply.
-
What information is required on Form 8233?
Completing Form 8233 requires detailed information including the individual’s name, U.S. taxpayer identification number (if any), visa type, residency country, and a detailed description of the personal services rendered. Additionally, the individual must cite the specific tax treaty and article under which they are claiming exemption. It's crucial to attach a statement that supports the claim for exemption as specified in the form instructions.
-
How is Form 8233 submitted?
Form 8233 must be completed and submitted to the withholding agent—usually the employer or entity paying the compensation—rather than directly to the IRS. The withholding agent is then responsible for reviewing the form, ensuring its completeness, and forwarding a copy to the IRS. It is important to submit the form well before the compensation is paid to ensure the withholding agent does not inadvertently withhold taxes that the individual is exempt from paying.
-
What happens after Form 8233 is submitted?
After receiving Form 8233, the withholding agent will begin applying the treaty benefits and exempt qualified payments from federal income tax withholding. They also have a responsibility to send a copy of the form to the IRS. This submission should occur within five business days of accepting the form. The IRS may contact the withholding agent or the individual if additional information is needed or if there is a problem with the form.
-
Are there any deadlines for filing Form 8233?
There is no hard deadline for filing Form 8233; however, it must be filed before the compensation is paid to claim exemption from withholding. If the form is submitted after payment, the individual may need to seek a refund from the IRS for any taxes wrongly withheld, which can be a more complex process. It's advisable to submit the form as soon as the terms of compensation are known.
-
Can Form 8233 be amended if a mistake is made?
Yes, if an individual discovers an error on their submitted Form 8233, they should promptly complete a new form with the correct information and provide it to the withholding agent. The withholding agent will then forward the corrected form to the IRS. It's essential to communicate any changes or corrections as soon as possible to ensure that the withholding reflects the individual's correct tax liability.
Common mistakes
-
Not thoroughly reading the instructions: Before even putting pen to paper, many individuals dive into filling out the form without a thorough understanding of the instructions. This oversight can lead to incorrect or incomplete information being provided, which may delay the processing of the form.
-
Incorrect taxpayer identification information: Providing incorrect taxpayer identification numbers, such as a Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), is a significant error. This mistake can lead to processing delays or the incorrect allocation of treaty benefits.
-
Failing to claim a specific treaty benefit: The IRS 8233 form allows individuals to claim specific treaty benefits. Often, filers neglect to specify the article of the treaty under which they are claiming exemption, leading to the form being processed without the desired exemption being applied.
-
Omitting dates of service: For the IRS to accurately determine eligibility for treaty benefits, applicants must provide their dates of service. Omitting this information can result in the rejection of the application for treaty benefits.
-
Incomplete personal information: Not filling out the form with complete personal information, including address and contact details, can cause issues. Incomplete information may lead to difficulties in communications or the processing of the form.
-
Not including a valid reason for exemptions: Those filing need to include a valid reason for exemptions based on the tax treaty. A lack of a clear, valid reason may lead to the form being questioned or the exemption not being granted.
-
Incorrectly categorizing the type of income: Misclassifying the type of income can lead to applying the wrong tax treaty benefits. It's crucial to accurately categorize the income based on the services provided.
-
Forgetting to sign and date the form: Perhaps the simplest yet most commonly overlooked mistake is failing to sign and date the form. This omission can result in the form being considered invalid and therefore not processed until corrected.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires careful attention to detail and a clear understanding of the form’s requirements. When in doubt, consulting tax experts or the IRS directly can help ensure that the form is completed accurately and efficiently, paving the way for a smoother processing experience.
Documents used along the form
When dealing with international financial affairs, especially those involving compensation that may be exempt from U.S. withholding tax under a tax treaty, the IRS 8233 form is vital. However, it's seldom the only document required. Various forms and documentation work in tandem to ensure compliance with tax laws, providing a clear picture of an individual's tax responsibilities and treaty benefits. Here's a look at eight common forms and documents that are often used alongside the IRS 8233 form.
- W-8BEN Form: This form is crucial for nonresident aliens performing services in the United States, as it helps to establish their foreign status and eligibility for reduced withholding under a tax treaty.
- W-9 Form: Typically required from U.S. citizens or resident aliens to certify their Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and to confirm they are not subject to backup withholding. It contrasts the W-8BEN form, which is for nonresidents.
- 1042-S Form: This document is essential for reporting amounts paid to foreign persons, including those claiming tax treaty benefits. It summaries the income paid and any withholding taken from payments subject to treaty benefits.
- W-4 Form: Used by employees to indicate their tax withholding preferences. Although not specific to foreign individuals, it is often part of the broader tax paperwork process for individuals working in the U.S.
- W-8ECI Form: Relevant for nonresident aliens who have income effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business, this form asserts that income is, or is expected to be, exempt from withholding due to its connection to U.S. operations.
- SS-4 Form: Required to apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN), which could be necessary for foreign entities or individuals conducting business in the U.S. and needing to comply with tax reporting requirements.
- 8833 Form: This treaty-based return position disclosure form is critical for individuals or entities that take a tax treaty position, including those exempt from reporting certain information under a treaty.
- W-7 Form: Essential for nonresident aliens who need an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) to comply with U.S. tax reporting requirements, yet who aren't eligible for a Social Security Number.
Each of these forms and documents plays a unique role in the comprehensive process of tax compliance and reporting for individuals and entities navigating through U.S. and international tax obligations. Proper completion and submission of these documents, along with the IRS 8233 form, can ensure that treaty benefits are correctly applied and that all regulatory requirements are met.
Similar forms
IRS Form W-8BEN: This form is used by individuals who are not U.S. citizens or residents to certify their foreign status and claim exemptions from certain U.S. withholding taxes, similar to how the IRS 8233 allows nonresident aliens to claim exemption from withholding on compensation due to treaty benefits.
IRS Form W-9: Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification, commonly used by U.S. persons to provide their Social Security Number or Employer Identification Number to entities that will pay them income. Similar to the 8233, it's a form of taxpayer identification and certification but for U.S. residents and citizens.
IRS Form 1042-S: Foreign Person's U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding, reports income paid to a foreign person that is subject to withholding. This form works in tandem with 8233, as the income and withholding reported on the 1042-S may be affected by the claims filed on Form 8233.
IRS Form W-4: Employee's Withholding Certificate, used by employees to determine the amount of federal income tax to withhold from their paychecks. While targeting a different audience, it shares the concept of managing withholding taxes with the 8233 form.
IRS Form W-8ECI: Certificate of Foreign Person's Claim That Income Is Effectively Connected With the Conduct of a Trade or Business in the United States, similar to the 8233 form in that it is used by non-U.S. residents to claim that their income is related to U.S. operations and thus subject to different withholding rules.
IRS Form 8802: Application for United States Residency Certification, used to request a certification of residency in the U.S. for the purposes of claiming benefits under an income tax treaty. The form is related to the 8233 in the context of tax treaty benefits but from the perspective of U.S. residents.
IRS Form 8854: Initial and Annual Expatriation Statement, which is filed by individuals who have renounced their U.S. citizenship or long-term residency. While focused on a different topic, it intersects with the purpose of the 8233 form as it involves international tax considerations.
IRS Form 8966: FATCA Report, filed to report accounts held by U.S. taxpayers in foreign financial institutions or certain other non-financial foreign entities. The link to the 8233 form comes from the international nature of the tax reporting and the focus on nonresident issues.
IRS Form W-7: Application for IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number, needed by those who are not eligible for a Social Security Number but must file a U.S. tax return or claim a refund. This form is akin to the 8233 in providing a means for non-U.S. residents to comply with tax laws.
IRS Form W-8IMY: Certificate of Foreign Intermediary, Foreign Flow-Through Entity, or Certain U.S. Branches for United States Tax Withholding, is completed by entities acting in intermediary capacities. It parallels the 8233's role in facilitating the correct processing and withholding of payments to non-U.S. individuals under the tax code.
Dos and Don'ts
Things You Should Do
Ensure all your personal information is accurate, including your name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN).
Clearly identify the type of income that qualifies for exemption from withholding under the tax treaty between the United States and your country of residence.
Closely review the tax treaty between the United States and your home country to understand the specific provisions that apply to your situation.
Complete all required sections of Form 8233 based on the specifics of your case and the type of income you are receiving.
Attach a statement to Form 8233 that includes a detailed explanation of the basis for your claim of tax treaty benefits, as required by the form's instructions.
Sign and date the form to certify that all information provided is true, complete, and correct.
Keep a copy of your completed Form 8233 and any attached statements for your records.
Submit the form to the withholding agent, not to the IRS, unless specifically instructed otherwise.
Be mindful of deadlines and submit the form well in advance to avoid any potential withholding that could affect your financial situation.
Consult with a tax professional or advisor who has experience with nonresident alien taxation if you have questions or need guidance.
Things You Shouldn't Do
Don't leave any required fields blank. Incomplete forms may result in automatic denial of your request for exemption.
Don't forget to attach the specific statement required for claiming tax treaty benefits, as failure to do so may invalidate your claim.
Don't provide false or misleading information, as this can lead to penalties, interest, or even criminal charges.
Don't submit the form to the IRS unless directed. The form should typically be provided directly to your withholding agent.
Don't overlook the importance of checking the specific tax treaty articles cited in your claim, as misinterpretation can result in an unsuccessful application.
Don't assume the withholding agent is familiar with your specific tax situation. Provide clear explanations and documentation as needed.
Don't delay in addressing any follow-up inquiries or requests for additional information from the withholding agent or the IRS.
Don't neglect to review the form and accompanying documents for any changes in tax laws that may affect your eligibility for exemption.
Don't misunderstand the purpose of the form as a catch-all for any and all tax issues. Understand its specific use for claiming exemptions under tax treaties.
Don't hesitate to seek assistance from a tax professional if the process feels overwhelming or complex.
Misconceptions
The IRS Form 8233 is only for non-residents of the U.S. This is a misconception because the form is actually used by non-resident aliens to claim a tax treaty benefit that exempts them from certain withholding on compensation for independent personal services or dependent personal services.
Another common misconception is that the Form 8233 must be filed annually. In reality, it needs to be submitted for each tax year that a non-resident alien is claiming an exemption from withholding under a tax treaty.
Some people believe that the IRS Form 8233 can be submitted electronically. As of the last update, the IRS requires this form to be filed in paper format, and it must be submitted to the payer of the income, not directly to the IRS.
There's also a confusion that any international person can use Form 8233 to avoid paying U.S. taxes. This isn't accurate. Only those individuals from countries that have a specific tax treaty with the U.S., which allows for exemption, can use this form based on the specific criteria outlined in the treaty.
Some think that once you submit Form 8233, the withholding exemption is automatic. However, the payer must review the form and determine if the exemption is valid before applying it. If there are mistakes or the form is incomplete, the payer must withhold taxes accordingly.
It's a common misunderstanding that Form 8233 also covers income from scholarships or grants. This form is specifically for compensation related to personal services. Non-resident aliens receiving scholarships or grants must file Form 8233 Exemption from Withholding on Compensation for Independent (and certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual.
Many believe that filling out Form 8233 is complicated and requires a tax professional. While getting professional advice is often helpful, the form comes with instructions that, if followed carefully, allow individuals to complete it on their own.
Finally, there's a misconception that if you don't qualify for a tax treaty benefit one year, you never will. Eligibility for tax treaty benefits can change from year to year based on changes in the tax treaty, your circumstances, or both. Always review the current year's criteria and tax treaties to determine eligibility.
Key takeaways
The following are essential takeaways for individuals and entities considering the use of the IRS 8233 form:
- The IRS 8233 form is specifically designed for nonresident aliens to claim exemption from withholding on income for personal services in the United States, pursuant to a tax treaty. Each section should be filled out carefully to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Before completing the form, individuals should verify their eligibility under a tax treaty between the United States and their country of residence. Not all countries have tax treaties with the U.S., and not all types of income are covered under these treaties.
- It is crucial for the taxpayer to obtain a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) before submitting the form. The IRS uses TINs to process tax returns and monitor tax law compliance. Without a TIN, the exemption may not be granted.
- After thorough completion and review, the form should be submitted to the withholding agent, not directly to the IRS. The withholding agent is then responsible for applying the treaty benefits and ensuring the proper amount of tax is withheld.
Popular PDF Forms
Employee Equipment Checkout Form - Provides a clear and concise method for employees to request and receive approval for equipment use off-campus.
Bravecto Rebate 2023 - Designed for customers who have bought Bravecto, this form helps you get a portion of your money back.
Safety Patrol Awards - A tribute to exceptional service, this commendation acknowledges the vital contributions of a Safety Patrol Sergeant in fostering a safe and nurturing school environment.