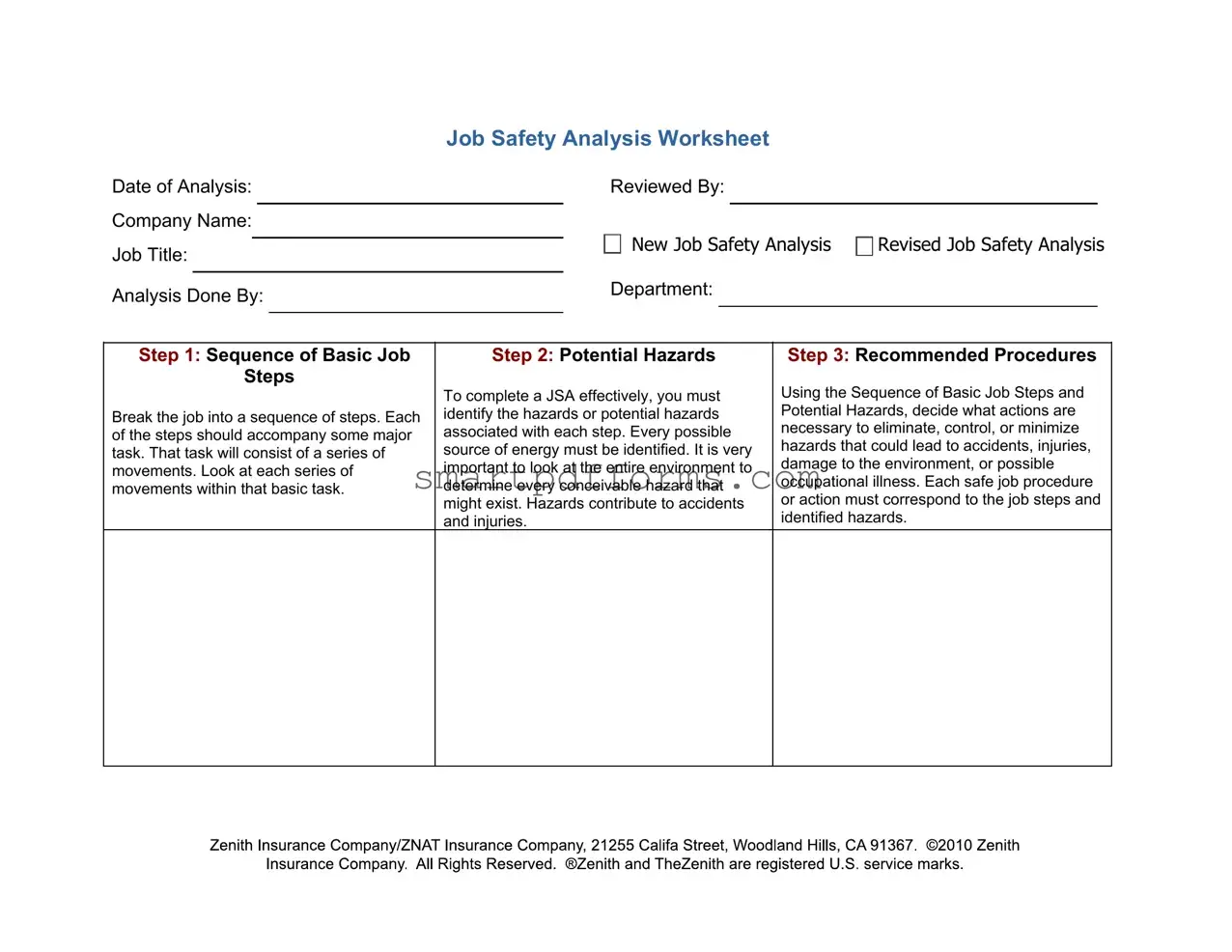
Blank Job Hazard Analysis PDF Template
In the modern workplace, safety management is a cornerstone of operational excellence, and the Job Hazard Analysis form plays a pivotal role in this area. This document serves as a comprehensive blueprint, guiding companies through the meticulous process of identifying and mitigating risks associated with various job tasks. Starting with a systematic breakdown of job duties into basic steps, it facilitates a granular examination of the workflow, ensuring that no aspect of a task is left unscrutinized. The essence of the form is not only to highlight potential hazards inherent in each step of a job but also to foster an environment where every possible source of energy and environmental factor is considered. This thorough analysis paves the way for the formulation of recommended procedures that aim to eliminate, control, or at the very least, minimize the hazards identified, thereby reducing the likelihood of accidents, injuries, or occupational illnesses. With a structure that prompts a review by involved parties and accommodates both new and revised analyses, the Job Hazard Analysis form is an indispensable tool in the quest for a safer and more efficient workplace.
Preview - Job Hazard Analysis Form
Job Safety Analysis Worksheet
Date of Analysis: |
|
Reviewed By: |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Company Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Job Safety Analysis |
|
Revised Job Safety Analysis |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Job Title: |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Department: |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Analysis Done By: |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 1: Sequence of Basic Job
Steps
Break the job into a sequence of steps. Each of the steps should accompany some major task. That task will consist of a series of movements. Look at each series of movements within that basic task.
Step 2: Potential Hazards
To complete a JSA effectively, you must identify the hazards or potential hazards associated with each step. Every possible source of energy must be identified. It is very important to look at the entire environment to determine every conceivable hazard that might exist. Hazards contribute to accidents and injuries.
Step 3: Recommended Procedures
Using the Sequence of Basic Job Steps and Potential Hazards, decide what actions are necessary to eliminate, control, or minimize hazards that could lead to accidents, injuries, damage to the environment, or possible occupational illness. Each safe job procedure or action must correspond to the job steps and identified hazards.

Job Safety Analysis Worksheet
Step 1: Sequence of Basic Job Steps |
Step 2: Potential Hazards |
Step 3: Recommended Procedures |
CONTINUED… |
CONTINUED… |
CONTINUED… |
|
|
|
Form Data
| Fact Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The Job Safety Analysis (JSA) Worksheet is utilized to identify and control hazards associated with specific job tasks. |
| 2 | The analysis is divided into three main steps: Identifying the sequence of basic job steps, identifying potential hazards, and developing recommended procedures. |
| 3 | A new JSA or a revised JSA can be initiated, depending on whether the job or process is new or if a review of an existing job is required due to changes or identified hazards. |
| 4 | Details such as the date of analysis, the individuals reviewing, and the company name are recorded at the beginning of the worksheet to ensure accountability and traceability. |
| 5 | In Step 1, breaking the job into basic steps helps in understanding the task flow and the complexity of the job, making it easier to identify where hazards might occur. |
| 6 | Step 2 focuses on identifying all potential hazards, including environmental and energy sources, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of all risks involved. |
| 7 | Recommended procedures in Step 3 are aimed at eliminating, controlling, or minimizing hazards, thereby protecting employees, the environment, and preventing occupational illnesses. |
| 8 | For state-specific JSA forms, governing laws might vary, impacting how analyses are conducted and what specific hazards or controls need to be considered. |
| 9 | The completion of a JSA worksheet contributes to a safer workplace by systematically addressing and mitigating job-related hazards. |
Instructions on Utilizing Job Hazard Analysis
Filling out a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) form is a crucial step in identifying and mitigating risks in the workplace. This process not only helps in ensuring the safety and health of employees but also aids in creating a more efficient work environment by identifying potential hazards and recommending procedures to handle them. The goal here is to break down jobs into individual steps, identify potential hazards within those steps, and then outline procedures to either eliminate or minimize the risks associated with those hazards. Let's walk through the steps needed to complete this important document effectively.
- Date of Analysis: Begin by entering the current date when the analysis is being conducted.
- Reviewed By: Note the name of the person who will review the completed analysis. This is typically a safety officer or supervisor.
- Company Name: Insert the name of the company conducting the Job Safety Analysis.
- Mark whether this is a New Job Safety Analysis or a Revised Job Safety Analysis by ticking the appropriate box.
- Job Title: Specify the job title of the employee or the position being analyzed.
- Department: State the department where the job is performed.
- Analysis Done By: Write the name of the person completing the JSA. This could be the employee performing the job, a safety officer, or any other designated person.
- Step 1: Sequence of Basic Job Steps
- Break the job being analyzed into its basic steps.
- Describe each step along with its major task and the series of movements it involves.
- Step 2: Potential Hazards
- Identify all potential hazards associated with each step identified in Step 1.
- Consider every source of energy and the entire work environment to pinpoint any possible hazards.
- Step 3: Recommended Procedures
- Based on the job steps and identified hazards, recommend procedures to eliminate, control, or minimize the risks.
- Ensure each procedure is directly related to the corresponding job steps and hazards.
After carefully completing each step, the Job Hazard Analysis form should be reviewed and approved by the designated reviewer. This is a continuous process, and the form should be updated regularly to reflect any changes in job procedures or to add new information on identified hazards and safety measures. Regularly revising and updating the JHA is key to maintaining a safe work environment.
Obtain Answers on Job Hazard Analysis
What is a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA)?
A Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) is a process that helps in identifying and controlling potential hazards associated with specific job tasks. The purpose of conducting a JHA is to prevent job-related injuries, illnesses, and accidents by eliminating or minimizing hazards. This process involves breaking down a job into its individual steps, identifying potential hazards for each step, and then determining the most effective measures to control or eliminate these hazards. It’s a proactive approach aimed at ensuring the safety and well-being of employees in the workplace.
How often should a Job Hazard Analysis be conducted?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this, as the frequency of JHA reviews depends on various factors such as the nature of the job, changes in job processes or equipment, and past incident records. However, it is widely recommended to conduct a JHA:
- Before introducing new processes, equipment, or substances into the workplace.
- Following an accident or near miss to prevent future occurrences.
- Whenever there are changes in job procedures or the working environment.
- Periodically, to ensure that previous control measures are still effective.
Who should be involved in the Job Hazard Analysis process?
The success of a JHA largely depends on the involvement of both management and employees. It’s crucial for employees, especially those who are directly involved with the job being analyzed, to participate since they are the most familiar with the tasks and potential hazards. In addition to employees, the process should involve safety professionals who have the expertise to identify less obvious hazards and recommend effective controls. Representatives from management should also be involved to ensure that necessary resources and support are available for implementing recommended safety measures.
What are the steps involved in conducting a Job Hazard Analysis?
Conducting a Job Hazard Analysis involves a systematic approach consisting of three main steps:
- Breaking the job into a sequence of basic steps. This helps in analyzing the job systematically, identifying every major task along with its series of movements.
- Identifying potential hazards associated with each step. This includes looking at all sources of energy and examining the entire environment to determine all possible hazards that might exist.
- Recommending procedures or actions necessary to eliminate, control, or minimize the identified hazards. These recommendations should be specific to the job steps and hazards identified and aim at preventing accidents, injuries, or any environmental damage.
What should be done after completing a Job Hazard Analysis?
After completing a Job Hazard Analysis, the next steps involve implementing the recommended safety measures and controls. This requires coordinating with relevant departments and ensuring that employees are trained on new safety procedures or use of protective equipment. It’s also essential to monitor the effectiveness of implemented controls and make adjustments as necessary. Finally, the completed JHA should be documented and easily accessible for future reference, training, or reviews. Ongoing communication and training ensure that all employees understand their roles in maintaining a safe workplace and are aware of any changes resulting from the JHA.
Common mistakes
Filling out a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) form correctly is crucial for identifying and mitigating workplace hazards. However, several common mistakes can undermine the effectiveness of the analysis. Paying attention to these errors can improve workplace safety management.
Not breaking down the job into detailed steps. People often list job steps in broad terms, missing the finer movements where hazards can lurk. Each task must be broken into its component actions to capture all potential risks.
Overlooking potential hazards. A thorough review of the environment and job process is required to identify all possible hazards. Sometimes, seemingly insignificant sources of risk get overlooked, which could lead to accidents.
Skipping the identification of all energy sources. Mechanical, electrical, chemical, and even thermal energies can pose risks. Every source must be considered to ensure comprehensive hazard identification.
Not involving employees in the JHA process. Workers performing the jobs often have insight into hazards not immediately obvious to others. Their input is invaluable in both identifying potential dangers and developing practical solutions.
Lack of specificity in recommended procedures. Vague safety recommendations can lead to inconsistent application and confusion. Procedures should be clear, actionable, and directly tied to the hazards identified.
Failure to update the JHA regularly. Job roles, equipment, and processes evolve, which can introduce new hazards. Periodic reviews ensure the analysis remains relevant and effective.
Ignoring environmental factors. Weather, location, and other environmental conditions can significantly impact safety. Not considering these aspects can leave gaps in hazard analysis.
Assuming one JHA fits multiple jobs. Each job is unique, and a one-size-fits-all approach can miss specific hazards or procedures. Tailoring the analysis to each job is essential for accuracy.
Focusing solely on compliance rather than safety improvement. The goal of a JHA is not just to meet regulatory standards but to genuinely enhance workplace safety. Prioritizing the latter fosters a stronger safety culture.
Not prioritizing identified hazards. All hazards are not created equal. Without prioritizing risks based on severity and likelihood, efforts may not be efficiently directed towards preventing the most significant potential incidents.
By addressing these common mistakes, employers can better safeguard their workforce and create a safer, more productive environment. A detailed and employee-involved JHA is a key tool in achieving this goal.
Documents used along the form
When discussing workplace safety and compliance, the Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) form plays a pivotal role in identifying and mitigating potential risks in the work environment. However, to build a comprehensive safety program, several other documents are often utilized alongside the JHA. These documents not only complement the analysis provided by the JHA but also ensure a more structured approach to managing and communicating safety procedures within the organization. Exploring these additional forms can offer insights into a more integrated safety management system.
- Safety Training Records: These documents are vital for tracking the completion of safety training sessions by employees. They typically include information such as the type of training, the date it was conducted, the participants, and the trainer’s name. Ensuring that employees are properly trained on the hazards identified in the JHA and know the recommended procedures to mitigate these risks is crucial for maintaining a safe workplace.
- Incident/Accident Reports: When incidents or accidents occur, these reports provide a structured method for documenting what happened, when, and to whom. They often include witness statements, the conditions that led to the incident, and any immediate action taken. Analyzing these reports can offer valuable insights for updating the JHA and improving safety measures.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Assessment Forms: These forms are used to document the process of selecting appropriate PPE based on the hazards identified in a job hazard analysis. They detail the specific type of PPE required for different tasks and ensure that employees are equipped to safely perform their duties.
- Emergency Response Plans: These documents outline the procedures to be followed in case of an emergency, such as a fire, chemical spill, or natural disaster. They are designed to ensure a swift and organized response to incidents, minimizing harm to personnel, property, and the environment. Integrating the findings from job hazard analyses ensures that these plans are relevant and effective.
Collectively, these documents form the backbone of an effective safety management system, with each playing a unique role in safeguarding the work environment. The Job Hazard Analysis form identifies potential hazards and recommends procedures to mitigate them, while the accompanying documents ensure those procedures are implemented, tracked, and refined over time. Together, they create a dynamic framework that promotes a culture of continuous safety improvement, aligning closely with regulatory requirements and best practices. Embracing these tools empowers organizations to protect their most valuable asset: their people.
Similar forms
The Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) form is integral in identifying potential risks in the workplace and establishing necessary precautions. Several other documents share similarities with a Job Hazard Analysis form, each serving to enhance safety, compliance, or risk assessment in different contexts. Here are ten such documents:
- Risk Assessment Report: Similar to a JHA, this document evaluates potential hazards within a work environment or activity. It analyzes the likelihood of occurrence and potential impact, aiming to prioritize risks and implement mitigation strategies.
- Safety Audit Report: This document complements a JHA by systematically reviewing and evaluating the effectiveness of health and safety protocols within an organization. Its findings may lead to recommendations that influence a Job Hazard Analysis.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): SOPs detail the step-by-step processes for safely performing tasks, directly aligning with the "Recommended Procedures" section of a JHA. They operationalize the mitigation strategies identified in JHAs.
- Incident Report Forms: After an incident, these forms document what happened, when, and how. Analyzing these reports can inform a JHA by highlighting real-world hazards and potential preventive measures.
- Workplace Inspection Checklists: Similar to a JHA, these checklists are designed to systematically identify and record hazards in the workplace, though they tend to be more routine and less job-specific than a JHA.
- Emergency Action Plans: While a JHA focuses on preventing incidents, emergency action plans outline procedures to be taken in response to an emergency, ensuring employee safety in situations where hazards identified in a JHA materialize.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Assessments: These assessments identify specific personal protective gear required for various tasks or job roles, often as a result of the "Potential Hazards" identified in a JHA.
- Job Descriptions: They outline the duties and responsibilities of a position, including any inherent risks or necessary precautions, which should be considered when conducting a JHA for that role.
- Training Manuals: These documents contain information and guidelines for safely performing tasks, often drawing upon the findings and recommendations from a JHA to inform the training content.
- Hazard Communication Plans: These plans ensure that employees are aware of the chemicals and other hazards they may encounter, including protective measures – an aspect often covered in the "Potential Hazards" section of a JHA.
Each of these documents, while serving distinct purposes, shares the common goal of promoting workplace safety and preventing injuries or accidents. They often work in tandem, supporting and enhancing the effectiveness of a Job Hazard Analysis.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out a Job Hazard Analysis (JSA) form, it's vital to approach the task with diligence and care. To ensure your analysis is both thorough and effective, here are nine essential dos and don'ts to guide you through the process:
- Do take your time to understand each job step before proceeding. Rushing through this process can lead to important details being overlooked.
- Do involve employees who perform the job in the analysis. Their firsthand experience is invaluable in accurately identifying hazards and proposing practical solutions.
- Do be as specific as possible when identifying potential hazards. Vague descriptions can lead to inadequate preventive measures.
- Do consider all types of hazards, including physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic risks, to ensure a comprehensive analysis.
- Do prioritize the implementation of recommended procedures based on the level of risk associated with each hazard.
- Don't limit your analysis to the steps of a job alone. Take the entire work environment into account, as external factors can also contribute to potential hazards.
- Don't ignore the potential for changes in job conditions to introduce new hazards. A JSA should be a living document, updated as necessary.
- Don't forget to review and revise existing JSAs regularly or when the job changes. This ensures that the analysis remains relevant and effective.
- Don't underestimate the importance of communication. Share the findings and recommendations with all employees involved, and ensure they understand the procedures to mitigate risks.
By following these guidelines, you can create a Job Hazard Analysis that not only helps to prevent workplace accidents and injuries but also promotes a culture of safety within your organization.
Misconceptions
Many misconceptions surround the Job Hazard Analysis (JSA) form, leading to confusion and potentially incomplete or inaccurate assessments. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of employees. Here are nine common misunderstandings:
- It's only for high-risk industries: Some believe JSAs are only necessary in industries like construction or manufacturing. However, every workplace has potential hazards, meaning JSAs are valuable across all sectors.
- It's a one-time task: The notion that a JSA is a "set it and forget it" document is misleading. In reality, it should be reviewed and updated regularly, especially when changes in job roles, equipment, or processes occur.
- Only safety professionals can conduct JSAs: While safety professionals play a crucial role, employees performing the actual jobs can provide critical insights into everyday hazards and are integral to the process.
- It's too time-consuming: Some view JSAs as too lengthy and involved. However, the time invested in conducting thorough JSAs can prevent accidents, saving both time and resources in the long run.
- It hampers productivity: Contrary to the belief that JSAs slow down work, they can enhance efficiency by identifying and eliminating safety hazards that cause delays and accidents.
- It's just about identifying hazards: While identifying hazards is a key component, JSAs also require you to determine and implement actions to mitigate these risks effectively.
- It only focuses on the physical aspects of a job: A common misconception is that JSAs only assess physical risks. However, they should also consider environmental and organizational factors that could contribute to hazards.
- It covers every possible hazard: While JSAs aim to be comprehensive, it's challenging to foresee every potential hazard. This underscores the importance of regular updates and reviews.
- It's solely the employer's responsibility: Finally, there's a misconception that completing a JSA is only the employer's duty. In fact, a successful JSA requires cooperation between employers and employees, fostering a culture of safety and awareness.
By clarifying these misconceptions, companies can more effectively implement JSAs, improving workplace safety and reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Remember, a well-conducted JSA benefits everyone by creating a safer, more efficient work environment.
Key takeaways
Filling out and using a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) form is a critical process aimed at enhancing workplace safety and minimizing risks associated with various job tasks. Understanding its structure and purpose is key to its effective implementation. Below are nine key takeaways to guide the completion and utilization of the JHA form:
Breaking down the job into a sequence of basic steps is essential. It allows for a more detailed analysis of the tasks, making it easier to identify associated risks.
It is crucial to carefully assess each step for potential hazards. This includes examining all movements for possible dangers, thus ensuring a thorough evaluation of work processes.
Considering every possible source of energy during hazard identification can prevent overlooking risks that might not be immediately apparent.
The environment in which the job is performed must be comprehensively analyzed. Environmental factors can introduce additional hazards or exacerbate existing ones.
Identifying hazards is a fundamental step in preventing workplace accidents and injuries. It underpins the effectiveness of the Job Safety Analysis process.
Once hazards are identified, the next step is to determine how to eliminate, control, or minimize them. This proactive approach is critical in creating a safer workplace.
Recommended procedures or actions should directly correspond to the identified Hazards and job steps, ensuring that safety measures are both relevant and specific.
The completion of a JHA is not solely the responsibility of safety officers; it requires input from individuals who are most familiar with the job tasks. Engaging these employees can lead to a more accurate analysis.
A Job Hazard Analysis can be conducted for new job roles or revised for existing ones. This flexibility ensures that safety measures remain up-to-date with changing job requirements or conditions.
In summary, the Job Hazard Analysis form is a tool designed to systematically identify and address job-related hazards. Its effectiveness lies in its comprehensive approach to analyzing tasks, identifying potential risks, and implementing specific mitigation procedures. When completed thoughtfully, it serves as a foundation for a safer work environment, contributing to the well-being of all employees.
Popular PDF Forms
Utah Real Estate Forms - Ensures any contract modifications are clearly communicated and agreed upon.
Maintenance Bond - Outlines the financial responsibility of a principal and surety to the City of Plano for defective construction work rectification.