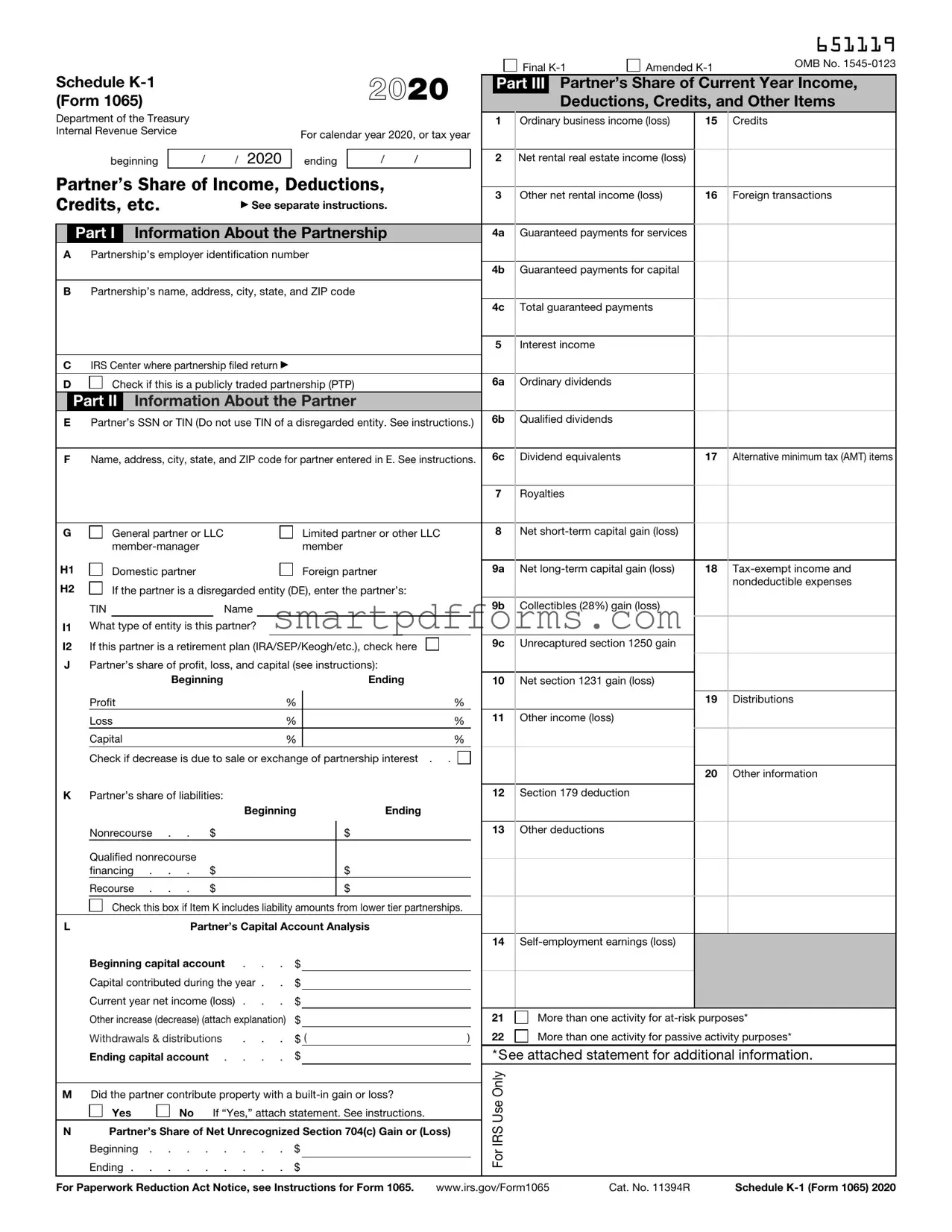
Blank IRS Schedule K-1 1065 PDF Template
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations for partnerships can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to understanding the IRS Schedule K-1 (Form 1065). This document plays a pivotal role in reporting the share of income, deductions, credits, and other financial data for each partner within a partnership. It's a critical piece of the puzzle in ensuring that partners fulfill their tax responsibilities accurately, reflecting their fair share of the partnership's financial activity for the year. Unlike standard tax forms that an individual or corporation might fill out, the Schedule K-1 requires careful attention to detail to ensure every piece of information is precise and aligned with the overall tax filings of the partnership. This form not only aids in maintaining transparency between the partnership and the IRS but also provides each partner with the necessary information to report on their individual tax returns. Understanding the major aspects of this form is essential for anyone involved in a partnership, as it directly impacts how income and taxes are reported and processed at both the state and federal levels.
Preview - IRS Schedule K-1 1065 Form
Schedule |
|
|
|
2020 |
||
(Form 1065) |
|
|
|
|||
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
For calendar year 2020, or tax year |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
ending |
|
|
|
beginning |
|
/ |
/ 2020 |
/ |
/ |
|
Partner’s Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc.
Part I Information About the Partnership
APartnership’s employer identification number
BPartnership’s name, address, city, state, and ZIP code
CIRS Center where partnership filed return ▶
D |
Check if this is a publicly traded partnership (PTP) |
Part II Information About the Partner
EPartner’s SSN or TIN (Do not use TIN of a disregarded entity. See instructions.)
FName, address, city, state, and ZIP code for partner entered in E. See instructions.
G |
General partner or LLC |
Limited partner or other LLC |
|
member |
|
H1 |
Domestic partner |
Foreign partner |
H2 |
If the partner is a disregarded entity (DE), enter the partner’s: |
|
|
TIN |
|
Name |
|
|
I1 |
What type of entity is this partner? |
|
|||
I2 |
If this partner is a retirement plan (IRA/SEP/Keogh/etc.), check here |
||||
JPartner’s share of profit, loss, and capital (see instructions):
Beginning |
|
Ending |
|
Profit |
% |
|
% |
|
|||
Loss |
% |
|
% |
Capital |
% |
|
% |
Check if decrease is due to sale or exchange of partnership interest . . |
|
||
KPartner’s share of liabilities:
|
|
|
Beginning |
Ending |
|
|||
|
Nonrecourse . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
||
|
Qualified nonrecourse |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
financing . . . |
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Recourse . . . |
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Check this box if Item K includes liability amounts from lower tier partnerships. |
|
||||||
L |
Partner’s Capital Account Analysis |
|
|
|||||
|
Beginning capital account . . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Capital contributed during the year . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Current year net income (loss) . . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Other increase (decrease) (attach explanation) |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Withdrawals & distributions |
. . . |
$ ( |
|
) |
|
||
|
Ending capital account . . . . |
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
MDid the partner contribute property with a
Yes |
No If “Yes,” attach statement. See instructions. |
NPartner’s Share of Net Unrecognized Section 704(c) Gain or (Loss) Beginning . . . . . . . . $
Ending . . . . . . . . . $
651119
Final |
Amended |
OMB No. |
||
|
||||
Part III |
Partner’s Share of Current Year Income, |
|||
|
Deductions, Credits, and Other Items |
|||
1 Ordinary business income (loss) |
15 Credits |
|
||
2Net rental real estate income (loss)
3 |
Other net rental income (loss) |
16 Foreign transactions |
4a |
Guaranteed payments for services |
|
|
||
4b |
Guaranteed payments for capital |
|
|
||
4c |
Total guaranteed payments |
|
|
5Interest income
6a |
Ordinary dividends |
|
6b |
Qualified dividends |
|
|
||
6c |
Dividend equivalents |
17 Alternative minimum tax (AMT) items |
7Royalties
8Net
9a |
Net |
18 |
|
|
|
|
nondeductible expenses |
9b |
Collectibles (28%) gain (loss) |
|
|
9c |
Unrecaptured section 1250 gain |
|
|
|
|
||
10 |
Net section 1231 gain (loss) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
Distributions |
11Other income (loss)
20 Other information
12Section 179 deduction
13Other deductions
14
21 More than one activity for
22 More than one activity for passive activity purposes*
*See attached statement for additional information.
For IRS Use Only
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see Instructions for Form 1065. |
www.irs.gov/Form1065 |
Cat. No. 11394R |
Schedule |
Form Data
| Fact Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The IRS Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) is used by partnerships to report each partner's share of the partnership's earnings, losses, deductions, and credits. |
| 2 | It serves as a conduit for partnership information to flow to the personal income tax returns of the partners. |
| 3 | Each partner must report the information from Schedule K-1 on their own tax return. |
| 4 | Schedule K-1 helps partners in determining the basis of their partnership interest, which is essential for calculating gains or losses on disposition of the partnership interest. |
| 5 | The form distinguishes between different types of income, such as rental income, interest income, and ordinary business income, which may be taxed differently on the partner’s return. |
| 6 | Partners are responsible for reporting items of profit, loss, or credit according to their partnership agreement, regardless of whether distributions were made. |
| 7 | Filing deadlines for the Schedule K-1 coincide with the partnership's tax return, typically due on March 15, or the 15th day of the third month after the end of the fiscal year, if on a fiscal year basis. |
| 8 | For states with income tax, there may be a state-specific version of Schedule K-1 required in addition to the federal form, governed by the applicable state revenue agency’s regulations. |
Instructions on Utilizing IRS Schedule K-1 1065
The IRS Schedule K-1 Form 1065 is used to report an individual's share of a partnership's income, deductions, credits, etc. Filling out this form correctly is essential for ensuring compliance with tax obligations and for accurately reporting your financial interest in a partnership. The instructions outlined below will guide you through the process of completing the form, ensuring that you provide all of the necessary information in the correct sections.
- Begin by gathering all required information about the partnership's financial activities for the tax year. This includes income statements, deductions, credits, and any other relevant financial details.
- Identify the partnership's IRS Center where your Form 1065 was filed. You will need this information to correctly fill out the form.
- On the top section of the Schedule K-1 Form 1065, enter the partnership's name, address, and EIN (Employer Identification Number).
- In the designated boxes, input your name and address as a partner in the partnership.
- Provide your Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) in the space provided.
- Indicate the beginning and end dates of the partnership's tax year on the form.
- Fill in your share of income, deductions, and credits for the year in Part III of the form. Refer to the partnership's financial documents to accurately report these amounts.
- If applicable, complete the sections regarding your share of the partnership's liabilities at the end of the year. This includes nonrecourse, qualified nonrecourse financing, and recourse liabilities.
- Review the instructions provided by the IRS for any additional information specific to your situation that may need to be included on the form. This can include foreign transactions, alternative minimum tax items, or other uncommon situations.
- Once all necessary information has been accurately completed, sign and date the bottom of the Schedule K-1 Form 1065 to certify the accuracy of the information provided. If you're filling out the form on behalf of the partnership, include your title or relationship to the partnership.
- Retain a copy of the completed Schedule K-1 Form 1065 for your records and provide the original to the IRS along with the Form 1065 if it's not already been filed. Distribute the relevant copies to the partners for their tax records and reporting purposes.
By following these steps, you ensure that the Schedule K-1 Form 1065 is completed thoroughly and accurately, facilitating the proper reporting of income, deductions, and credits associated with your involvement in a partnership. This careful approach helps in avoiding potential errors and the consequences that can come with inaccurate tax reporting.
Obtain Answers on IRS Schedule K-1 1065
-
What is an IRS Schedule K-1 1065 form?
The IRS Schedule K-1 1065 form is a document used by partnerships to report the income, deductions, gains, losses, and credits of each partner. It serves as a way to distribute the income or losses of the partnership to the individual partners based on their ownership interests, providing the necessary information to be reported on their personal tax returns.
-
Who needs to file IRS Schedule K-1 1065 form?
This form is required for partnerships operating in the United States. The responsibility for filing falls on the partnership itself, which must prepare a Schedule K-1 for each person or entity that was a partner in the partnership at any time during the fiscal year.
-
When is the IRS Schedule K-1 1065 form due?
The due date for filing the Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) typically aligns with the filing date of the partnership's tax return. This is usually the 15th day of the third month following the end of the partnership’s fiscal year. For partnerships operating on a calendar year, the due date would be March 15th of the following year.
-
What information is reported on the Schedule K-1 1065 form?
The form includes details such as the partner’s share of income, deductions, credits, and other items derived from the partnership's operations. Specific components reported include ordinary business income, real estate income, interest income, dividends, guaranteed payments, and distributions, among other financial activities.
-
How does a partner use the information on Schedule K-1 1065?
Partners utilize the information on Schedule K-1 to complete their own tax returns. The details provided indicate how much of the partnership's income or loss is attributable to them. This information must be reported on their individual tax returns and affects their tax liability based on their share of the partnership's business activities.
-
Can Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) be filed electronically?
Yes, the Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) can be filed electronically, which is encouraged by the IRS. Filing electronically can expedite processing times, reduce errors, and provide instant confirmation that the IRS has received the form.
-
What are the common mistakes to avoid when filling out a Schedule K-1 1065?
- Inaccurate allocation of income, deductions, and credits among partners.
- Failing to report or improperly reporting the sale or exchange of partnership interests.
- Omitting required supplemental information.
- Missing the filing deadline, which can lead to penalties.
Attention to detail and thoroughness in completing the form can help avoid these common errors.
-
What should partners do if they receive an incorrect Schedule K-1 1065?
If a partner believes the Schedule K-1 they received contains inaccuracies, they should immediately contact the partnership to request a corrected form. It is crucial to rectify any errors before the partner files their individual tax return to prevent misreporting and the potential for penalties or audits from the IRS.
-
How do partnerships determine each partner's share of income or losses?
Partnerships determine each partner’s share of income or losses according to the partnership agreement. This legal document outlines how profits, losses, and distributions will be allocated among the partners. The specific allocations should be consistent with the provisions outlined in the agreement to ensure proper reporting on Schedule K-1.
-
Where can additional information and assistance regarding Schedule K-1 1065 be found?
Additional information and resources can be found on the IRS official website, including detailed instructions for completing the form and answers to frequently asked questions. Partnerships and partners may also consider consulting with a tax professional or accountant who can provide personalized advice and guidance based on their specific circumstances.
Common mistakes
-
Not reporting all income: Many people forget to include all sources of income on their Schedule K-1. Every penny received from the partnership must be reported to the IRS.
-
Mixing personal and business expenses: It's essential to strictly separate personal expenses from those of the business. Claiming personal expenses as business deductions is a mistake that can attract penalties.
-
Incorrectly reporting international transactions: Partners in a partnership that has international transactions must pay extra attention to accurately report these activities, as there are specific reporting requirements and tax treatments involved.
-
Omitting information: Leaving any section blank if it applies to you could flag your return for further review by the IRS.
-
Incorrect Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN): Ensure these numbers are accurate. A simple typo can result in processing delays or incorrect tax assessments.
-
Failing to apply the correct tax basis: Partners must use their tax basis for calculating the deductible loss, which can be different from the amount reported by the partnership. Not adjusting for this can lead to incorrect filings.
-
Disregarding state-level instructions: Some states have specific requirements for how partnership income is reported. Failing to adhere to these guidelines can cause issues with state tax returns.
-
Not attaching required additional forms: Depending on your situation, you might need to attach other forms or schedules to your K-1. Overlooking this requirement can result in incomplete filings.
-
Misunderstanding distribution amounts: Distributions are reported on the Schedule K-1, but they are not always taxable income. Misinterpreting these amounts can lead to incorrect income reporting.
-
Using outdated forms: The IRS updates its forms regularly. Using an outdated version can mean missing new instructions or making errors based on old rules.
Additionally, some other considerations include:
Ensuring that the form is signed and dated.
Double-checking the math; errors in calculations can lead to discrepancies and trigger audits.
Keeping a thorough record of documents and worksheets used in preparing the Schedule K-1 in case the IRS requires clarification or substantiation of reported amounts.
Avoiding these mistakes can save taxpayers from headaches down the line. It's often beneficial to consult with a tax professional when filling out the IRS Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) to ensure accuracy and compliance with the complex tax rules and regulations.
Documents used along the form
The IRS Schedule K-1 Form 1065 is a crucial document for partnerships, as it provides necessary information about the share of profits, losses, credits, and deductions attributed to each partner. In the realm of tax preparation and compliance, several other forms and documents commonly accompany the Schedule K-1 1065 to ensure a comprehensive overview of an entity's financial and tax status. These documents play pivotal roles in clarifying and supporting the information reported on the Schedule K-1 and other related tax filings.
- Form 1065, U.S. Return of Partnership Income: This form is the core document for reporting a partnership's financial results for the year. It includes summaries of the partnership's income, deductions, and credits, and it lays the groundwork for the detail provided in each partner's Schedule K-1.
- Form 4562, Depreciation and Amortization: Often used in conjunction with Schedule K-1 and Form 1065, this form reports the depreciation and amortization expenses for assets used in the partnership’s business, which can affect the partnership's income and consequently the information reported on the Schedule K-1.
- Form 8865, Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Partnerships: For partnerships with foreign activities or partners, Form 8865 is required to report the foreign partnership's financial activities, similar to how domestic partnerships use Form 1065. Certain elements of Form 8865 can directly impact the information provided in Schedule K-1.
- Form 8949, Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets: This form is used to list all capital asset transactions which can affect capital gains and losses reported on the Schedule K-1 for each partner, highlighting the partnership’s buying and selling of capital assets throughout the year.
- Form 8308, Report of a Sale or Exchange of Certain Partnership Interests: If there's a transfer of partnership interests, this form is necessary to report the sale or exchange, which may have implications for individual partners' capital accounts and ultimately their Schedule K-1.
- Form 7004, Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns: While not directly associated with the income reporting process, Form 7004 is crucial for partnerships that require additional time to file their Form 1065 and, subsequently, the Schedule K-1s.
Together, these documents provide a comprehensive picture of a partnership's financial activities and tax obligations. By effectively managing and accurately completing these forms, partnerships can ensure compliance with tax laws and support the precise distribution of income, deductions, credits, and losses to their partners as detailed in the Schedule K-1 Form 1065.
Similar forms
Schedule K-1 (Form 1120-S): Like the Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), this form is used by shareholders in an S corporation to report their share of the corporation's income, deductions, credits, and other items. Both forms serve a similar purpose in that they provide the necessary information to include on an individual's tax return but pertain to different types of entities; Form 1065 for partnerships and Form 1120-S for S corporations.
Schedule C (Form 1040): This form is for a sole proprietor to report income or loss from a business they operated or a profession they practiced as a sole proprietor. Similar to Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), Schedule C summarizes income, costs, and expenses associated with operating a business. However, while Schedule C is for individuals running their own business, Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) is for reporting an individual's income from a partnership.
Schedule E (Form 1040): Schedule E is used by taxpayers to report income from rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, estates, trusts, and residual interests in REMICs. The similarity to Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) lies in reporting pass-through income from partnerships and S corporations. Taxpayers use information from Schedule K-1 to fill out parts of Schedule E.
Form 1040 (U.S. Individual Income Tax Return): The central form for individual income tax returns in the U.S. While not exclusive to income from partnerships, it is directly related in that income, deductions, credits, etc., from Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) are reported on Form 1040. Thus, it serves as the final destination for information recorded on Schedule K-1 (Form 1065).
Form 8865 (Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Partnerships): Similar to Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), Form 8865 is used by U.S. persons who are involved in certain foreign partnerships. It requires the reporting of the partnership's income, losses, and other financial activities, akin to domestic partnerships' reporting requirements. This form demonstrates the international counterpart to the domestic reporting requirements seen in Schedule K-1 (Form 1065).
Form 1065 (U.S. Return of Partnership Income): The broader form that includes Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) as a component. Form 1065 is used by partnerships to report the partnership's income, gains, losses, deductions, credits, etc., to the IRS. Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) is a part of this larger document, designed to pass along each partner's share of these items. It's a direct relationship where the Schedule K-1 is a necessary detail of the comprehensive partnership reporting package.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS Schedule K-1 (1065) form, it's crucial to pay attention to detail and accuracy. Below are lists of things one should do and shouldn't do during this process.
Do:
- Review the instructions provided by the IRS carefully to ensure understanding of the requirements.
- Double-check all the information from your partnership records to ensure accuracy before inputting them into the form.
- Include all necessary attachments and schedules as required by the IRS to avoid delays or questions.
- Use the IRS's electronic filing system if available for your filing to expedite the process and reduce the risk of errors.
- Report all income, deductions, and credits accurately to maintain compliance and avoid potential audits.
- Seek advice from a tax professional if there are any uncertainties or complex issues with your partnership's finances to ensure correct filing.
Don't:
- Avoid guessing on figures or making estimations. Ensure all amounts are accurate and backed by documentation.
- Do not ignore IRS notices or instructions related to Schedule K-1 (1065) filing requirements.
- Refrain from filing late. Be mindful of the IRS deadlines to avoid penalties and interest.
- Do not omit any partner's information. Every partner's share of income, deductions, and credits must be accurately reported.
- Avoid using ink that is not black on the form if submitting by mail, as this can cause readability issues.
- Do not forget to sign and date the form if required, as an unsigned form is considered invalid and may result in processing delays.
Misconceptions
Understanding the IRS Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) is crucial for partners in a partnership or members of a multi-member LLC taxed as a partnership. However, there are common misconceptions that can lead to confusion or errors when dealing with this form. By clarifying these misconceptions, individuals can better navigate their tax obligations.
- Only the partnership needs to file Schedule K-1: While it's true that the partnership files the form with the IRS, each partner must also receive a copy of Schedule K-1 to report their share of the partnership's income, deductions, and credits on their own tax returns.
- Income reported on Schedule K-1 is taxed at the partnership level: This is incorrect. The partnership itself is not subject to income tax. Instead, the income, deductions, gains, losses, and credits reported on Schedule K-1 flow through to the partners' individual tax returns where they are taxed.
- Schedule K-1 is only for reporting income: This misconception overlooks the form's broader scope. Schedule K-1 also reports deductions, credits, and the partner’s share of partnership liabilities, among other financial information. It's a comprehensive document that affects various parts of the tax return.
- All partners receive identical K-1 forms: Each partner's Schedule K-1 may differ based on their share of the partnership and the agreement's terms. The form reflects each partner’s specific financial interest in the partnership.
- Filing Schedule K-1 is only necessary if the partnership made a profit: Regardless of whether the partnership made a profit or incurred a loss, a Schedule K-1 must be filed for each partner. This form is necessary to allocate the partnership's income, deductions, gains, losses, and credits to the partners.
- Schedule K-1 affects only the income tax return: The information on Schedule K-1 can influence more than just the income tax owed. For example, it may impact self-employment taxes or the calculation of the taxpayer's adjusted gross income.
- Partners can wait until the partnership files its return to deal with Schedule K-1: Partners should not wait to receive their K-1 to start their own tax return process. They need this document to complete their tax returns accurately. Since partnerships must file their returns (and furnish K-1 forms to their partners) by March 15 (for calendar year taxpayers), partners should plan accordingly.
By addressing these misconceptions, partners can ensure they comply with tax laws, avoid potential penalties, and make informed decisions about their finances related to Schedule K-1 (Form 1065).
Key takeaways
Filling out the IRS Schedule K-1 (1065) form is crucial for partners in a partnership to accurately report their share of the business's income, deductions, credits, etc. Here are key takeaways to guide you through the process:
- The Schedule K-1 (1065) form is a document that all partners in a partnership must file with their personal tax returns. It outlines each partner's share of the partnership’s profits, losses, deductions, and credits.
- Accuracy is key when completing the Schedule K-1. Errors can lead to audits or penalties from the IRS.
- Each partner's income reported on Schedule K-1 must match the partnership's total income reported on Form 1065. Discrepancies will raise red flags with the IRS.
- The form requires detailed information, including the partnership's name, Employer Identification Number (EIN), and the partner’s share of income or loss. Ensure all details are correctly and completely filled out.
- Deadlines are important. The Schedule K-1 must be filed with the IRS and provided to each partner by the deadline stated by the IRS, typically the 15th day of the third month after the end of the partnership’s tax year.
- If a partner’s share of any item has changed during the year, they might receive an amended K-1. It's crucial to report the income from the latest K-1 received.
- Partners must report items shown on their K-1 on their personal tax returns. For example, income from Schedule K-1 must be included on Form 1040.
- Keep a copy of the Schedule K-1 for your records. In case of an audit, you will need to present your documentation.
- If you have questions or if the tax situation is complex, it’s advisable to consult with a tax professional. Misinterpretation of tax laws can lead to costly mistakes.
Understanding these key points can help ensure that the process of completing and filing the Schedule K-1 (1065) form is as smooth and error-free as possible.
Popular PDF Forms
Alabama Ppt - Electronic filing options are highlighted to expedite the submission process and reduce paper waste.
How to Sell a Car Privately in Florida - It is a critical document for ensuring compliance with state motor vehicle regulations.
Massage Intake Form Pdf - The document is designed to foster clear communication between client and therapist for a therapeutic and positive massage experience.