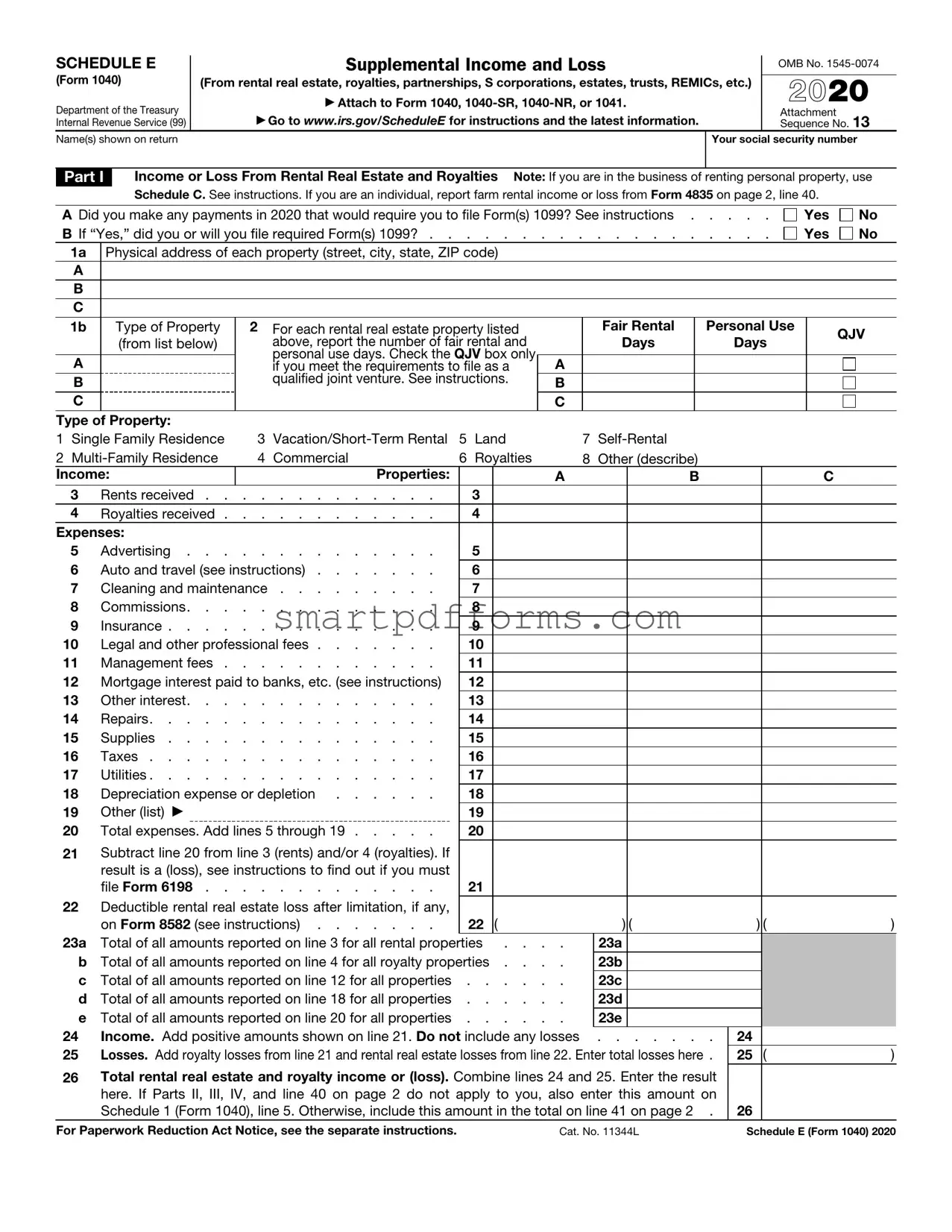
Blank IRS Schedule E 1040 PDF Template
Navigating the intricacies of the tax system presents a daunting task for many, particularly when it comes to reporting income from rental properties, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. This is where the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) becomes pivotal. Designed to accommodate the diverse sources of additional income one might have beyond standard wages, salaries, and tips, the form serves as a critical tool in ensuring taxpayers accurately report earnings and, consequently, are assessed the correct amount of tax. It not only enables individuals to delineate the various streams of supplementary income but also offers a structured way to calculate allowable deductions associated with them, thereby affecting the overall tax liability. The Schedule E's significance is underscored by its role in painting a comprehensive picture of an individual's fiscal footprint, a necessity in the quest to achieve transparency and adherence to tax laws. Given the complexities associated with its fields and schedules, understanding this form's nuances can make a substantial difference in navigating the financial responsibilities that accompany unique income sources.
Preview - IRS Schedule E 1040 Form
SCHEDULE E |
|
|
|
Supplemental Income and Loss |
|
|
OMB No. |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
(Form 1040) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
(From rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, REMICs, etc.) |
|
2020 |
|||||||||||||||||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
▶ Attach to Form 1040, |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/ScheduleE for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
Attachment |
|
13 |
||||||||||||||
Internal Revenue Service (99) |
|
|
|
Sequence No. |
||||||||||||||||
Name(s) shown on return |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your social security number |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Part I |
Income or Loss From Rental Real Estate and Royalties Note: If you are in the business of renting personal property, use |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Schedule C. See instructions. If you are an individual, report farm rental income or loss from Form 4835 on page 2, line 40. |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
A Did you make any payments in 2020 that would require you to file Form(s) 1099? See instructions . |
. . . . |
Yes |
|
No |
||||||||||||||||
B If “Yes,” did you or will you file required Form(s) 1099? . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
. . . . |
Yes |
|
No |
||||||||||||||
|
1a |
Physical address of each property (street, city, state, ZIP code) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1b |
|
Type of Property |
2 |
For each rental real estate property listed |
|
|
Fair Rental |
|
Personal Use |
|
QJV |
||||||||
|
|
|
(from list below) |
|
above, report the number of fair rental and |
|
|
Days |
|
Days |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
personal use days. Check the |
QJV box only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
if you meet the requirements to file as a |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
qualified joint venture. See instructions. |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Type of Property: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
Single Family Residence |
3 |
5 |
Land |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
2 |
4 |
Commercial |
6 |
Royalties |
8 |
Other (describe) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Income: |
|
|
|
|
Properties: |
|
|
|
A |
B |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
||||
|
3 |
Rents received |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
4 |
Royalties received |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
5 |
Advertising |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
6 |
Auto and travel (see instructions) |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
7 |
Cleaning and maintenance |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
8 |
Commissions |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
9 |
Insurance |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
10 |
Legal and other professional fees |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
11 |
Management fees |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12 |
Mortgage interest paid to banks, etc. (see instructions) |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
13 |
Other interest |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
14 |
Repairs |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
15 |
Supplies |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
16 |
Taxes |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
17 |
Utilities |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
18 |
Depreciation expense or depletion |
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
19 |
Other (list) |
▶ |
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
20 |
Total expenses. Add lines 5 through 19 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
21Subtract line 20 from line 3 (rents) and/or 4 (royalties). If result is a (loss), see instructions to find out if you must
file Form 6198 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22Deductible rental real estate loss after limitation, if any,
|
on Form 8582 (see instructions) |
22 ( |
) ( |
|
) ( |
) |
23a |
Total of all amounts reported on line 3 for all rental properties . . . . |
23a |
|
|
|
|
b |
Total of all amounts reported on line 4 for all royalty properties . . . . |
23b |
|
|
|
|
c |
Total of all amounts reported on line 12 for all properties |
23c |
|
|
|
|
d |
Total of all amounts reported on line 18 for all properties |
23d |
|
|
|
|
e |
Total of all amounts reported on line 20 for all properties |
23e |
|
|
|
|
24 |
Income. Add positive amounts shown on line 21. Do not include any losses |
. . . . . . . |
24 |
|
|
|
25 |
Losses. Add royalty losses from line 21 and rental real estate losses from line 22. Enter total losses here . |
25 |
( |
) |
||
26 |
Total rental real estate and royalty income or (loss). Combine lines 24 and 25. Enter the result |
|
|
|
||
|
here. If Parts II, III, IV, and line 40 on page 2 do not apply to you, also enter this amount on |
|
|
|
||
|
Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 5. Otherwise, include this amount in the total on line 41 on page 2 . |
26 |
|
|
||
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the separate instructions. |
Cat. No. 11344L |
Schedule E (Form 1040) 2020 |
||||

Schedule E (Form 1040) 2020 |
Attachment Sequence No. 13 |
Page 2 |
Name(s) shown on return. Do not enter name and social security number if shown on other side.
Your social security number
Caution: The IRS compares amounts reported on your tax return with amounts shown on Schedule(s)
Part II Income or Loss From Partnerships and S Corporations — Note: If you report a loss, receive a distribution, dispose of stock, or receive a loan repayment from an S corporation, you must check the box in column (e) on line 28 and attach the required basis computation. If you report a loss from an
27Are you reporting any loss not allowed in a prior year due to the
|
|
|
see instructions before completing this section |
. . . . . . . . |
. |
. |
|
Yes |
No |
|||||||||||||||||
28 |
|
|
|
(a) Name |
|
|
|
|
(b) |
Enter P for |
(c) Check if |
|
|
(d) Employer |
|
(e) |
Check if |
|
|
(f) Check if |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
partnership; S |
foreign |
|
|
identification |
|
basis computation |
|
any amount is |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for S corporation |
partnership |
|
|
number |
|
is required |
|
|
|
not at risk |
||||||
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Passive Income and Loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonpassive Income |
and Loss |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(g) Passive loss allowed |
|
(h) Passive income |
|
(i) Nonpassive loss allowed |
(j) Section 179 expense |
|
(k) |
Nonpassive income |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
(attach Form 8582 if required) |
|
from Schedule |
|
(see Schedule |
|
deduction from Form 4562 |
|
from Schedule |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29a |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
b |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
Add columns (h) and (k) of line 29a |
. . . . . . . |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
31 |
|
Add columns (g), (i), and (j) of line 29b |
. . . . . . . |
|
31 |
|
( |
|
|
|
) |
|||||||||||||||
32 |
|
Total partnership and S corporation income or (loss). Combine lines 30 and 31 . . . . |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Part III |
Income or Loss From Estates and Trusts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) Employer |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
identification number |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Passive Income and Loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonpassive Income and Loss |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
(c) Passive deduction or loss allowed |
|
(d) Passive income |
|
(e) Deduction or loss |
|
|
(f) Other income from |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
(attach Form 8582 if required) |
|
from Schedule |
|
from Schedule |
|
|
Schedule |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34a |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
b |
Totals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
Add columns (d) and (f) of line 34a |
. . . . . . . |
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
36 |
|
Add columns (c) and (e) of line 34b |
. . . . . . . |
|
36 |
|
( |
|
|
|
) |
|||||||||||||||
37 |
|
Total estate and trust income or (loss). Combine lines 35 and 36 . . . |
. . . . . . . |
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Part IV |
Income or Loss From Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits |
Holder |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
38 |
|
|
(a) Name |
|
(b) Employer identification |
|
|
(c) Excess inclusion from |
(d) Taxable income (net loss) |
|
|
(e) Income from |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Schedules Q, line 2c |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number |
|
|
|
(see instructions) |
from Schedules Q, line 1b |
|
|
Schedules Q, line 3b |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
Combine columns (d) and (e) only. Enter the result here and include in the total on line 41 below |
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Part V |
Summary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
40 |
|
Net farm rental income or (loss) from Form 4835. Also, complete line 42 below |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
41 |
|
Total income or (loss). Combine lines 26, 32, 37, 39, and 40. Enter the result here and on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 5 ▶ |
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42Reconciliation of farming and fishing income. Enter your gross farming and fishing income reported on Form 4835, line 7; Schedule
43Reconciliation for real estate professionals. If you were a real estate professional
(see instructions), enter the net income or (loss) you reported |
anywhere on Form |
|
|
|
|
1040, Form |
in which |
|
|
|
|
you materially participated under the passive activity loss rules |
. . . |
. . . |
43 |
|
|
Schedule E (Form 1040) 2020
Form Data
| Fact | Description |
|---|---|
| Form Name | IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) |
| Purpose | Used to report income and losses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. |
| Main Users | Individual taxpayers with the aforementioned types of income. |
| Filing Requirement | Must be filed by taxpayers who receive income as specified above and are required to file a Form 1040 individual income tax return. |
| Attachment to Main Form | Schedule E is attached to and filed along with Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR. |
| Reporting Categories | Divided into sections for reporting income or loss from Rental Real Estate, Royalties, Partnerships and S corporations, Estates and Trusts, and REMICs. |
| Key Sections | Includes sections for reporting property description, income, expenses, and totals. |
| Governing Law | Federal tax law, as enforced by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). |
Instructions on Utilizing IRS Schedule E 1040
After gathering all necessary documentation and information related to rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs, individuals ready to report supplemental income and loss encounter the IRS Schedule E 1040 form. This crucial part of tax filing requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with IRS regulations. The process involves a series of steps that guide the filer through various types of income and expenses associated with the properties or entities owned.
- Start by providing your name and Social Security Number at the top of the form to ensure that your Schedule E is correctly associated with your main Form 1040.
- In Part I, focus on income or loss from rental real estate and royalties. Fill in properties individually, including address and type. Specify your income, expenses, and any depreciation related to each property to calculate the net gain or loss.
- For those who received income through partnerships or S corporations, Part II requires information on each entity. Include the entity's name, EIN, and the net income (or loss) reported to you. This section requires careful attention to detail to properly report your share of income or deductions.
- In Part III, income or loss from estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs should be recorded. Similar to Part II, you'll need to list each entity separately, detailing the income or loss attributed to you.
- For each part, it’s crucial to accurately calculate the total income or loss and report these figures in the summary sections provided at the end of each part. This ensures that your total supplemental income or loss is correctly captured for tax purposes.
- Review the form for accuracy and completeness. Double-check all your calculations and ensure that all required information is presented clearly and correctly.
- Attach Schedule E to your Form 1040 and include it with your other tax documents when you file your taxes. Make sure to keep a copy of Schedule E for your records.
Completing IRS Schedule E 1040 accurately is key to accurately reporting supplemental income and avoiding potential issues with the IRS. Take your time to review all instructions related to your specific situation and consult with a tax professional if you encounter any uncertainties or complex scenarios. By following these steps carefully, you'll be well on your way to successfully filing your tax return.
Obtain Answers on IRS Schedule E 1040
-
What is the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) used for?
This form is designed for reporting income or losses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. By filling out Schedule E, taxpayers can calculate the total income or loss from these sources to report on their Form 1040. It's essential for those who receive income other than regular wages, salaries, or tips, allowing for a more comprehensive declaration of earnings and potential tax deductions.
-
Who needs to file a Schedule E with their 1040 form?
Individuals who have received income from rental property, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, or trusts should file a Schedule E alongside their 1040 form. Additionally, participates in residual interests in REMICs must also provide this information. Essentially, if you've received income from any of these sources over the tax year, this form is necessary to accurately report your earnings and determine your tax obligations.
-
Can losses reported on Schedule E be used to offset other income?
Yes, losses reported on Schedule E can often offset other sources of income, such as wages or salaries, thereby potentially reducing overall taxable income. However, there are limitations and rules governing how losses can be deducted, especially with regard to passive activity losses and real estate professionals. These rules can be complex, and taxpayers may benefit from consulting a tax professional to navigate the limitations and determine how best to report their income and losses for tax purposes.
-
How do I report income from partnerships or S corporations on Schedule E?
To report income from partnerships or S corporations on Schedule E, taxpayers must fill out Part II of the form. You'll need a Schedule K-1 form from the partnership or S corporation, which details your share of the income, deductions, and credits. This information is then transferred to your Schedule E, helping to calculate your total income or loss from these entities to report on your 1040 form.
-
What information do I need to complete Schedule E?
To successfully complete Schedule E, you'll need detailed information about your income and expenses from each source required to be reported on this form. This includes rental income and expenses, royalty income, income and losses from partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and REMICs. Specifically, you should have records of any rent collected, mortgage interest, property taxes, operating expenses, insurance costs, and any improvements made to the property. For partnerships and S corporations, you will need the Schedule K-1 form provided by the entity.
-
Where can I find Schedule E (Form 1040)?
Schedule E (Form 1040) is available on the IRS website. You can download the form directly from there. Besides, tax preparation software often includes the ability to fill out this schedule electronically. For those who prefer a more guided approach, professional tax preparers or tax preparation services can help complete and file Schedule E alongside your other tax forms.
Common mistakes
When individuals prepare their taxes, specifically when using the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) to report income or losses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs, several common mistakes can occur. These errors can delay the processing of your tax return, lead to an audit, or result in penalties. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can navigate the completion of Schedule E with greater accuracy and confidence.
Not Reporting All Income: Many individuals fail to report all of the income received from rental properties or royalties. This oversight includes forgetting to declare payments received for lease cancellations, expenses paid by tenants, or the fair market value of goods or services received in lieu of money.
Incorrect Expense Reporting: Overstating expenses or deducting personal expenses as rental expenses are common mistakes. Only expenses directly related to the rental property and its maintenance as a rental can be deducted.
Improper Classification of Properties: Failing to correctly classify properties between rental and personal use affects the reportable income and deductible expenses. Accurate classification is crucial for proper tax calculation.
Forgetting to Depreciate: Rental property owners sometimes neglect to claim depreciation on their properties, an oversight that can result in paying more tax than necessary. Depreciation recoups the cost of the property over time and is a legitimate deduction.
Mixing Up Passive and Non-Passive Activities: Incorrectly classifying income as passive when it is not, or vice versa, can significantly affect your tax obligations. It's vital to understand the distinctions between passive and non-passive income and expenses.
Not Keeping Accurate Records: Inadequate record-keeping of income and expenses throughout the year makes it challenging to accurately complete Schedule E. This practice can lead to mistakes or omissions in reporting.
Overlooking Carryover Losses: Taxpayers sometimes forget to include losses carried over from previous years. These carryover losses can reduce taxable income and should not be overlooked.
Failing to Report Foreign Real Estate: Those who own rental properties in foreign countries often neglect to report this fact. The IRS requires the reporting of all rental income, regardless of where the property is located.
Understanding these common errors and taking steps to avoid them can help ensure that your Schedule E is filled out accurately and completely. This not only minimizes the chance of IRS scrutiny but also helps ensure that you are not paying more tax than necessary. Always consider consulting with a tax professional if you're unsure about the specifics of your situation. Remember, a small effort towards accuracy and completeness now can save a significant amount of time and trouble later.
Documents used along the form
When filing the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) for reporting income or losses from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs, it’s important to have all the necessary documents at hand. This form is pivotal for taxpayers with supplemental income or losses. However, completing Schedule E accurately often requires additional forms and documents to ensure a complete and correct tax return. Let’s explore some of these essential documents.
- Form 4562: This form is used for reporting depreciation and amortization. For rental property owners, this includes detailing the depreciation of the property and improvements, which can lower taxable income.
- Schedule K-1 (Form 1065): Partners in partnerships and S corporation shareholders receive this form. It shows the share of income or loss to report on Schedule E.
- Form 1099-MISC or Form 1099-NEC: These forms report income received as a landlord from rents or as a royalty owner, making them critical for accurately filling out Schedule E.
- Form 8825: This form is similar to Schedule E but is specifically used by partnerships and S corporations to report rental real estate income and expenses. It often accompanies Schedule K-1 when filing.
- Property Expense Records: While not a form, keeping thorough records of property-related expenses, such as repairs, management fees, and utilities, is essential. These records support the deductions claimed on Schedule E.
Gathering and preparing these documents can streamline the process of filing your taxes and help ensure the accuracy of your Schedule E. Moreover, they provide the necessary backup for your tax return, which can be invaluable in the event of an IRS inquiry. Remember, maintaining good records throughout the year not only aids in tax preparation but also contributes to the successful management of your investments.
Similar forms
IRS Form 1040 Schedule C - This form is used by individuals who are self-employed or are sole proprietors of a business. It's similar to Schedule E in that both forms are attachments to the main Form 1040 used for reporting different types of income. However, Schedule C focuses on business income and expenses, whereas Schedule E is for supplemental income, like rental income or royalties.
IRS Form 1040 Schedule D - Schedule D is used to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of capital assets. Both Schedule D and E are necessary for providing a complete picture of an individual's additional income sources outside of regular employment, contributing to the total tax liability on the main Form 1040.
IRS Form 4797 - This form is used for reporting the sale of business property. It's similar to Schedule E, as both involve declaring income that does not originate from wages, salaries, or tips. They uniquely cater to different types of assets, highlighting the varied nature of income sources that individuals might have.
IRS Form 8582 - Form 8582 is designed to report passive activity loss limitations. It complements Schedule E closely, as passive income generators, like rental activities reported on Schedule E, often need to calculate and report passive activity losses through Form 8582. Both play a crucial role in accurately reporting income and losses from passive activities.
IRS Schedule B - Schedule B is attached to Form 1040 for reporting interest and ordinary dividends. It is similar to Schedule E in that it's another type of supplemental form to the main tax return, used to report specific types of income. While Schedule B deals with interest and dividends, Schedule E focuses on rental, royalty, partnership, and other passive income sources.
IRS Form 6251 - Form 6251 is used for calculating alternative minimum tax (AMT). This form can become relevant for individuals who fill out Schedule E, as certain income sources reported on Schedule E may trigger the need to calculate AMT. The similarity lies in their potential contribution to the individual's overall tax situation, though they serve very different purposes.
Dos and Don'ts
Understanding how to properly fill out the IRS Schedule E 1040 form is essential for accurately reporting your supplementary income. Below is a helpful list of do's and don'ts:
Do's:- Review all sources of income: Before you begin, make sure you have all documentation related to rental properties, royalties, and income from estates, trusts, partnerships, S corporations, or REMICs. This will ensure a smooth process.
- Report all income: It's critical to report every dollar of income received from these sources. Overlooking even small amounts could lead to discrepancies and potential audits.
- Deduct permissible expenses: Certain expenses related to rental property, such as maintenance, repairs, property management fees, and depreciation, can be deducted. Ensure these are accurately accounted for to reduce your taxable income.
- Use the correct section: Schedule E is divided into parts for different types of income. Make sure you're filling out the correct section(s) based on the income you're reporting.
- Seek professional help if needed: If you're unsure about any aspect of your Schedule E filing, don't hesitate to consult with a tax professional. It can save you from making costly mistakes.
- Don't estimate income or expenses: Always use actual figures when reporting income and expenses. Estimates can lead to inaccuracies and issues with the IRS.
- Don't forget to include all relevant properties: If you own multiple rental properties, make sure each one is accounted for on the Schedule E.
- Don't neglect local and state tax laws: In addition to federal tax obligations, be aware of any state and local taxes that may apply to your rental income.
- Don't overlook carryover losses: If you had a net loss in a previous year that was not fully deductible, remember to carry it over to the current year if applicable.
Approaching the task of filling out Schedule E with a thorough and careful mindset will help you accurately report your income and reduce the likelihood of errors. Remember, honest and precise reporting not only keeps you compliant with tax laws but also maximizes your eligible deductions, potentially saving you money.
Misconceptions
Filing taxes can be complex, and the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) is no exception. There are several misconceptions about this form that can confuse taxpayers. Here, we clarify some of the most common misunderstandings:
It's only for rental income. While Schedule E is commonly used to report income or loss from rental real estate, it's also required for reporting income from royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits (REMICs). This misconception might lead individuals to incorrectly file their income, potentially causing issues with the IRS.
Filing this form means you owe more taxes. Not necessarily. Schedule E is used to report both income and losses. If your expenses for a rental property or other qualifying source exceed your income, you might actually reduce your taxable income, leading to a lower tax bill. It's essential to understand that reporting losses to offset income is a legitimate and common practice, within the guidelines provided by the IRS.
You can't use it for vacation rentals. This is not true. If you rent out a vacation home, you're likely required to report that income on Schedule E. However, specific rules determine how to report these earnings, based on the number of days used for personal use versus rental. Understanding these rules is crucial to correctly filing your taxes and avoiding potential penalties.
Schedule E income doesn't affect your Social Security taxes. In fact, the income or loss reported on Schedule E can affect your adjusted gross income (AGI), which in turn might impact the taxes you pay on Social Security benefits. As your AGI increases, the proportion of Social Security benefits subject to tax can also increase. So, it's important to consider how income from Schedule E contributes to your overall tax situation.
Personal expenses are deductible if your property is rented out. The IRS is very clear that only expenses directly related to the rental activity are deductible. Personal use expenses for a rental property cannot be deducted. This includes any time that you or your family use the property for personal vacations. Keeping accurate records of expenses and usage of the property is essential for correctly reporting to the IRS and avoiding penalties.
Understanding these misconceptions can help guide taxpayers in correctly filing their Schedule E and avoid potential pitfalls. Always consult a tax professional if you're unsure about your specific situation.
Key takeaways
The IRS Schedule E 1040 form is critical for taxpayers who earn rental income from real estate or royalties, or who receive income through partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. Understanding the essentials of completing and utilizing this form can help in accurate and compliant tax filing. Here are five key takeaways:
- Identify All Income Sources: Before filling out Schedule E, taxpayers must identify all sources of income that pertain to this form. This includes rental income, royalties, and incomes from estates, trusts, partnerships, and S corporations. Accurate reporting of these incomes is crucial for proper tax calculation.
- Understanding Fair Rental Days: For rental property owners, it's important to accurately report the number of days a property was rented at fair market value versus personal use. This affects how expenses can be deducted and how income is reported.
- Accurately Deduct Expenses: Schedule E allows for the deduction of expenses related to the generation of income from the properties or entities listed on the form. These deductions can include mortgage interest, property taxes, maintenance costs, and advertising. Accurate record-keeping throughout the year will aid in correct deductions.
- Dealing with Losses: There are specific rules and limits concerning the reporting of losses on Schedule E. Understanding passive activity loss limitations and at-risk rules is vital for accurately reporting and utilizing losses to offset income.
- Utilize Professional Help if Unsure: Due to the complexities associated with real estate, partnership, and trust income taxation, it may be beneficial to seek professional tax advice. A tax professional can offer guidance tailored to an individual's unique financial situation, ensuring compliance and optimization of tax liabilities.
Properly filling out the IRS Schedule E 1040 form is fundamental for those with applicable types of income. By staying informed on these key points, taxpayers can take steps towards ensuring their tax filings are accurate and compliant with IRS regulations.
Popular PDF Forms
IRS 1099-INT - Earned interest on your investments? The 1099-INT form is how this income gets reported to the IRS, keeping your taxes accurate.
Abortion Paperwork - It details the obligations of healthcare providers to report specific details, enhancing transparency and accountability in medical procedures.