Blank Key Control Log PDF Template
In the realm of property management, ensuring the safety and security of buildings is paramount. One vital tool that assists in this endeavor is the Key Control Log form. This form meticulously records various crucial details regarding the issuance and return of keys. It includes specific columns for the serial number of the key, the location it opens, the time and date the key was issued, the name of the individual to whom the key was given, their signature, the time and date the key was returned, and finally, the signature of the Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge (NCOIC) overseeing the process. The Key Control Log form underwent its most recent revision on February 15, 2000, underscoring its enduring significance in maintaining operational security and accountability in key management processes. By meticulously tracking who has access to which keys and when, organizations can significantly mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized access and loss of keys.
Preview - Key Control Log Form
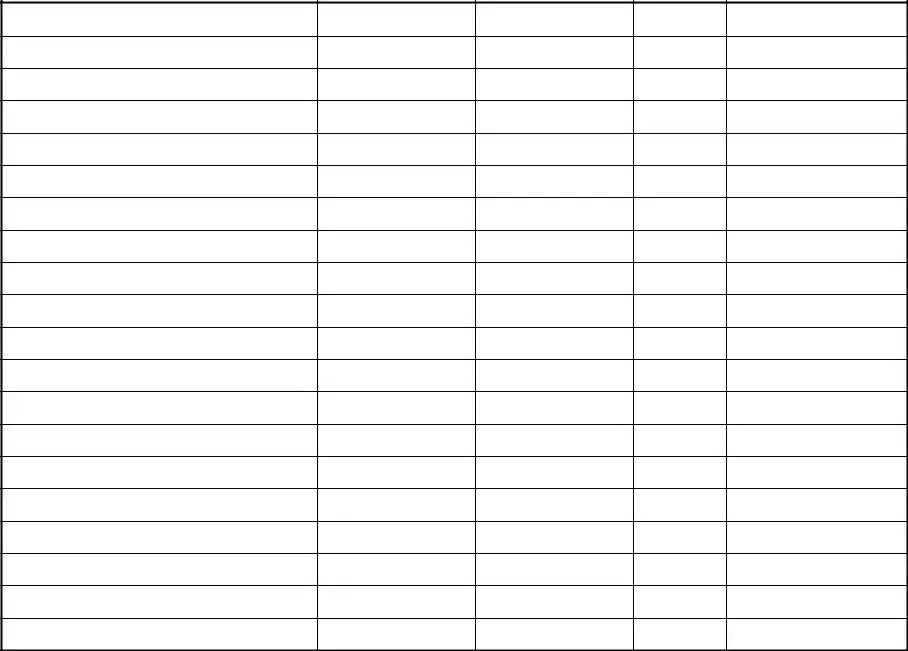
KEY CONTROL LOG
KEY SERIAL NUMBER |
LOCATION |
TIME/DATE |
|
OF LOCK |
ISSUED |
|
|
|
NAME
SIGNATURE
TIME/DATE RETURNED
NCOIC'S SIGNATURE
Key Control Log |
Revised 2/15/2000 |
Form Data
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The Key Control Log is used to track the issuance and return of keys to ensure security and accountability. |
| Components | It includes columns for key serial number, location, time/date of lock issued, name, signature, time/date returned, and NCOIC's signature. |
| Revision Date | The form was last revised on February 15, 2000. |
| NCOIC's Role | The Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge (NCOIC) signs off on the return of the keys, assuming responsibility for overseeing the process. |
| Record Keeping | It serves as a formal record to track the distribution and collection of keys, minimizing the risk of loss or unauthorized access. |
| Applicability | The form is used in various organizations that require secure key management practices, especially in military settings. |
| Governing Law(s) | While the form itself does not specify governing laws, its use is regulated by organizational policies and may be influenced by state-specific security guidelines where applicable. |
Instructions on Utilizing Key Control Log
Filling out a Key Control Log is an essential task for managing and documenting the issuance and return of keys within an organization. It ensures that each key can be accounted for, linking it to the person who was issued the key, and recording when the key was given out and when it was returned. This process involves accurately filling out various fields in the form to maintain reliable records. Below are step-by-step instructions to complete this form accurately.
- Start by finding the KEY SERIAL NUMBER of the key being issued. This number is usually engraved or stamped on the key. Enter this number in the corresponding field to clearly identify the key in question.
- In the LOCATION field, write down the specific area or door the key accesses. This detail helps in quickly identifying the purpose of the key.
- Record the TIME/DATE OF LOCK ISSUED. This should be the exact time and date when the key was handed over to the individual. It’s important for tracking how long the key has been outside of its secure location.
- Under NAME, write the full name of the person to whom the key is issued. Ensure the name is clear and legible to avoid any confusion about who is responsible for the key.
- The SIGNATURE field is for the recipient of the key to sign. This acts as an acknowledgment that the key has been received by the person named in the previous field.
- When the key is returned, note the TIME/DATE RETURNED. Just like when the key was issued, recording the exact time and date is critical for accurate tracking.
- Finally, the NCOIC'S SIGNATURE (Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge) field should be signed by the supervisor or individual in charge of the key control log. This signature validates the return of the key and the completion of the transaction.
By following these steps, individuals responsible for the Key Control Log will maintain a precise record of key issuances and returns, upholding the security and accessibility of designated areas within an organization.
Obtain Answers on Key Control Log
-
What is a Key Control Log?
A Key Control Log is a critical document used to track the issuance and return of keys. It records several essential details: the key's serial number, the location the key accesses, the time and date the key is issued, the name of the individual to whom the key is issued, their signature, the time and date the key is returned, and the signature of the Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge (NCOIC). This document serves to enhance security and accountability for access to sensitive or secured areas.
-
Why is it important to keep a Key Control Log?
Maintaining a Key Control Log is vital for several reasons. It helps in ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to certain areas, thereby enhancing security. Additionally, it assists in tracking the whereabouts of keys, minimizing the risk of loss or unauthorized use. In case a key goes missing, the log can provide valuable information to help resolve the issue promptly. It also supports accountability among personnel and can serve as an audit tool to verify compliance with security protocols.
-
How do I fill out a Key Control Log?
To accurately fill out a Key Control Log, start by recording the key's serial number, which uniquely identifies the key. Next, specify the location that the key unlocks. When a key is issued, record the time and date of issuance, followed by the name of the individual receiving the key. The recipient should then sign the log to acknowledge receipt. Upon the key's return, note the time and date, and the NCOIC must sign to verify the key's return. It's crucial to fill out each section clearly and completely to maintain integrity and accuracy of the log.
-
Who is responsible for the Key Control Log?
The Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge (NCOIC) is primarily responsible for the Key Control Log. The NCOIC ensures the log is accurately maintained and securely stored. They also verify the issuance and return of keys by providing their signature upon a key's return. Additionally, they may delegate responsibilities to other personnel for day-to-day management but ultimately hold accountability for the log's integrity.
-
What should be done if a key is not returned?
If a key is not returned as scheduled, immediate actions are necessary. Firstly, attempt to contact the individual who was issued the key to ascertain its status. If the key cannot be recovered promptly, assess the security risk posed by the missing key and consider changing locks or access codes if necessary. Report the incident to the appropriate security officer and log the event, detailing actions taken and any further measures required to mitigate risk.
-
Can digital signatures be used on the Key Control Log?
Depending on the organization's policy and the security requirements, digital signatures may be accepted on the Key Control Log. Digital signatures can provide a secure and verifiable method for acknowledging the issuance and return of keys. However, it's essential to ensure that the digital signature process complies with relevant security standards and legal requirements. Consult with your security officer or legal advisor to confirm if digital signatures are permissible.
-
What happens if there are discrepancies in the Key Control Log?
Any discrepancies in the Key Control Log should be addressed immediately. Review the log entries for accuracy, and verify them against any backup documentation or electronic records. Speak with the individuals involved to clarify any inconsistencies. If a discrepancy cannot be resolved, escalate the matter to the appropriate authority for further investigation. Taking prompt and thorough action is key to maintaining security and accountability.
Common mistakes
When filling out the Key Control Log, attention to detail is crucial for maintaining security and accountability. Here are some common mistakes people make:
- Not recording the key serial number accurately.
This mistake can lead to confusion in key tracking, making it difficult to identify which key was issued or returned.
- Omitting the specific location.
It's essential to be precise about the location where the key is used. General or vague entries can complicate the process of locating a key when needed.
- Using incorrect or unclear time/date format for lock issuance and return.
Consistency in date and time format is vital for tracking and auditing purposes. Mixing formats can cause misunderstandings and errors in logging.
- Forgetting to include the name of the person to whom the key was issued.
Not identifying the individual responsible for the key at any given time undermines the purpose of the log, affecting accountability and security.
- Neglecting to obtain signatures for key issuance and return.
Signatures verify the transaction occurred, adding a layer of security and responsibility. Missing signatures weaken the integrity of the control system.
- Overlooking the need for the NCOIC's signature upon key return.
This final check ensures that keys are accounted for and returned properly, closing the loop on the key control process.
Avoiding these common mistakes helps maintain a robust Key Control Log, ensuring keys are tracked accurately and responsibly.
Documents used along the form
When managing access to facilities or secure areas, a Key Control Log is a fundamental tool for tracking the issuance and return of keys. It ensures accountability and enhances security by documenting who has access to specific locations at any given time. However, for comprehensive security and facility management, several other documents are often used in conjunction with the Key Control Log. Each plays a vital role in creating a robust framework for access control and management.
- Access Control Policy: This document outlines the rules and procedures for granting, controlling, and revoking access to facilities. It sets the foundation for why and how keys are issued, identifying who is authorized to approve key requests.
- Employee Identification Form: This form collects personal information, including a photo ID, to verify an individual's identity before they are issued keys. It helps ensure that keys are only given to authorized personnel.
- Visitor Log: A record of all visitors to the facility, including their name, company, reason for visit, and the time/date of entry and exit. This log complements the Key Control Log by tracking non-employee access.
- Incident Report Form: In the case of lost or stolen keys, an incident report form is filled out. This form documents the circumstances of the incident, actions taken, and any security breaches that occurred.
- Key Issuance Authorization Form: This form is required to request the issuance of keys. It must be approved by a supervisor or manager, ensuring that key issuance aligns with the Access Control Policy.
- Floor Plan: A detailed layout of the facility showing all access points. When used alongside the Key Control Log, it helps in planning key assignments based on the areas an individual needs access to.
- Key Receipt Acknowledgement Form: Individuals receiving keys sign this form to acknowledge their responsibility for the keys and agree to comply with the key use and return policies.
- Key Inventory List: A comprehensive list of all keys, including their serial numbers and the doors or areas they open. It assists in key control and ensures duplicates are not issued unnecessarily.
- Security Briefing Document: A briefing provided to all key holders, detailing security protocols, emergency procedures, and the importance of maintaining control and confidentiality of their keys.
Together, these documents create a secure and efficient system for key management. They ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive areas, while also providing a clear audit trail and accountability. Managing physical keys can be a complex process, but with the right forms and documents in place, organizations can protect their assets and ensure the safety of their personnel and facilities.
Similar forms
Inventory Management Log: Similar to the Key Control Log, an Inventory Management Log tracks assets within an organization. Both documents record the allocation of resources to individuals and the timing of their issue and return. However, the Inventory Management Log may also include additional details like the condition and value of items.
Equipment Checkout Form: This form operates on a similar principle, documenting when specific equipment is borrowed and then returned by individuals. It mirrors the Key Control Log by recording the timing of these transactions and identifying the person responsible for the item, thus ensuring accountability and tracking of the organization's assets.
Vehicle Usage Log: Although focusing on vehicles, this log shares the Key Control Log's purpose of tracking the allocation and return of organizational resources. It indicates who used the vehicle, along with the date/time of checkout and return, ensuring responsible use of organizational assets.
Library Borrowing Record: This document tracks the books or materials checked out to library patrons, including the dates of issue and return. It is similar to the Key Control Log by ensuring accountability and efficient management of resources, although it specifically applies to library inventories.
Visitor Sign-in/Sign-out Log: While focusing on tracking individual visitors rather than items, this log similarly records the entry and exit times of visitors to a premise, correlating closely with how the Key Control Log notes the issue and return of keys. It's part of ensuring security and proper record-keeping within an organization.
Asset Maintenance Log: This type of log is akin to the Key Control Log in that it documents when specific maintenance activities are performed on assets, tracking who was responsible for the oversight and the date/time it was done. The primary focus is on ensuring the upkeep and condition of organizational assets, similar to tracking the use and return of keys.
Dos and Don'ts
When it comes to managing keys within an organization, keeping an accurate Key Control Log is essential. This log helps in tracking the movement of keys, ensuring security, and minimizing the risk of loss or unauthorized access. To make sure the Key Control Log serves its purpose effectively, here are some dos and don'ts to consider:
Things You Should Do
- Ensure that all fields are filled out completely and legibly. This includes the key serial number, location, time/date of lock issue, name of the individual receiving the key, their signature, the time/date the key was returned, and the NCOIC's signature.
- Double-check details for accuracy before submitting the form. Mistakes can lead to security breaches and confusion in key management.
- Keep the Key Control Log in a secure location. While it needs to be accessible to authorized personnel, it should not be openly available to everyone.
- Update the log immediately after a key is issued or returned. Prompt updating ensures the log accurately reflects the current status of all keys.
Things You Shouldn't Do
- Do not leave any fields blank. If a section is not applicable, mark it with "N/A" to indicate this. Leaving fields empty creates ambiguity and potential security risks.
- Avoid using vague descriptions for locations or individuals. Be as specific as possible to avoid misunderstandings or misplacement.
- Do not allow unauthorized individuals to make entries in the log. Only personnel responsible for key control should fill out or amend the log to maintain its integrity.
- Never falsify or alter information after it has been entered. If corrections need to be made, they should be done clearly and with a note explaining the reason for the change.
Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions about the Key Control Log form that need to be clarified to ensure its effective use and management of keys. Here's a breakdown:
- Only for military or government use: Many believe that the Key Control Log is exclusively for military or government applications, particularly because it mentions an NCOIC's signature. However, this format can be adapted for any organization needing to track key issuance and return, including businesses, schools, and residential complexes.
- Outdated: The revision date, "Revised 2/15/2000," might lead some to think that the Key Control Log is outdated. While this particular form shows a revision date from 2000, the concepts and the overall format remain applicable. Organizations are encouraged to update or modify the form to meet their current requirements.
- Complex to use: Another misconception is that the Key Control Log is complex and difficult to maintain. In reality, the form is designed to be straightforward. By keeping accurate records of key serial numbers, locations, issuance, and return times/dates, as well as names and signatures, organizations can effectively manage their keys.
- NCOIC's signature is mandatory: While the form indicates a space for the NCOIC's (Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge) signature, this role is specific to certain organizations, like the military. In a civilian context, this can simply be adapted to the relevant authority responsible for the key control, such as a security manager or facilities director.
- Electronic versions are not acceptable: Some might assume that a Key Control Log must be maintained in paper format. However, digital versions can be equally effective and, in some cases, preferable due to ease of access, the ability to make quick updates, and enhanced security features such as access controls and audit trails.
- Limited to tracking physical keys: While the form is primarily designed for physical keys, its basic structure can be applied to tracking electronic access cards and fobs. Organizations can modify the "KEY SERIAL NUMBER" field to record electronic access device identifiers, accommodating modern security needs.
Understanding and dispelling these misconceptions about the Key Control Log form can aid organizations in optimizing their key management processes effectively.
Key takeaways
When it comes to managing and safeguarding keys, particularly in settings requiring strict security measures, the Key Control Log serves as an indispensable tool. This document, designed to meticulously track the issuance and return of keys, plays a vital role in ensuring that access to sensitive areas is strictly regulated. Here are four key takeaways for effectively filling out and using the Key Control Log form:
- Accuracy is paramount. Each entry in the Key Control Log must be complete and accurate. This includes recording the key serial number, the specific location the key accesses, and precise times and dates for when the key is issued and returned. In environments where security is a top priority, even a minor oversight can lead to significant vulnerabilities.
- Clear accountability. The Key Control Log establishes clear accountability for those who are granted access to locked or restricted areas. By requiring both the name and signature of the individual issued the key, as well as the Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge's (NCOIC) signature upon return, the log ensures that each transaction is fully documented. This dual-signature requirement fosters an environment of mutual responsibility and trust.
- Review and audit readiness. Regular reviews of the Key Control Log are essential for maintaining a secure environment. These logs should be checked periodically to ensure that all keys are accounted for and that there are no discrepancies in the records. Being prepared for audits, whether internal or external, is crucial. The log serves as a primary record that can demonstrate compliance with security policies and procedures.
- Maintenance of historical records. The Key Control Log serves not only as a real-time tracking tool but also as a historical record of key issuance and return. This information can be invaluable for investigating security breaches or other incidents. By meticulously maintaining these logs, organizations can identify patterns or issues related to key access, reinforcing their overall security posture.
Effectively utilizing the Key Control Log form is not just about keeping up with keys; it's about safeguarding access to the most sensitive areas of an organization. By adhering to the practices outlined above, organizations can enhance their security measures and ensure that access to critical areas is both monitored and controlled.
Popular PDF Forms
Form 10-583 - Part two of the form is reserved for the exclusive use of Veterans Affairs to record the decision on the claim.
Religious Exemption Georgia - The form is part of a broader discourse on the ethics of vaccination, individual rights, and community health responsibilities.
Ky Cdl Self-certification Online - It acts as a preventive measure, ensuring that only medically certified drivers operate commercial vehicles, thus mitigating risks associated with unfit drivers on the road.