Blank Ssa 1099 PDF Template
Every year, millions of Americans who receive Social Security benefits are issued a Form SSA-1099, known formally as the Social Security Benefit Statement. This crucial document serves multiple purposes, primarily detailing the benefits paid and any benefits repaid to the Social Security Administration (SSA) during the tax year, effectively providing recipients with a clear snapshot of their net benefits. The form includes specific sections for the recipient's name, Social Security number, the total benefits paid in the year (Box 3), the amount of any benefits repaid to SSA (Box 4), and the resultant net benefits for the year (Box 3 minus Box 4). Additionally, it mentions any voluntary federal income tax withheld from these benefits (Box 6), as well as the beneficiary's address and a claim number, which is vital for any communication with the SSA. With the information provided on the SSA-1099, recipients can determine if a portion of their benefits may be considered taxable income, indicating the form's significant role not just in tax preparation but also in personal financial planning. Understanding and accurately reporting the figures on the SSA-1099 form is essential, as it influences one's tax obligations and ensures compliance with federal tax laws, underlining the form's blend of administrative function and impact on individual fiscal health.
Preview - Ssa 1099 Form

 US001_002BW_14TNH0_PREP6.indd 2
US001_002BW_14TNH0_PREP6.indd 2
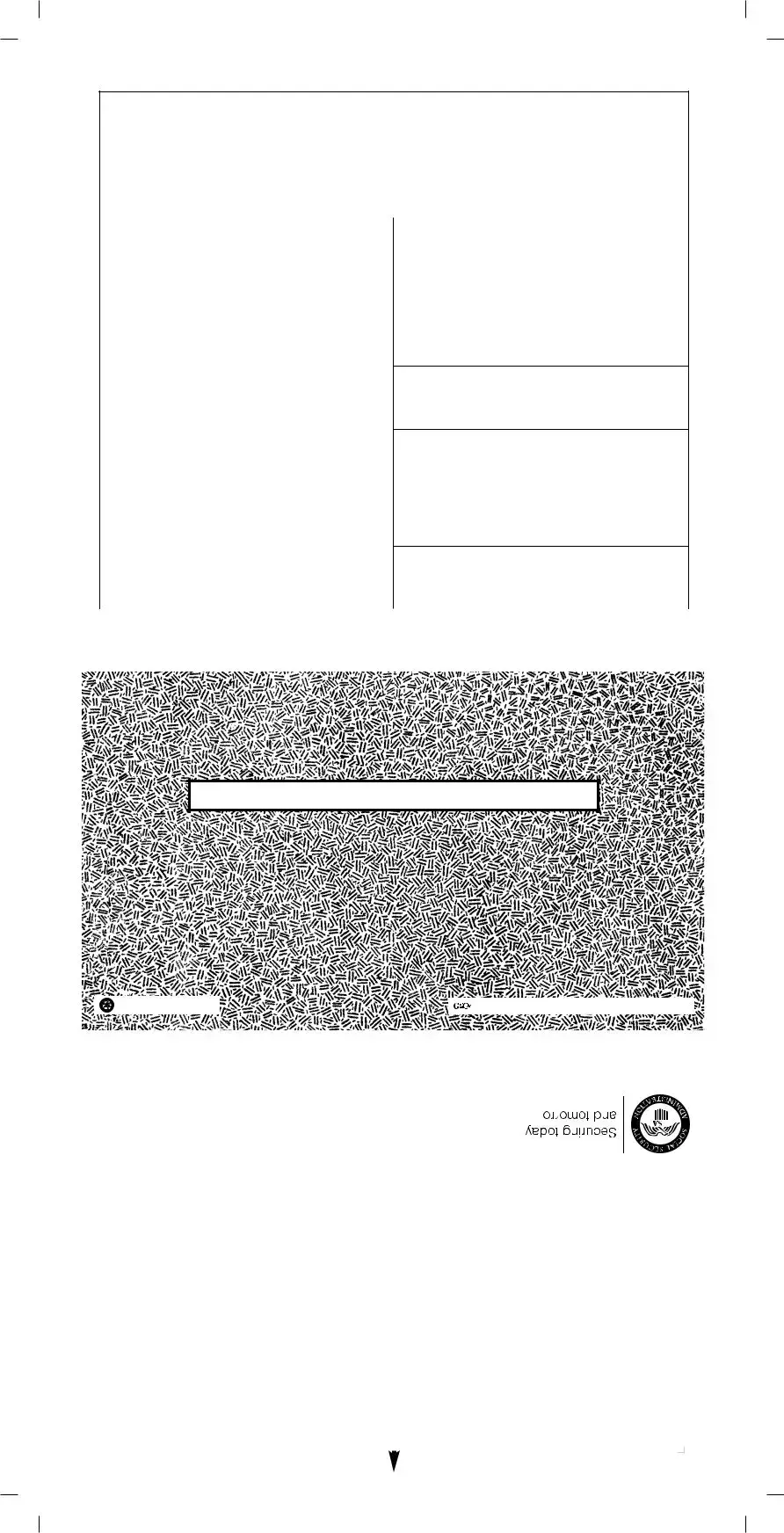
FORM
2016 • PART OF YOUR SOCIAL SECURITY BENEFITS SHOWN IN BOX 5 MAY BE TAXABLE INCOME.
• SEE THE REVERSE FOR MORE INFORMATION.
Box 1. Name |
|
|
Box 2. Beneficiary’s Social Security Number |
|
|
|
|
Box 3. Benefits Paid in 2016 |
Box 4. Benefits Repaid to SSA in 2016 |
Box 5. Net Benefits for 2016 (Box 3 minus Box 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION OF AMOUNT IN BOX 3 |
DESCRIPTION OF AMOUNT IN BOX 4 |
||
Box 6. Voluntary Federal Income Tax Withheld
Box 7. Address
Box 8. Claim Number (Use this number if you need to contact SSA.)
Form |
DO NOT RETURN THIS FORM TO SSA OR IRS |
|
FOLD & TEAR OFF STUB
IMPORTANT: TAX INFORMATION ENCLOSED
KEEP THIS FORM FOR PROOF OF SOCIAL SECURITY BENEFITS
VISIT OUR WEBSITE WWW.SOCIALSECURITY.GOV
Printed on recycled paper |
U.S. GOVERNMENT PUBLISHING OFFICE: |
gov.SocialSecurity account yS Social my a nOpe
nOpe
$300 USE, PRIVATE FOR PENALTY BUSINESS OFFICIAL
FOLD & TEAR OFF STUB
11/21/16 3:37 PM
LIFT TO OPEN
Form Data
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Form Purpose | The SSA-1099 form is a Social Security Benefit Statement used for tax purposes. |
| Taxability of Benefits | Part of the social security benefits shown in Box 5 may be considered taxable income. |
| Content Description | The form includes the recipient's name, Social Security number, benefits paid and repaid, net benefits, voluntary federal income tax withheld, address, and claim number. |
| Document Importance | Recipients are advised to keep Form SSA-1099 as proof of Social Security benefits for tax filing purposes. |
| Accessibility | The form, along with additional Social Security information, can be accessed through the official Social Security website. |
Instructions on Utilizing Ssa 1099
After receiving a Form SSA-1099, individuals often need guidance on how to accurately complete it. This document is crucial for those receiving Social Security benefits, as it outlines the amount received and what portion might be taxable. Following a systematic approach will simplify the process, ensuring accuracy and compliance with IRS requirements.
- Box 1: Enter your full name as it appears on your Social Security benefits statement.
- Box 2: Fill in your Social Security Number (SSN). Ensure this number matches the one used by the Social Security Administration.
- Box 3: Report the total amount of benefits paid to you in the year. This figure includes any monthly benefits before deductions.
- Box 4: Indicate any benefits you repaid to the SSA in the year. Repayments could be due to an overpayment or other adjustments.
- Box 5: Calculate your net benefits for the year. Subtract the amount in Box 4 from the amount in Box 3 and enter the result.
- Box 6: If you have chosen to have federal income tax withheld from your benefits, enter the total amount withheld during the year.
- Box 7: Provide your current mailing address, including any apartment or unit number, city, state, and ZIP code.
- Box 8: Write down the claim number. This number is essential if you need to contact the Social Security Administration regarding your benefits.
Once all sections are completed, review the form for accuracy. The SSA-1099 serves as an official record of the Social Security benefits received and any taxes withheld. Keeping this document for your records is crucial, and it should not be returned to the Social Security Administration or IRS. It holds significance not only for tax filing purposes but also as proof of the benefits you receive, which can be pertinent for various financial matters.
Obtain Answers on Ssa 1099
What is Form SSA-1099?
Form SSA-1099, also known as the Social Security Benefit Statement, is a tax form that the Social Security Administration sends each
Common mistakes
Filling out the SSA-1099 form, which is the Social Security Benefit Statement, is an important process for accurately reporting your Social Security benefits come tax time. However, there are common mistakes that can occur during this process. Being aware of these mistakes can help ensure that the information is reported correctly, potentially avoiding unnecessary complications. Below is a detailed look at ten of these mistakes.
Incorrectly reporting the Net Benefits (Box 5) by either not subtracting the Benefits Repaid to SSA (Box 4) from the Benefits Paid in 2016 (Box 3). This calculation must be done accurately to ensure the correct taxable amount is reported.
Not including the Form SSA-1099 when filing taxes, if any Social Security benefits were received. This document is crucial for tax purposes as it shows the total Social Security benefits paid.
Misreading or misunderstanding the amount in Box 3, which represents the total benefits paid in 2016. It's important to note that this amount is before any deductions are made.
Incorrectly or not entering the amount of Voluntary Federal Income Tax Withheld (Box 6). This is crucial for accurately reporting taxes that have already been paid on the benefits.
Failing to update the address (Box 7) if it has changed. This ensures that all future correspondence and necessary documentation from the Social Security Administration (SSA) is received.
Overlooking the Importance of Keeping the Form for Proof of Social Security Benefits. Keeping this form is essential for your records and future reference.
Misplacing or not keeping a personal copy of the form. Since this form is not returned to the SSA or IRS, it's important to keep a personal copy for your records and future reference.
Not understanding that part of your Social Security benefits shown in Box 5 may be taxable income. This can significantly affect your tax obligations and potential refunds.
Using the incorrect Claim Number (Box 8) when contacting the SSA for any inquiries or issues. This unique number is vital for identification and expedited service.
Failing to visit www.SocialSecurity.gov for additional information or assistance. The website provides essential resources and guidance for managing your Social Security benefits.
Ensuring that every detail on the SSA-1099 form is filled out correctly and understood can save you from unnecessary headaches and complications with your taxes. Double-check your entries, keep your form safe, and don't hesitate to seek guidance if you're unsure about any part of the process.
Documents used along the form
When managing Social Security benefits, the Form SSA-1099 – Social Security Benefit Statement is a critical document that outlines the total benefits received, any benefits repaid, net benefits for the year, and taxes withheld. This form is essential for tax purposes, detailing the income from Social Security that may be taxable. However, it often requires additional documentation for a comprehensive financial or tax management strategy. Here’s a list of other forms and documents that are commonly used alongside the SSA-1099 form.
- Form 1040 or 1040-SR: U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, used to report an individual’s annual income, including Social Security benefits, to the IRS. This form collects detailed information about income sources, deductions, and tax credits.
- Form 1040-ES: Estimated Tax for Individuals, for taxpayers who need to pay quarterly estimated taxes because their income is not subject to withholding. This might be relevant for individuals with significant income aside from Social Security.
- Form W-4V: Voluntary Withholding Request, allows recipients of Social Security benefits to request federal tax withholding directly from their benefits.
- Schedule B (Form 1040): Interest and Ordinary Dividends, for reporting interest or dividend income, which might be necessary if a recipient's total income affects the taxation of Social Security benefits.
- Schedule D (Form 1040): Capital Gains and Losses, for reporting the sale or exchange of capital assets. This could impact the tax situation of an individual receiving Social Security benefits.
- Schedule C (Form 1040): Profit or Loss from Business, for individuals who operate a business or practice a profession as a sole proprietor. Incorporating business income is vital for a comprehensive overview of one’s financial situation.
- Form 8962: Premium Tax Credit, for individuals who purchase health insurance through the Marketplace and want to reconcile or claim the premium tax credit, potentially affecting their taxable income.
- Form 8853: Archer MSAs and Long-Term Care Insurance Contracts, for reporting contributions to an Archer MSA and distributions from long-term care insurance contracts, which can influence taxable Social Security benefits.
Collectively, these documents play a significant role in accurately reporting income, managing taxes, and planning financially around Social Security benefits. They ensure that individuals comply with tax regulations and make the most of possible deductions and credits. In essence, alongside the SSA-1099, these forms help paint a complete picture of an individual’s financial landscape for any given year.
Similar forms
The W-2 Form, officially known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is akin to the SSA-1099. Both provide essential income information for tax purposes. The W-2 Form outlines the wages earned and taxes withheld for employees, similar to how the SSA-1099 details the Social Security benefits received and taxes withheld.
The 1099-MISC Form shares similarities with the SSA-1099 in that it reports income other than wages, salaries, and tips. Specifically, the 1099-MISC is used to report payments made in the course of a business to a person who's not an employee, which parallels the SSA-1099's role in declaring Social Security benefits.
1040 Form, or the U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, while generally more comprehensive, involves sections that require information similar to what is found on the SSA-1099. Income from SSA-1099 is often reported on the 1040 Form to calculate the total income, showcasing their interconnectedness in tax reporting.
The 1099-INT Form is used to report interest income, paralleling the SSA-1099 in its purpose to report a specific type of income. Just as the 1099-INT summarizes the interest income from various sources, the SSA-1099 compiles the total Social Security benefits received.
RMD Statements (Required Minimum Distribution) resemble the SSA-1099 as they both deal with income that affects tax liability. RMD Statements detail the minimum amount that must be withdrawn from retirement accounts each year, similar to how the SSA-1099 outlines received Social Security benefits.
The 1099-R Form, which reports distributions from pensions, annuities, retirement or profit-sharing plans, IRAs, and insurance contracts, shares similarities with the SSA-1099 by reporting income that can impact one's taxable income and tax obligations.
Dos and Don'ts
When completing the SSA-1099 form, it is vital to pay close attention to detail and ensure accuracy. Here are 5 practices to follow and 5 to avoid that will assist in filling out this form effectively.
Do:
- Review the information such as the name, Social Security number, and address for accuracy before submitting the form. Errors could complicate your tax situation.
- Report the benefits paid (found in Box 3) and benefits repaid to SSA (found in Box 4) precisely to calculate the net benefits correctly (Box 5).
- Include the voluntary federal income tax withheld (Box 6), if applicable, to ensure that your tax withholding is accurately reported on your tax return.
- Keep a personal copy of the completed SSA-1099 form for your records. This document is essential for tax preparation and future reference.
- Utilize the claim number in Box 8 if any questions or issues arise, ensuring you can easily communicate with the Social Security Administration (SSA).
Don't:
- Do not discard the form upon receipt thinking it is not critical. The SSA-1099 contains crucial tax information needed for your tax return.
- Do not overlook the "Benefits Paid" and "Benefits Repaid to SSA" sections. Inaccurate reporting can affect the taxation of your Social Security benefits.
- Do not ignore the tax implications of box 5, "Net Benefits for 2016." This will impact your taxable income and potentially your tax liability.
- Do not return this form to the SSA or IRS unless specifically requested. It is meant for the recipient's record-keeping and tax filing purposes.
- Do not hesitate to visit www.socialsecurity.gov or use your mySocialSecurity account for additional information or clarification regarding your SSA-1099 form.
Misconceptions
There are many misconceptions about the SSA-1099 form, which is crucial for individuals who receive Social Security benefits. Let's clear up some common misunderstandings:
- Only retirees need it: It's not just retirees who should be aware of the SSA-1099. Anyone who receives Social Security benefits, including disability, survivors, and retirement benefits, will receive this form.
- It's the same as a W-2: No, the SSA-1099 is different. While a W-2 reports income earned from employment, the SSA-1099 reports the benefits paid by Social Security.
- Benefits are not taxable: This is false for some people. If your combined income is above a certain limit, you may have to pay taxes on a portion of your Social Security benefits.
- You can throw it away after filing taxes: It's best to keep this form with your tax records. You might need it for future reference, especially when dealing with the IRS.
- No need to report if benefits are repaid: If you have repaid any benefits to the SSA, this information is crucial for your tax return. Box 4 on the form details benefits repaid.
- The form is only available by mail: You can also access this form online through your my Social Security account, making it easier to retrieve if you misplace your paper copy.
- All Social Security benefits are reported on one form: If you receive different types of benefits, you may receive more than one SSA-1099 or similar forms, such as the SSA-1042S for noncitizens.
- Dependents don’t need to worry about it: If you're receiving benefits as a dependent or survivor, you may still need to file taxes if your combined income is above the IRS threshold.
- Voluntary tax withholding is not possible: Actually, you can request federal income tax to be withheld from your benefits by using Form W-4V, as indicated in Box 6 of the SSA-1099.
- The form isn’t important if you don’t file taxes: Keeping your SSA-1099 is important even if you don't file taxes. It's a record of the benefits you received, and you may need it for other government programs.
Understanding the SSA-1099 form is critical for everyone who receives Social Security benefits. It ensures that you can accurately report your income and avoid potential issues with the IRS. Always keep your SSA-1099 form in a safe place with your other important tax documents.
Key takeaways
The Form SSA-1099, also known as the Social Security Benefit Statement, is a critical document for individuals receiving Social Security benefits. It outlines the annual benefits paid and provides key information for tax purposes. Here are several important takeaways regarding filling out and using the SSA-1099 form:
- Identification of Benefits: Box 3 on the form displays the total benefits paid to the beneficiary during the year. This amount is essential for understanding the total annual benefit received.
- Benefits Reconciliation: Box 4 indicates any benefits that were repaid to the Social Security Administration (SSA) during the year. Comparing the amounts in Box 3 and Box 4 helps to identify the net benefits, which are outlined in Box 5.
- Net Benefits: Box 5 shows the net benefits for the year, calculated as the total benefits paid (Box 3) minus any benefits repaid to SSA (Box 4). This figure is critical for tax purposes as it reflects the actual amount received by the beneficiary.
- Tax Withholding: Box 6 details any voluntary federal income tax withheld from the Social Security benefits. This withholding can help manage the tax liabilities associated with the benefits.
- Contact Information: The claim number, found in Box 8, is an important identifier for the beneficiary. It should be used when contacting the SSA for any reason related to Social Security benefits.
- Taxable Income Considerations: Part of the Social Security benefits shown in Box 5 may be taxable income. Beneficiaries should review the reverse side of the form for more information on how their benefits may affect their tax situation.
- Record Keeping: Beneficiaries are advised to keep the SSA-1099 form for proof of the Social Security benefits they receive. This documentation is crucial for accurately reporting income to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and managing one's tax obligations.
In summary, the SSA-1099 form provides vital information for Social Security beneficiaries, especially regarding their annual benefits and tax implications. Understanding how to read and use this form is essential for proper tax reporting and financial planning.
Popular PDF Forms
How Do You Pay Back Unemployment - Use this document to inform the state about a new address, legal name, trade name, or contact details for your business.
Rehab Application - The request for extensive explanation regarding previous treatments underscores the commitment to fully understanding and building upon the client’s past experiences.
